| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5370799 | Biophysical Chemistry | 2015 | 6 Pages |
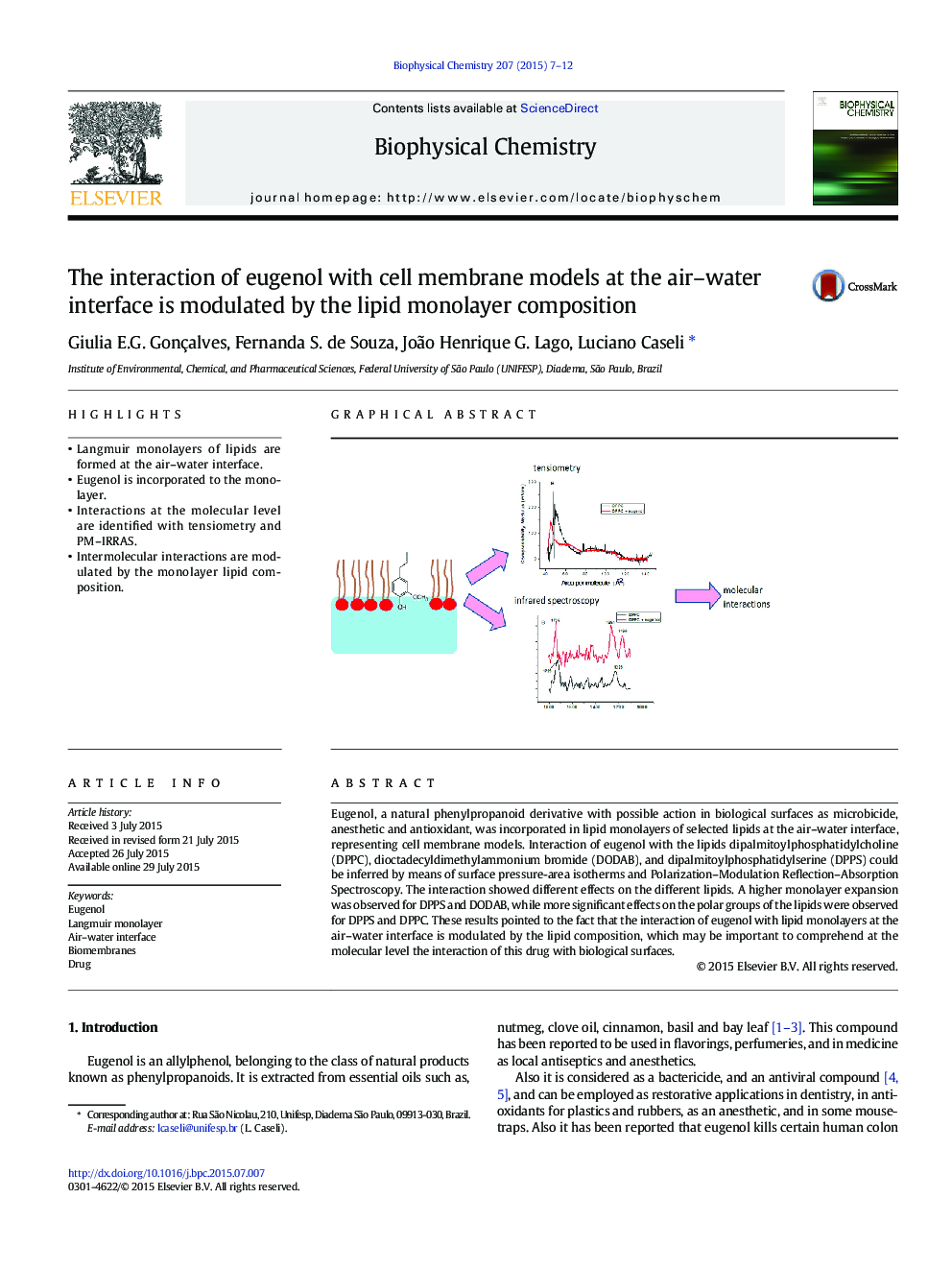
â¢Langmuir monolayers of lipids are formed at the air-water interface.â¢Eugenol is incorporated to the monolayer.â¢Interactions at the molecular level are identified with tensiometry and PM-IRRAS.â¢Intermolecular interactions are modulated by the monolayer lipid composition.
Eugenol, a natural phenylpropanoid derivative with possible action in biological surfaces as microbicide, anesthetic and antioxidant, was incorporated in lipid monolayers of selected lipids at the air-water interface, representing cell membrane models. Interaction of eugenol with the lipids dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), dioctadecyldimethylammonium bromide (DODAB), and dipalmitoylphosphatidylserine (DPPS) could be inferred by means of surface pressure-area isotherms and Polarization-Modulation Reflection-Absorption Spectroscopy. The interaction showed different effects on the different lipids. A higher monolayer expansion was observed for DPPS and DODAB, while more significant effects on the polar groups of the lipids were observed for DPPS and DPPC. These results pointed to the fact that the interaction of eugenol with lipid monolayers at the air-water interface is modulated by the lipid composition, which may be important to comprehend at the molecular level the interaction of this drug with biological surfaces.
Graphical abstractDownload full-size image