| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 623672 | Desalination | 2014 | 7 Pages |
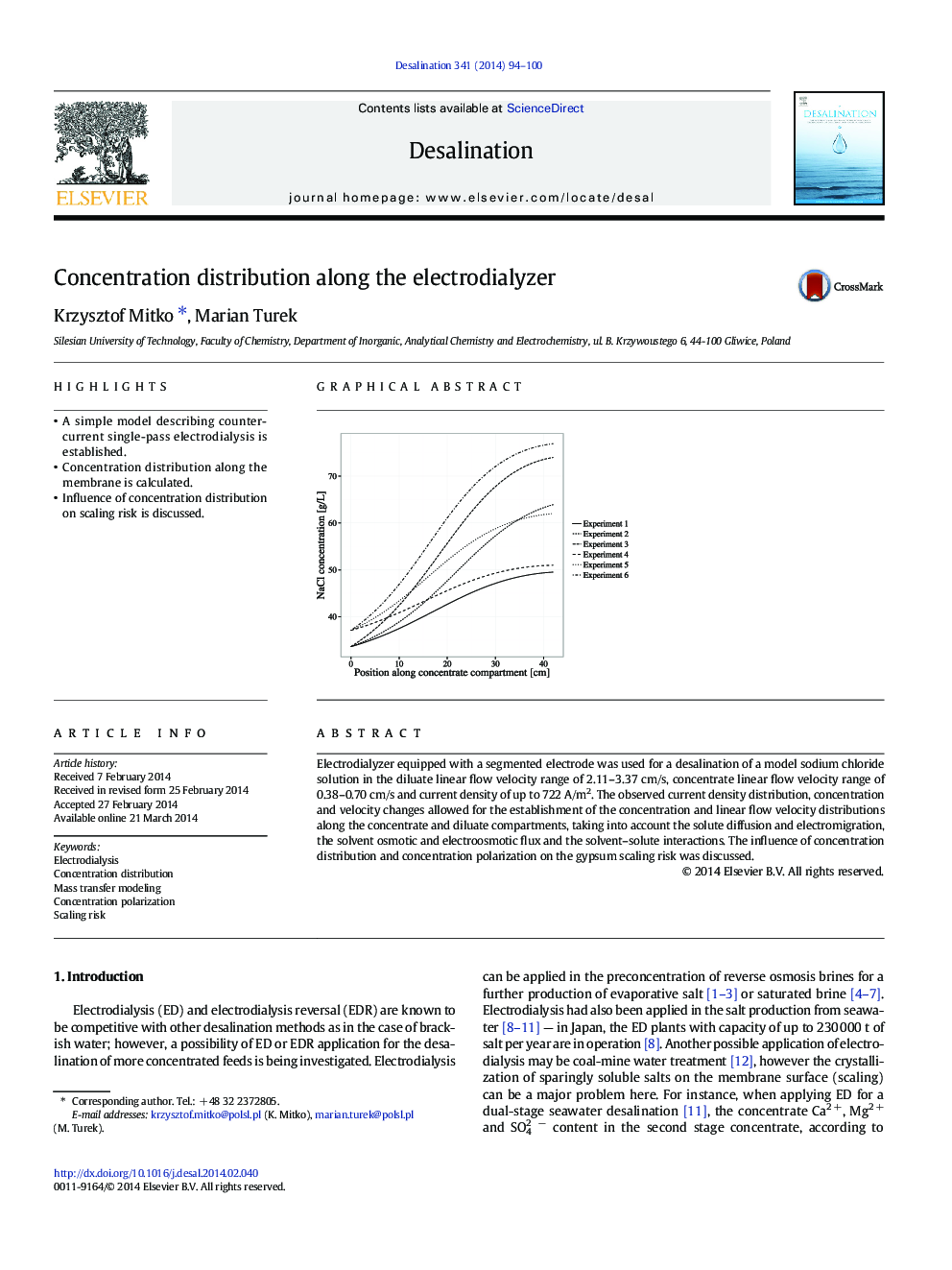
•A simple model describing counter-current single-pass electrodialysis is established.•Concentration distribution along the membrane is calculated.•Influence of concentration distribution on scaling risk is discussed.
Electrodialyzer equipped with a segmented electrode was used for a desalination of a model sodium chloride solution in the diluate linear flow velocity range of 2.11–3.37 cm/s, concentrate linear flow velocity range of 0.38–0.70 cm/s and current density of up to 722 A/m2. The observed current density distribution, concentration and velocity changes allowed for the establishment of the concentration and linear flow velocity distributions along the concentrate and diluate compartments, taking into account the solute diffusion and electromigration, the solvent osmotic and electroosmotic flux and the solvent–solute interactions. The influence of concentration distribution and concentration polarization on the gypsum scaling risk was discussed.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide