| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4408263 | Chemosphere | 2015 | 7 Pages |
•Guar gum & alum used to treat POPs: phenol,2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) and DEHP.•Guar gum removed 99.70% of phenol,2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) & 99.99% of DEHP.•Guar gum is nontoxic, biodegradable, inexpensive & easily available biopolymer.•Guar gum produced compact sludge thus reducing the cost of handling & disposal.
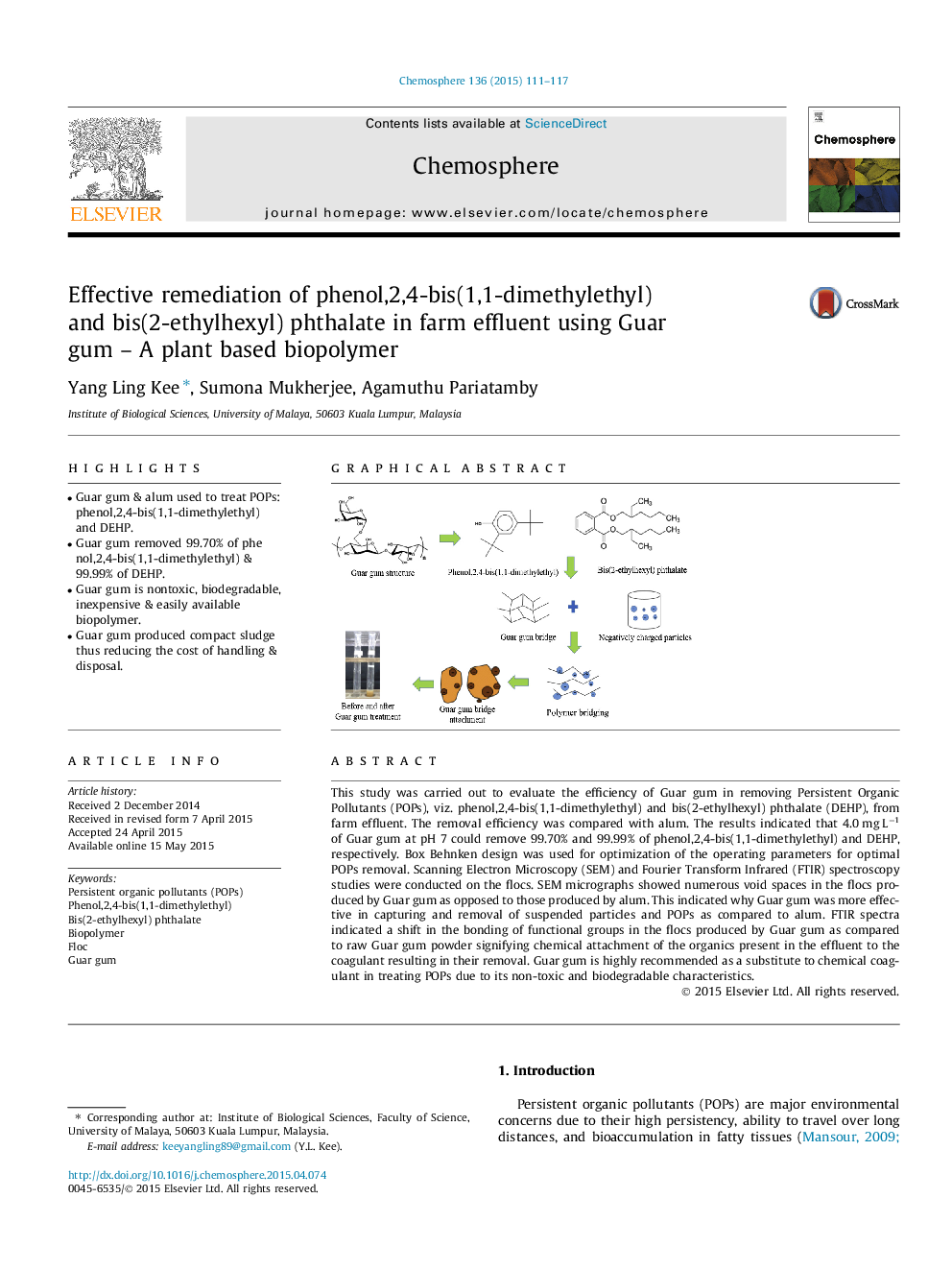
This study was carried out to evaluate the efficiency of Guar gum in removing Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs), viz. phenol,2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) and bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), from farm effluent. The removal efficiency was compared with alum. The results indicated that 4.0 mg L−1 of Guar gum at pH 7 could remove 99.70% and 99.99% of phenol,2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) and DEHP, respectively. Box Behnken design was used for optimization of the operating parameters for optimal POPs removal. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy studies were conducted on the flocs. SEM micrographs showed numerous void spaces in the flocs produced by Guar gum as opposed to those produced by alum. This indicated why Guar gum was more effective in capturing and removal of suspended particles and POPs as compared to alum. FTIR spectra indicated a shift in the bonding of functional groups in the flocs produced by Guar gum as compared to raw Guar gum powder signifying chemical attachment of the organics present in the effluent to the coagulant resulting in their removal. Guar gum is highly recommended as a substitute to chemical coagulant in treating POPs due to its non-toxic and biodegradable characteristics.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide