| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3352889 | Immunity | 2016 | 13 Pages |
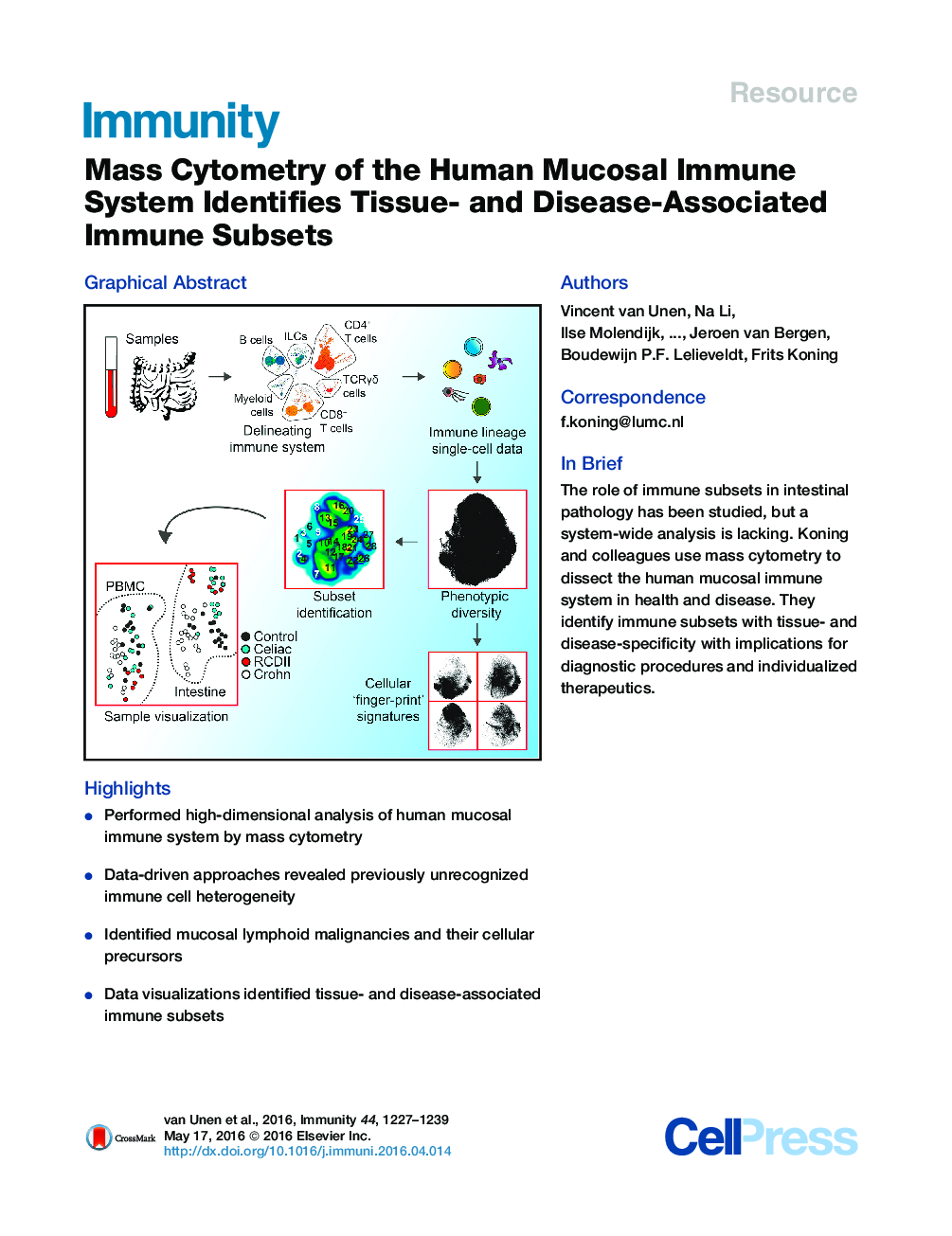
•Performed high-dimensional analysis of human mucosal immune system by mass cytometry•Data-driven approaches revealed previously unrecognized immune cell heterogeneity•Identified mucosal lymphoid malignancies and their cellular precursors•Data visualizations identified tissue- and disease-associated immune subsets
SummaryInflammatory intestinal diseases are characterized by abnormal immune responses and affect distinct locations of the gastrointestinal tract. Although the role of several immune subsets in driving intestinal pathology has been studied, a system-wide approach that simultaneously interrogates all major lineages on a single-cell basis is lacking. We used high-dimensional mass cytometry to generate a system-wide view of the human mucosal immune system in health and disease. We distinguished 142 immune subsets and through computational applications found distinct immune subsets in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and intestinal biopsies that distinguished patients from controls. In addition, mucosal lymphoid malignancies were readily detected as well as precursors from which these likely derived. These findings indicate that an integrated high-dimensional analysis of the entire immune system can identify immune subsets associated with the pathogenesis of complex intestinal disorders. This might have implications for diagnostic procedures, immune-monitoring, and treatment of intestinal diseases and mucosal malignancies.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (281 K)Download as PowerPoint slide