| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4343463 | Neuroscience Letters | 2015 | 7 Pages |
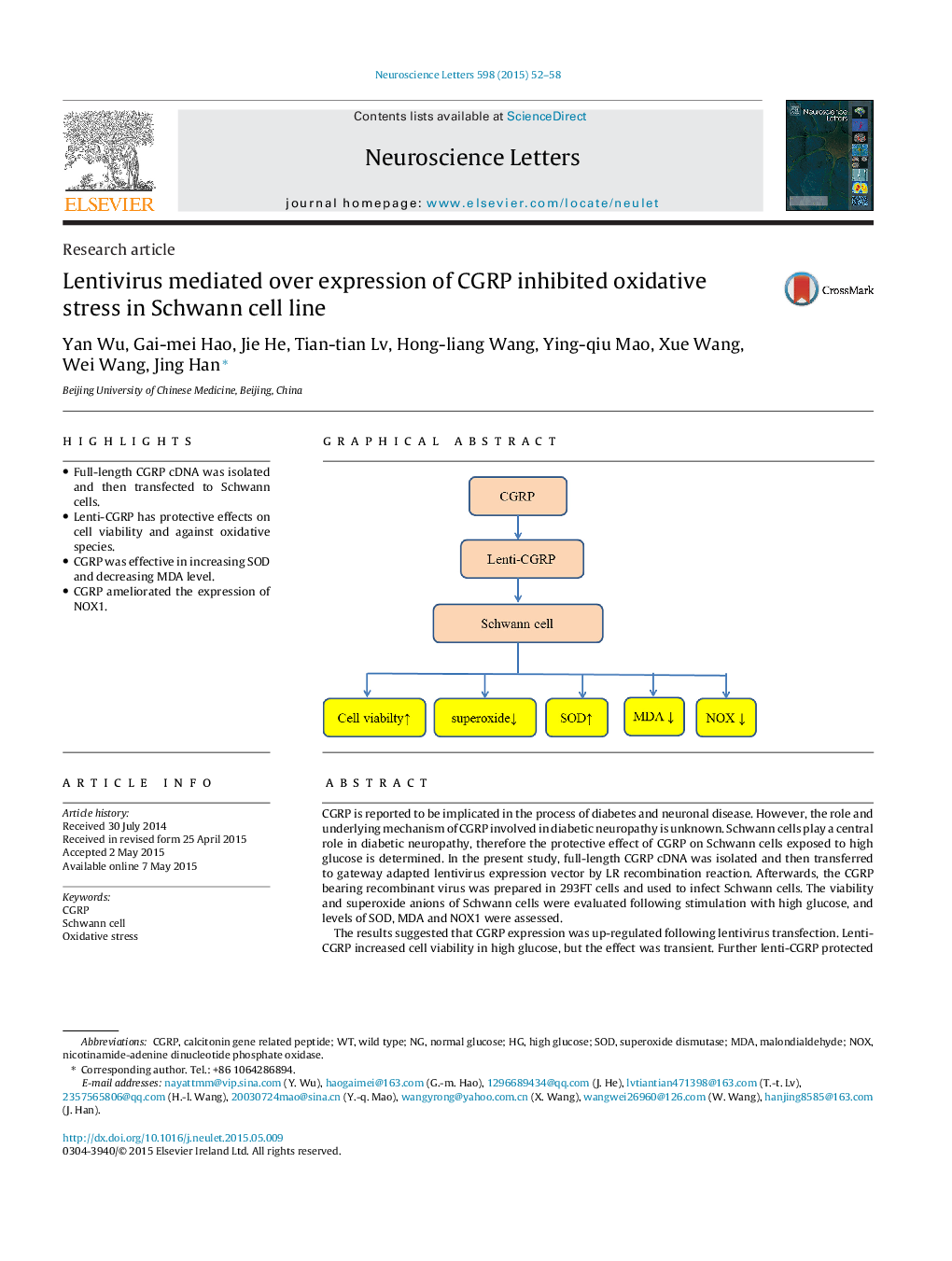
•Full-length CGRP cDNA was isolated and then transfected to Schwann cells.•Lenti-CGRP has protective effects on cell viability and against oxidative species.•CGRP was effective in increasing SOD and decreasing MDA level.•CGRP ameliorated the expression of NOX1.
CGRP is reported to be implicated in the process of diabetes and neuronal disease. However, the role and underlying mechanism of CGRP involved in diabetic neuropathy is unknown. Schwann cells play a central role in diabetic neuropathy, therefore the protective effect of CGRP on Schwann cells exposed to high glucose is determined. In the present study, full-length CGRP cDNA was isolated and then transferred to gateway adapted lentivirus expression vector by LR recombination reaction. Afterwards, the CGRP bearing recombinant virus was prepared in 293FT cells and used to infect Schwann cells. The viability and superoxide anions of Schwann cells were evaluated following stimulation with high glucose, and levels of SOD, MDA and NOX1 were assessed.The results suggested that CGRP expression was up-regulated following lentivirus transfection. Lenti-CGRP increased cell viability in high glucose, but the effect was transient. Further lenti-CGRP protected against oxidative stress in Schwann cells triggered by high glucose and lenti-CGRP was effective in increasing SOD and decreasing MDA level. Meanwhile, the increased level of NOX1 caused by high glucose was reversed by lenti-CGRP overexpression. We therefore, suggest that lenti-CGRP may play a role in inhibiting oxidative stress in Schwann cell lines following hyperglycemic stimulation.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (82 K)Download as PowerPoint slide