| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5741046 | Experimental Parasitology | 2017 | 6 Pages |
â¢An animal model for alveolar echinococcosis in a naturally resistant host.â¢Hepatic alveolar echinococcosis in dexamethasone treated rats after oral inoculation with parasite eggs.â¢Immunocompetent RccHanâ¢:WIST and F344/DuCrl rats are resistant to oral inoculation with parasite eggs.
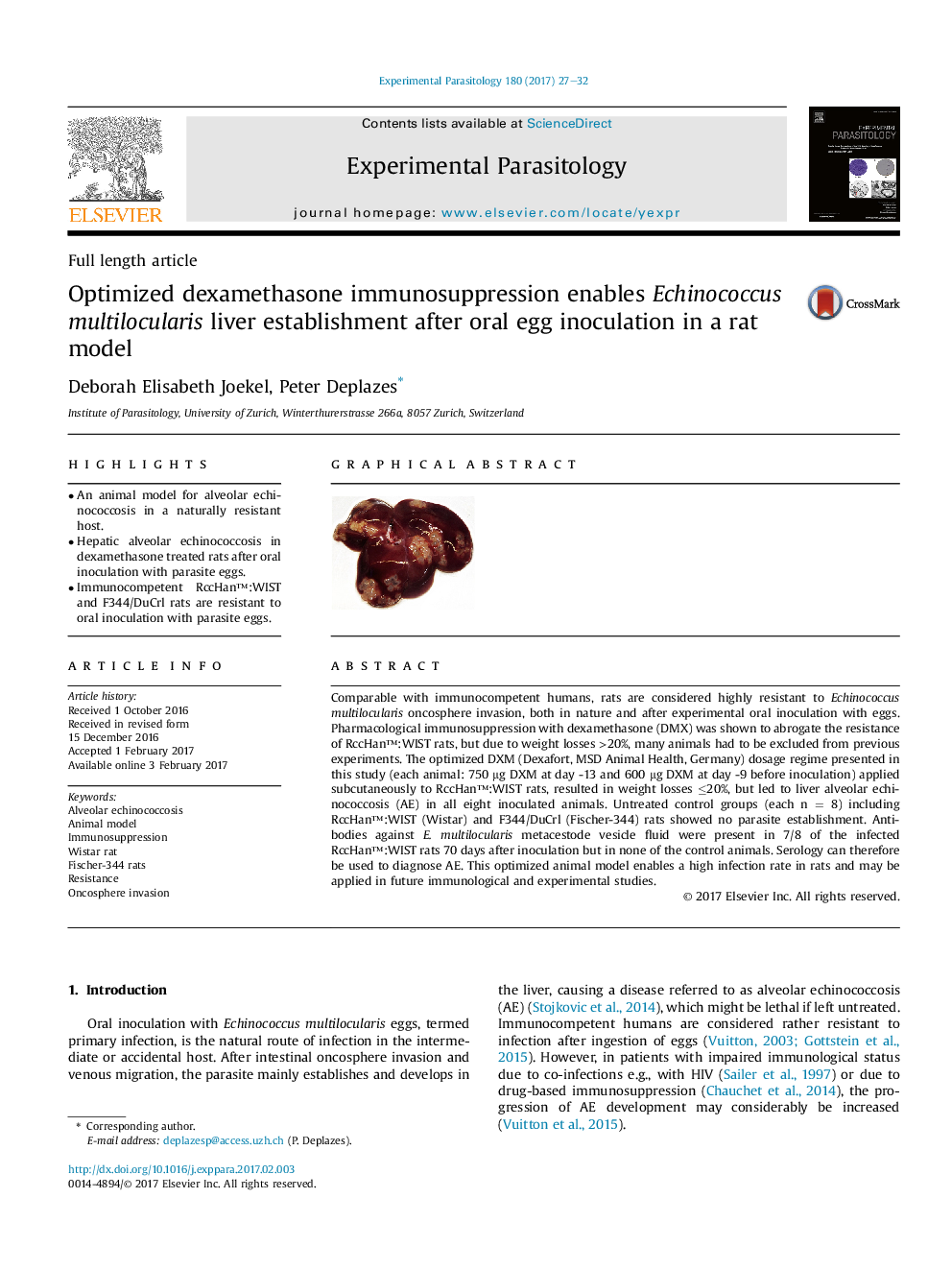
Comparable with immunocompetent humans, rats are considered highly resistant to Echinococcus multilocularis oncosphere invasion, both in nature and after experimental oral inoculation with eggs. Pharmacological immunosuppression with dexamethasone (DMX) was shown to abrogate the resistance of RccHanâ¢:WIST rats, but due to weight losses >20%, many animals had to be excluded from previous experiments. The optimized DXM (Dexafort, MSD Animal Health, Germany) dosage regime presented in this study (each animal: 750 μg DXM at day -13 and 600 μg DXM at day -9 before inoculation) applied subcutaneously to RccHanâ¢:WIST rats, resulted in weight losses â¤20%, but led to liver alveolar echinococcosis (AE) in all eight inoculated animals. Untreated control groups (each n = 8) including RccHanâ¢:WIST (Wistar) and F344/DuCrl (Fischer-344) rats showed no parasite establishment. Antibodies against E. multilocularis metacestode vesicle fluid were present in 7/8 of the infected RccHanâ¢:WIST rats 70 days after inoculation but in none of the control animals. Serology can therefore be used to diagnose AE. This optimized animal model enables a high infection rate in rats and may be applied in future immunological and experimental studies.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (220KB)Download full-size image