| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5371305 | Biophysical Chemistry | 2010 | 5 Pages |
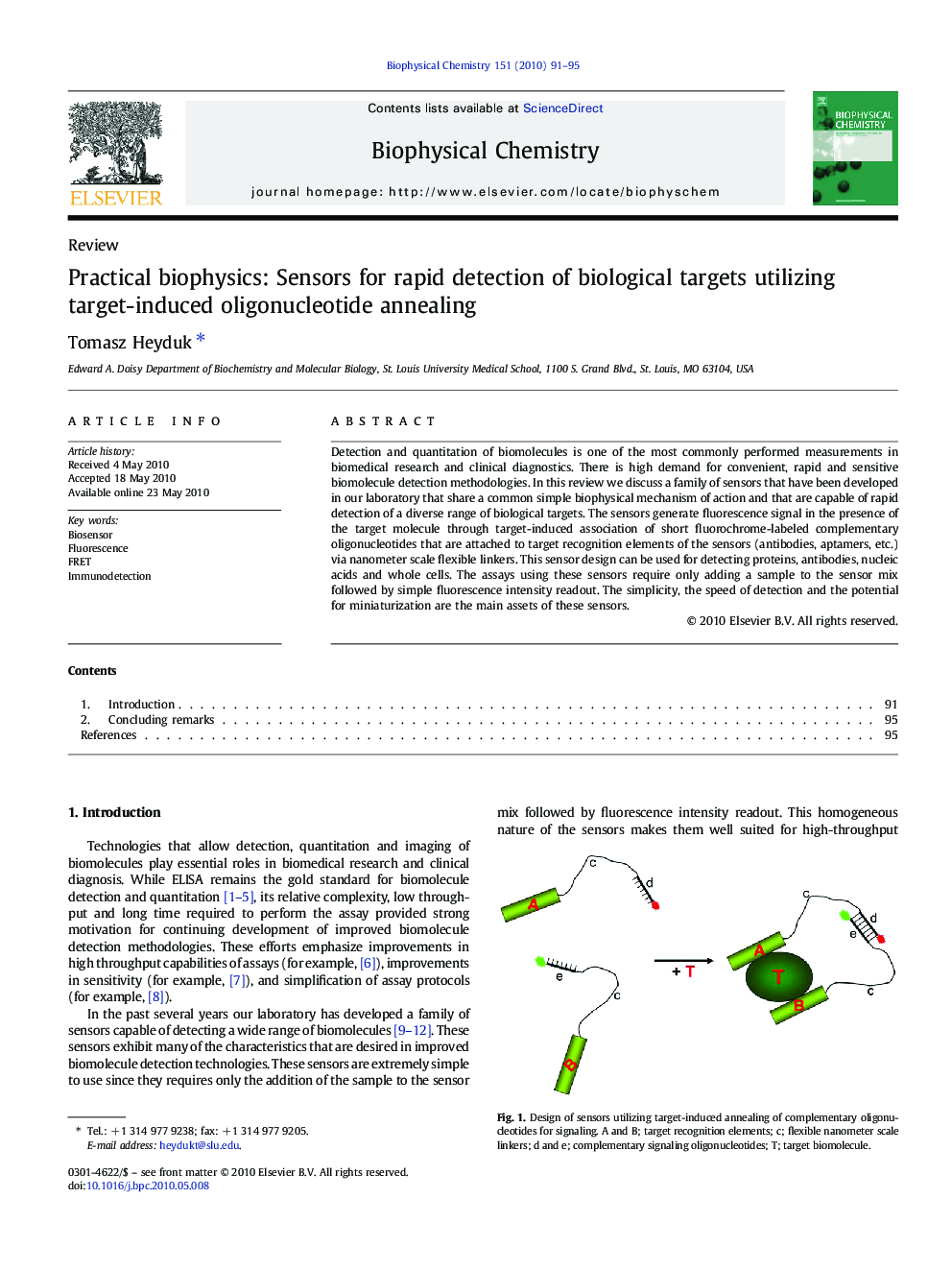
Detection and quantitation of biomolecules is one of the most commonly performed measurements in biomedical research and clinical diagnostics. There is high demand for convenient, rapid and sensitive biomolecule detection methodologies. In this review we discuss a family of sensors that have been developed in our laboratory that share a common simple biophysical mechanism of action and that are capable of rapid detection of a diverse range of biological targets. The sensors generate fluorescence signal in the presence of the target molecule through target-induced association of short fluorochrome-labeled complementary oligonucleotides that are attached to target recognition elements of the sensors (antibodies, aptamers, etc.) via nanometer scale flexible linkers. This sensor design can be used for detecting proteins, antibodies, nucleic acids and whole cells. The assays using these sensors require only adding a sample to the sensor mix followed by simple fluorescence intensity readout. The simplicity, the speed of detection and the potential for miniaturization are the main assets of these sensors.