| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 622744 | Desalination | 2016 | 11 Pages |
•MCM-48 nanospheres with 3-D pore structure were used to modify the TFC membrane.•The TFN membranes were prepared by dispersing MCM-48 in the aqueous or organic phase.•The hydrophilicity of MCM-48 modified TFN membranes was higher than TFC membrane.•MCM-48 modified TFN membranes exhibited improved desalination performance.•MCM-48 is stable in TFN membranes by dispersing ether in organic or aqueous phase.
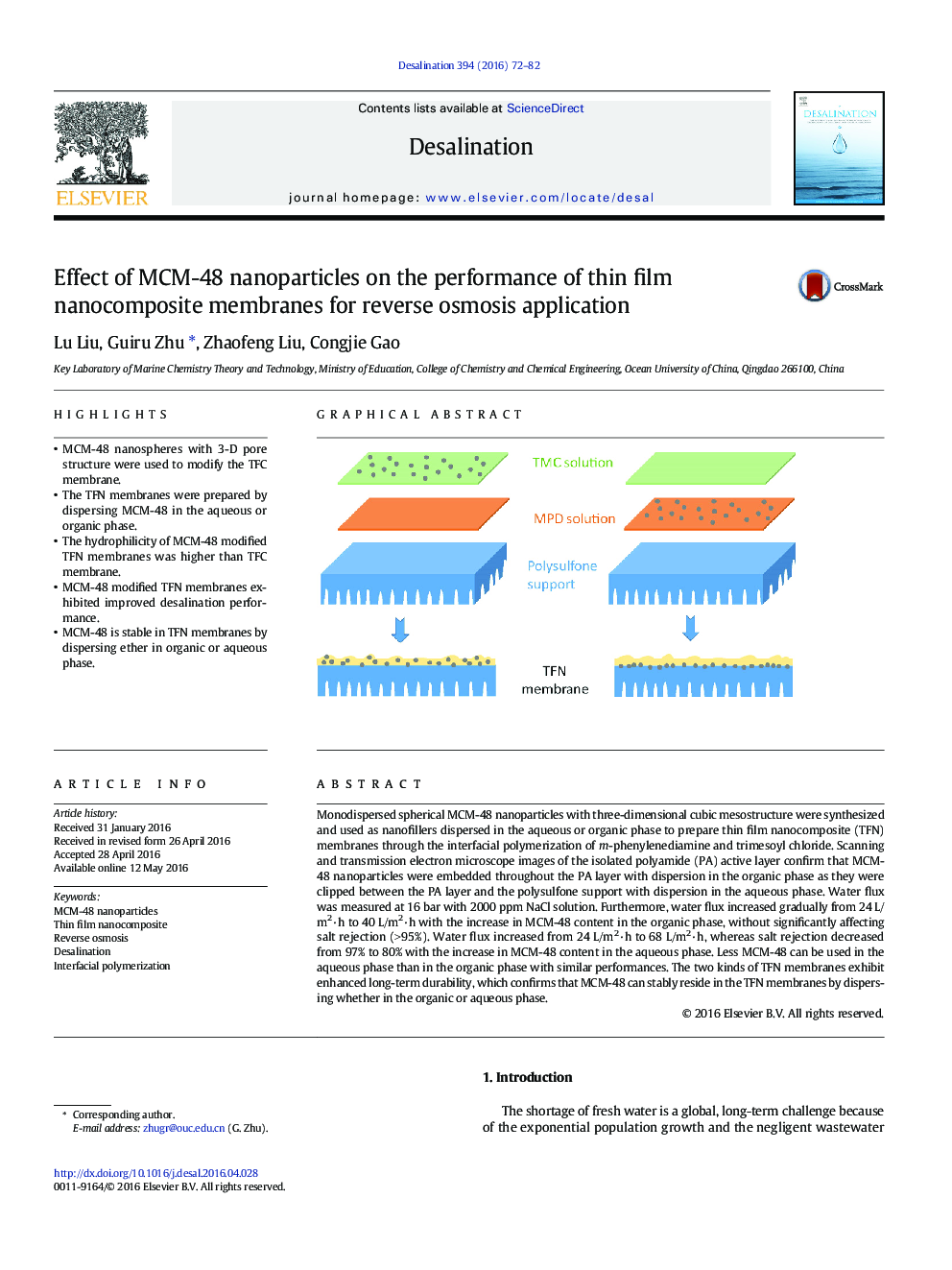
Monodispersed spherical MCM-48 nanoparticles with three-dimensional cubic mesostructure were synthesized and used as nanofillers dispersed in the aqueous or organic phase to prepare thin film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes through the interfacial polymerization of m-phenylenediamine and trimesoyl chloride. Scanning and transmission electron microscope images of the isolated polyamide (PA) active layer confirm that MCM-48 nanoparticles were embedded throughout the PA layer with dispersion in the organic phase as they were clipped between the PA layer and the polysulfone support with dispersion in the aqueous phase. Water flux was measured at 16 bar with 2000 ppm NaCl solution. Furthermore, water flux increased gradually from 24 L/m2·h to 40 L/m2·h with the increase in MCM-48 content in the organic phase, without significantly affecting salt rejection (>95%). Water flux increased from 24 L/m2·h to 68 L/m2·h, whereas salt rejection decreased from 97% to 80% with the increase in MCM-48 content in the aqueous phase. Less MCM-48 can be used in the aqueous phase than in the organic phase with similar performances. The two kinds of TFN membranes exhibit enhanced long-term durability, which confirms that MCM-48 can stably reside in the TFN membranes by dispersing whether in the organic or aqueous phase.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide