| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4080290 | Orthopaedics and Trauma | 2014 | 10 Pages |
Abstract
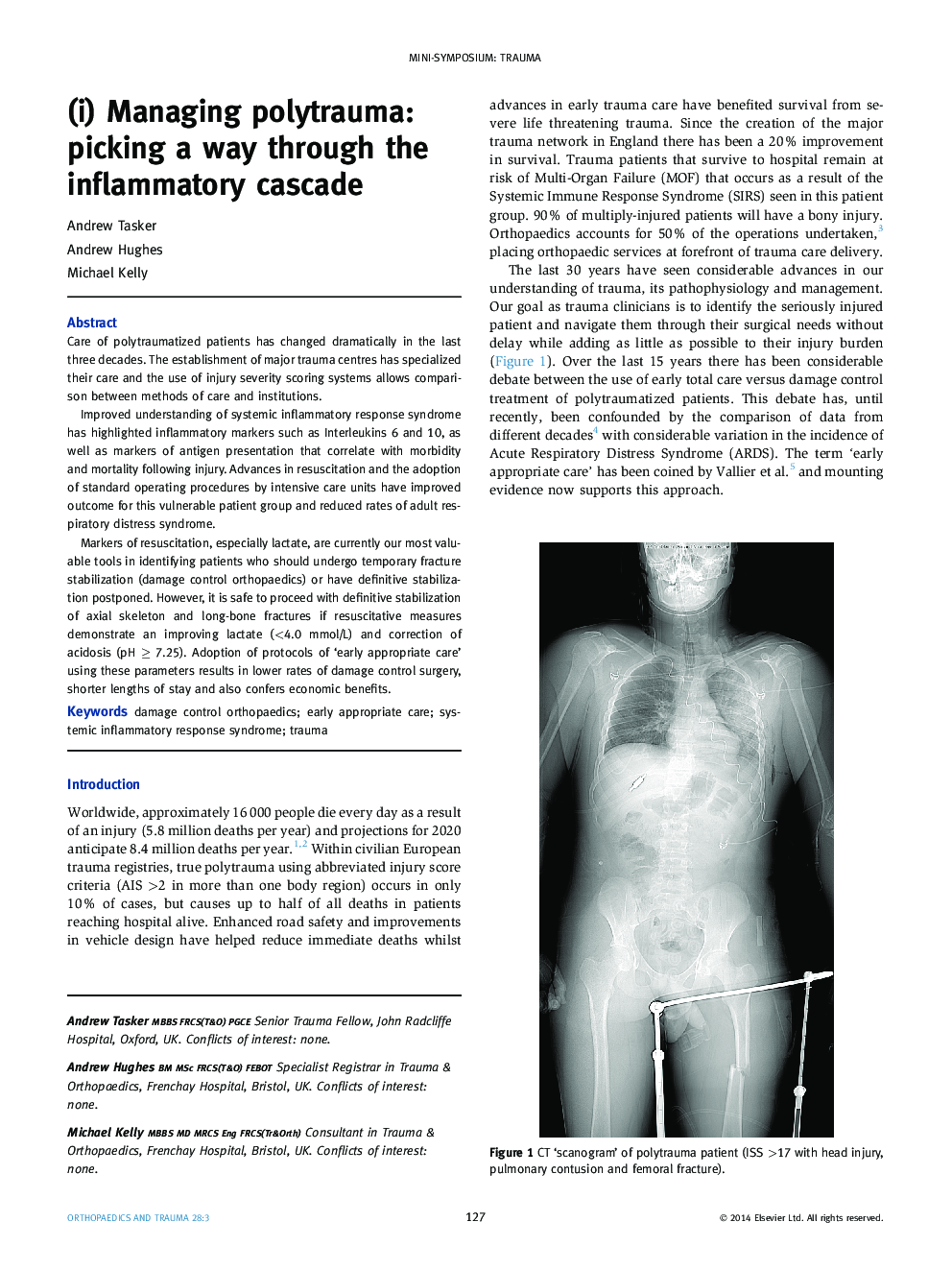
Markers of resuscitation, especially lactate, are currently our most valuable tools in identifying patients who should undergo temporary fracture stabilization (damage control orthopaedics) or have definitive stabilization postponed. However, it is safe to proceed with definitive stabilization of axial skeleton and long-bone fractures if resuscitative measures demonstrate an improving lactate (<4.0 mmol/L) and correction of acidosis (pH ⥠7.25). Adoption of protocols of 'early appropriate care' using these parameters results in lower rates of damage control surgery, shorter lengths of stay and also confers economic benefits.
Related Topics
Health Sciences
Medicine and Dentistry
Orthopedics, Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation
Authors
Andrew Tasker, Andrew Hughes, Michael Kelly,