| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5371139 | Biophysical Chemistry | 2013 | 7 Pages |
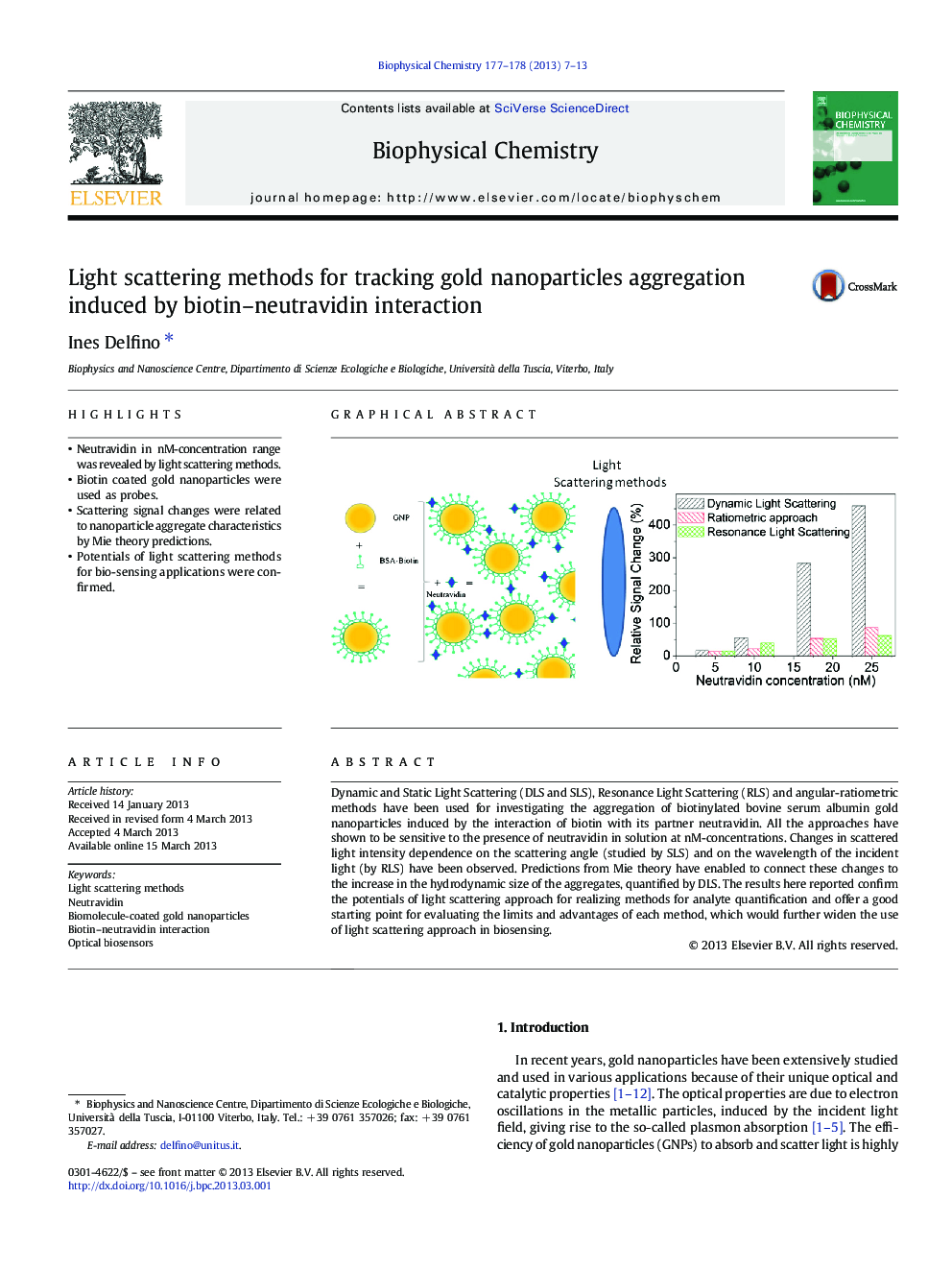
â¢Neutravidin in nM-concentration range was revealed by light scattering methods.â¢Biotin coated gold nanoparticles were used as probes.â¢Scattering signal changes were related to nanoparticle aggregate characteristics by Mie theory predictions.â¢Potentials of light scattering methods for bio-sensing applications were confirmed.
Dynamic and Static Light Scattering (DLS and SLS), Resonance Light Scattering (RLS) and angular-ratiometric methods have been used for investigating the aggregation of biotinylated bovine serum albumin gold nanoparticles induced by the interaction of biotin with its partner neutravidin. All the approaches have shown to be sensitive to the presence of neutravidin in solution at nM-concentrations. Changes in scattered light intensity dependence on the scattering angle (studied by SLS) and on the wavelength of the incident light (by RLS) have been observed. Predictions from Mie theory have enabled to connect these changes to the increase in the hydrodynamic size of the aggregates, quantified by DLS. The results here reported confirm the potentials of light scattering approach for realizing methods for analyte quantification and offer a good starting point for evaluating the limits and advantages of each method, which would further widen the use of light scattering approach in biosensing.
Graphical abstractDownload full-size image