| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4407934 | Chemosphere | 2016 | 9 Pages |
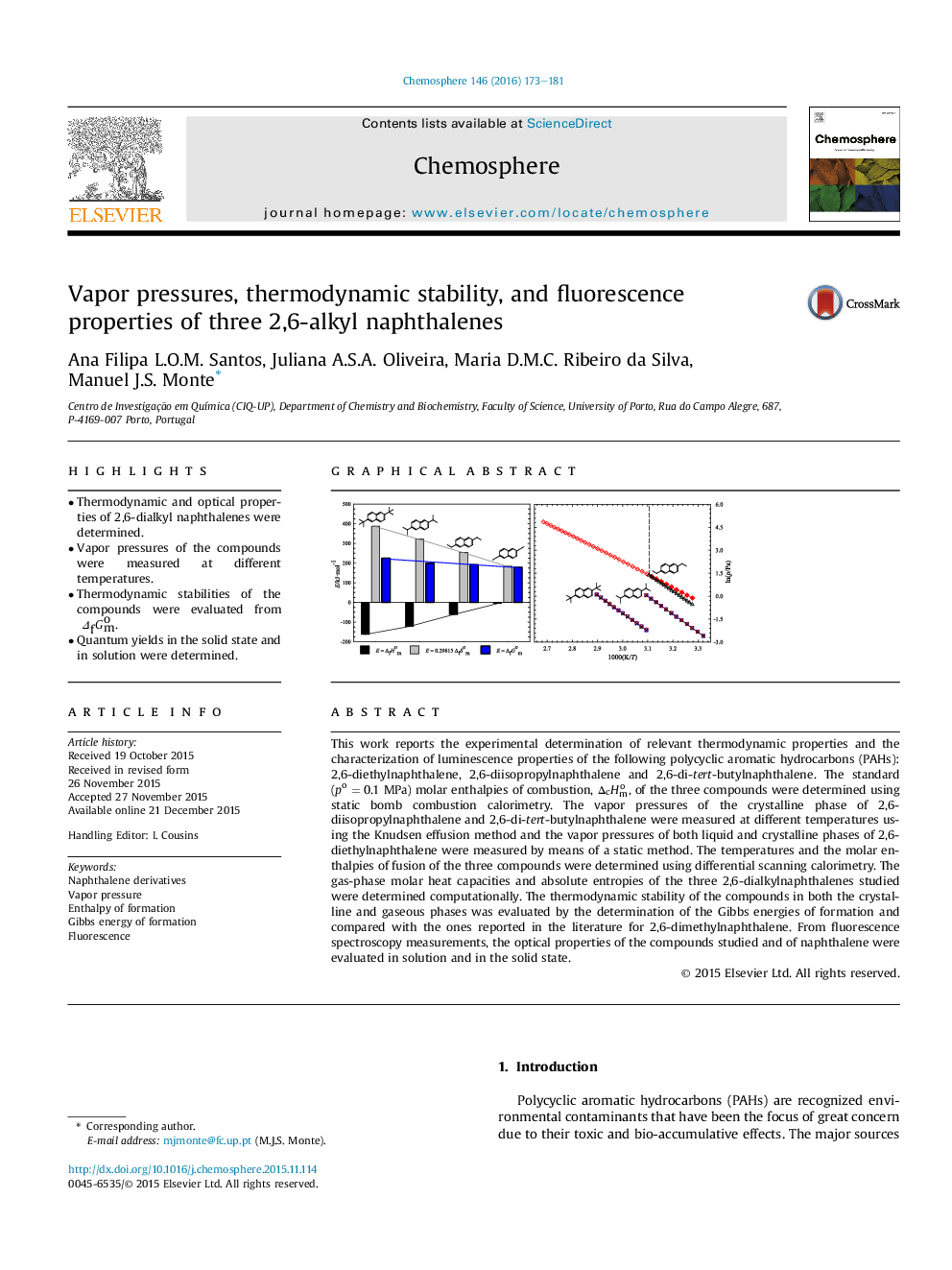
•Thermodynamic and optical properties of 2,6-dialkyl naphthalenes were determined.•Vapor pressures of the compounds were measured at different temperatures.•Thermodynamic stabilities of the compounds were evaluated from ΔfGmo.•Quantum yields in the solid state and in solution were determined.
This work reports the experimental determination of relevant thermodynamic properties and the characterization of luminescence properties of the following polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): 2,6-diethylnaphthalene, 2,6-diisopropylnaphthalene and 2,6-di-tert-butylnaphthalene. The standard (po = 0.1 MPa) molar enthalpies of combustion, ΔcHmo, of the three compounds were determined using static bomb combustion calorimetry. The vapor pressures of the crystalline phase of 2,6-diisopropylnaphthalene and 2,6-di-tert-butylnaphthalene were measured at different temperatures using the Knudsen effusion method and the vapor pressures of both liquid and crystalline phases of 2,6-diethylnaphthalene were measured by means of a static method. The temperatures and the molar enthalpies of fusion of the three compounds were determined using differential scanning calorimetry. The gas-phase molar heat capacities and absolute entropies of the three 2,6-dialkylnaphthalenes studied were determined computationally. The thermodynamic stability of the compounds in both the crystalline and gaseous phases was evaluated by the determination of the Gibbs energies of formation and compared with the ones reported in the literature for 2,6-dimethylnaphthalene. From fluorescence spectroscopy measurements, the optical properties of the compounds studied and of naphthalene were evaluated in solution and in the solid state.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide