| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4997657 | Bioresource Technology | 2017 | 9 Pages |
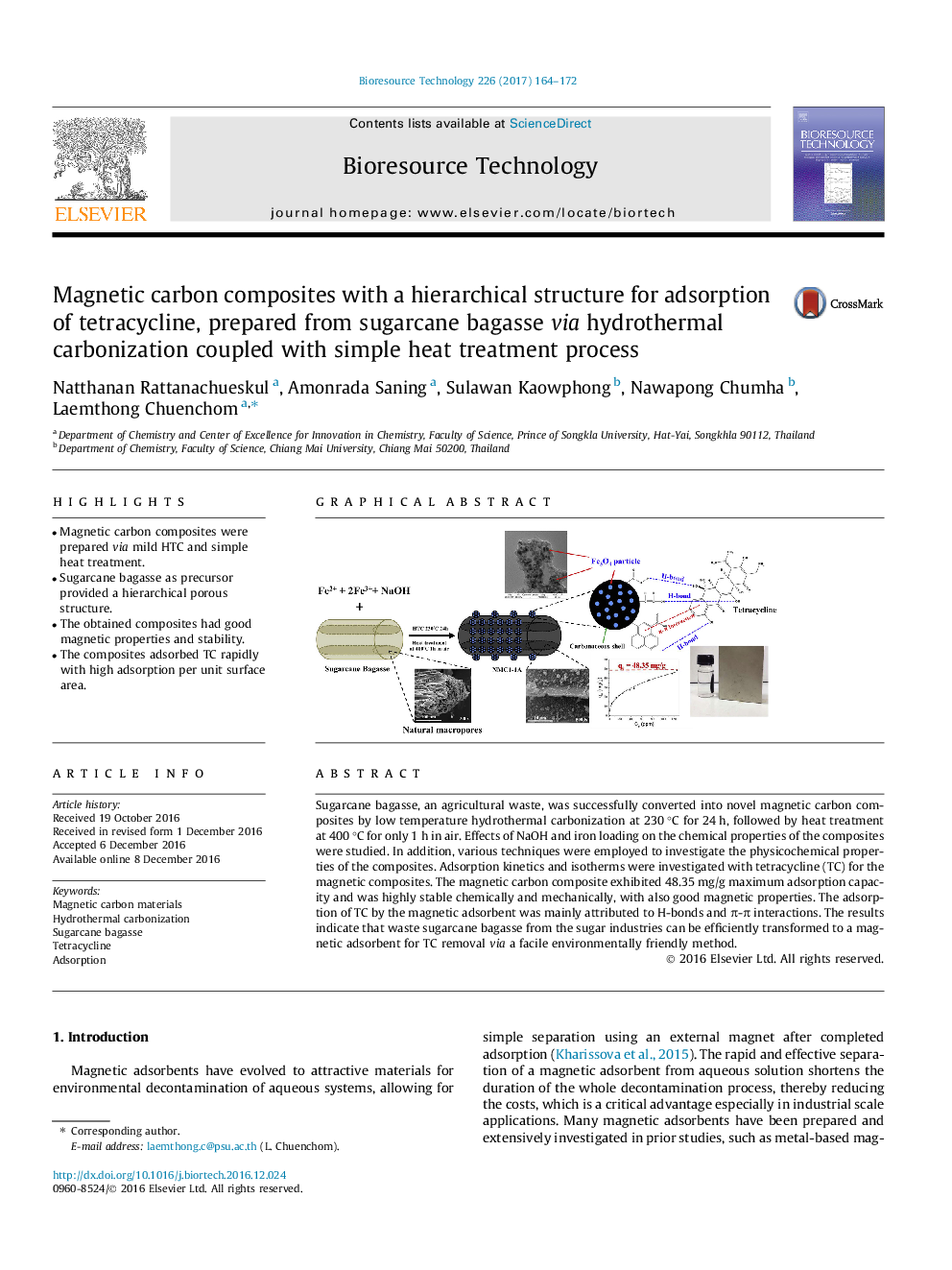
â¢Magnetic carbon composites were prepared via mild HTC and simple heat treatment.â¢Sugarcane bagasse as precursor provided a hierarchical porous structure.â¢The obtained composites had good magnetic properties and stability.â¢The composites adsorbed TC rapidly with high adsorption per unit surface area.
Sugarcane bagasse, an agricultural waste, was successfully converted into novel magnetic carbon composites by low temperature hydrothermal carbonization at 230 °C for 24 h, followed by heat treatment at 400 °C for only 1 h in air. Effects of NaOH and iron loading on the chemical properties of the composites were studied. In addition, various techniques were employed to investigate the physicochemical properties of the composites. Adsorption kinetics and isotherms were investigated with tetracycline (TC) for the magnetic composites. The magnetic carbon composite exhibited 48.35 mg/g maximum adsorption capacity and was highly stable chemically and mechanically, with also good magnetic properties. The adsorption of TC by the magnetic adsorbent was mainly attributed to H-bonds and Ï-Ï interactions. The results indicate that waste sugarcane bagasse from the sugar industries can be efficiently transformed to a magnetic adsorbent for TC removal via a facile environmentally friendly method.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (231KB)Download full-size image