| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5737308 | Journal of Neuroscience Methods | 2017 | 10 Pages |
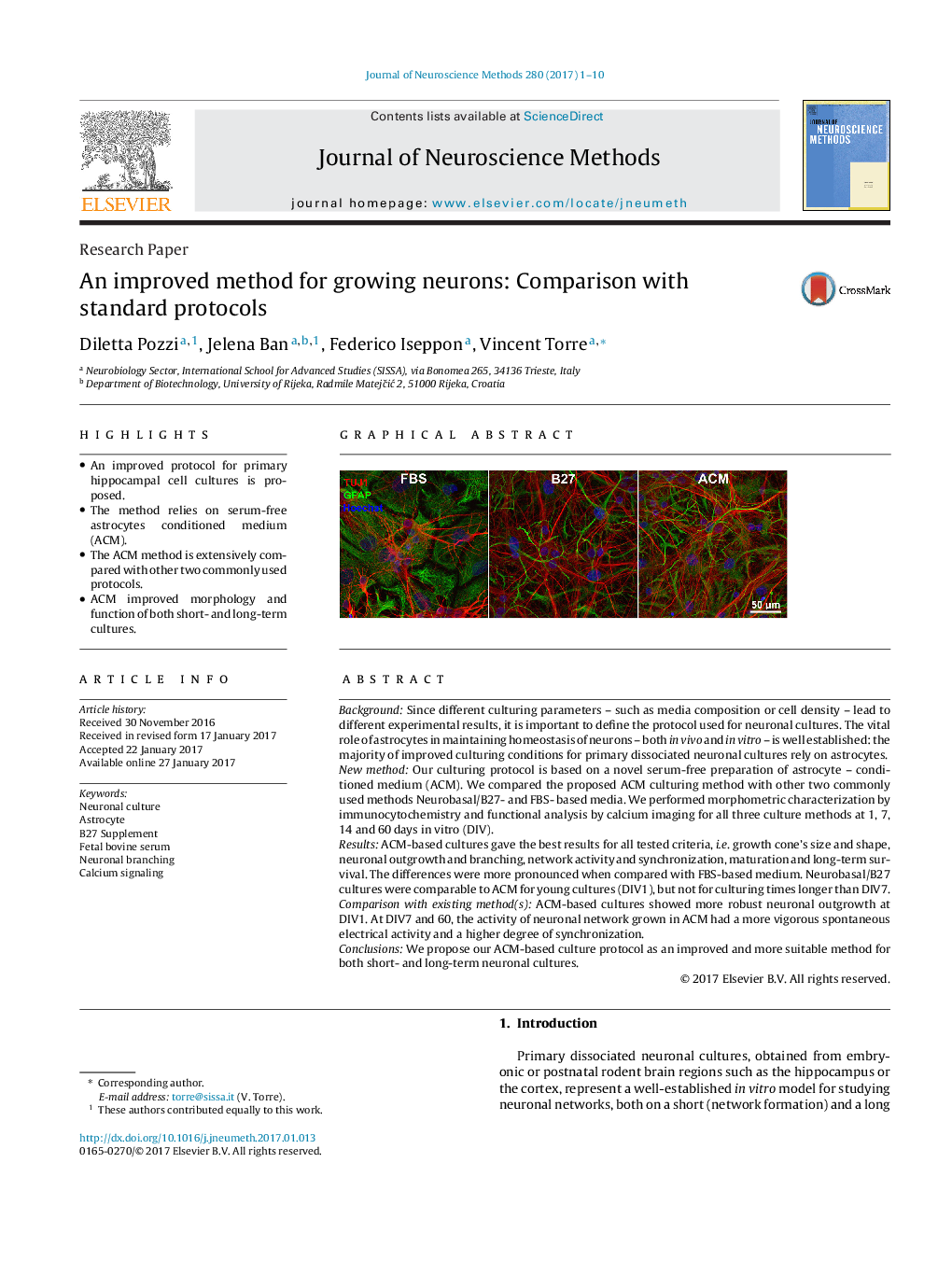
â¢An improved protocol for primary hippocampal cell cultures is proposed.â¢The method relies on serum-free astrocytes conditioned medium (ACM).â¢The ACM method is extensively compared with other two commonly used protocols.â¢ACM improved morphology and function of both short- and long-term cultures.
BackgroundSince different culturing parameters - such as media composition or cell density - lead to different experimental results, it is important to define the protocol used for neuronal cultures. The vital role of astrocytes in maintaining homeostasis of neurons - both in vivo and in vitro - is well established: the majority of improved culturing conditions for primary dissociated neuronal cultures rely on astrocytes.New methodOur culturing protocol is based on a novel serum-free preparation of astrocyte - conditioned medium (ACM). We compared the proposed ACM culturing method with other two commonly used methods Neurobasal/B27- and FBS- based media. We performed morphometric characterization by immunocytochemistry and functional analysis by calcium imaging for all three culture methods at 1, 7, 14 and 60Â days in vitro (DIV).ResultsACM-based cultures gave the best results for all tested criteria, i.e. growth cone's size and shape, neuronal outgrowth and branching, network activity and synchronization, maturation and long-term survival. The differences were more pronounced when compared with FBS-based medium. Neurobasal/B27 cultures were comparable to ACM for young cultures (DIV1), but not for culturing times longer than DIV7.Comparison with existing method(s)ACM-based cultures showed more robust neuronal outgrowth at DIV1. At DIV7 and 60, the activity of neuronal network grown in ACM had a more vigorous spontaneous electrical activity and a higher degree of synchronization.ConclusionsWe propose our ACM-based culture protocol as an improved and more suitable method for both short- and long-term neuronal cultures.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (554KB)Download full-size image