| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2879674 | The Annals of Thoracic Surgery | 2009 | 8 Pages |
Abstract
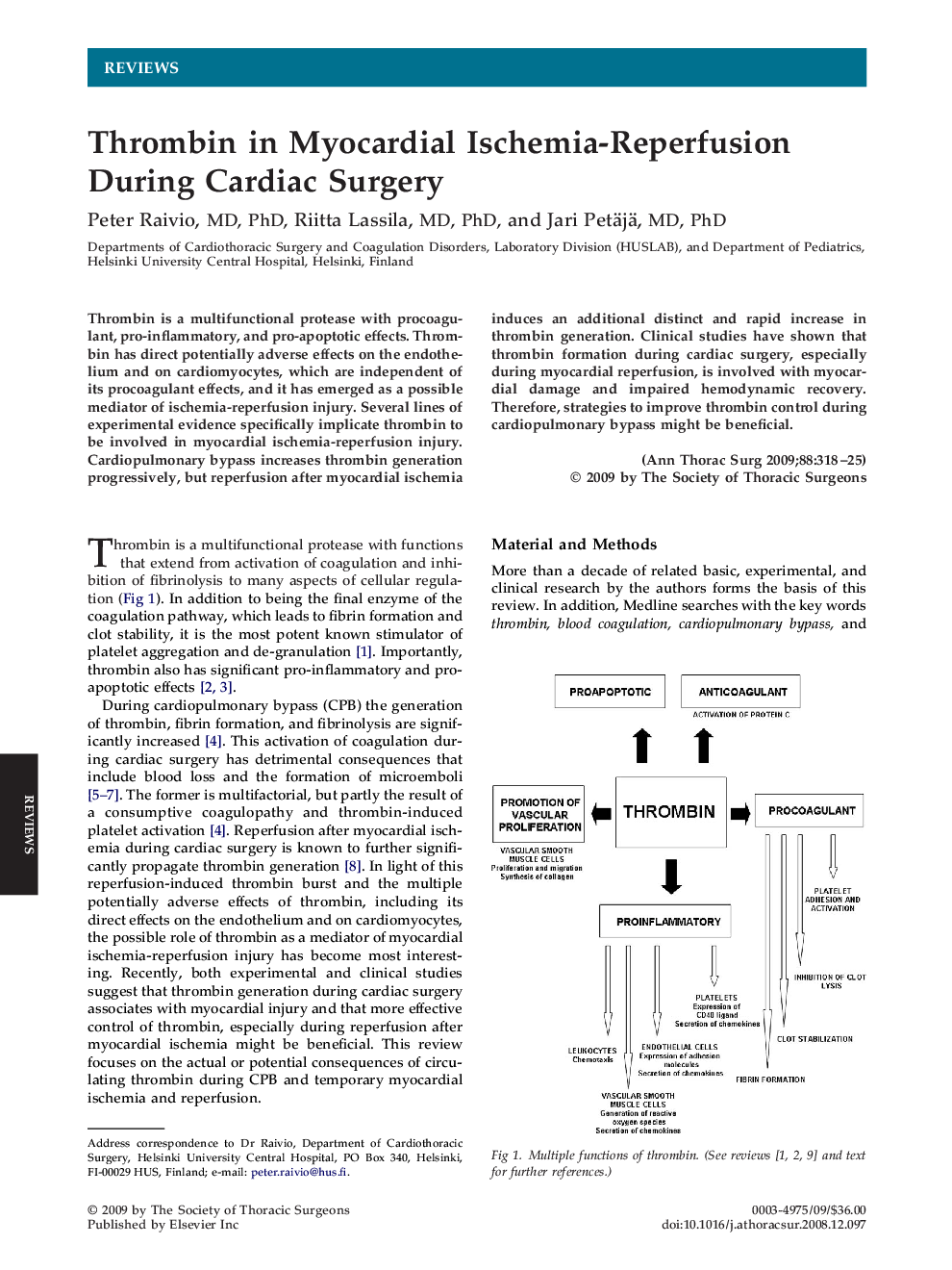
Thrombin is a multifunctional protease with procoagulant, pro-inflammatory, and pro-apoptotic effects. Thrombin has direct potentially adverse effects on the endothelium and on cardiomyocytes, which are independent of its procoagulant effects, and it has emerged as a possible mediator of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Several lines of experimental evidence specifically implicate thrombin to be involved in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cardiopulmonary bypass increases thrombin generation progressively, but reperfusion after myocardial ischemia induces an additional distinct and rapid increase in thrombin generation. Clinical studies have shown that thrombin formation during cardiac surgery, especially during myocardial reperfusion, is involved with myocardial damage and impaired hemodynamic recovery. Therefore, strategies to improve thrombin control during cardiopulmonary bypass might be beneficial.
Related Topics
Health Sciences
Medicine and Dentistry
Cardiology and Cardiovascular Medicine
Authors
Peter MD, PhD, Riitta MD, PhD, Jari MD, PhD,