| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 623673 | Desalination | 2014 | 6 Pages |
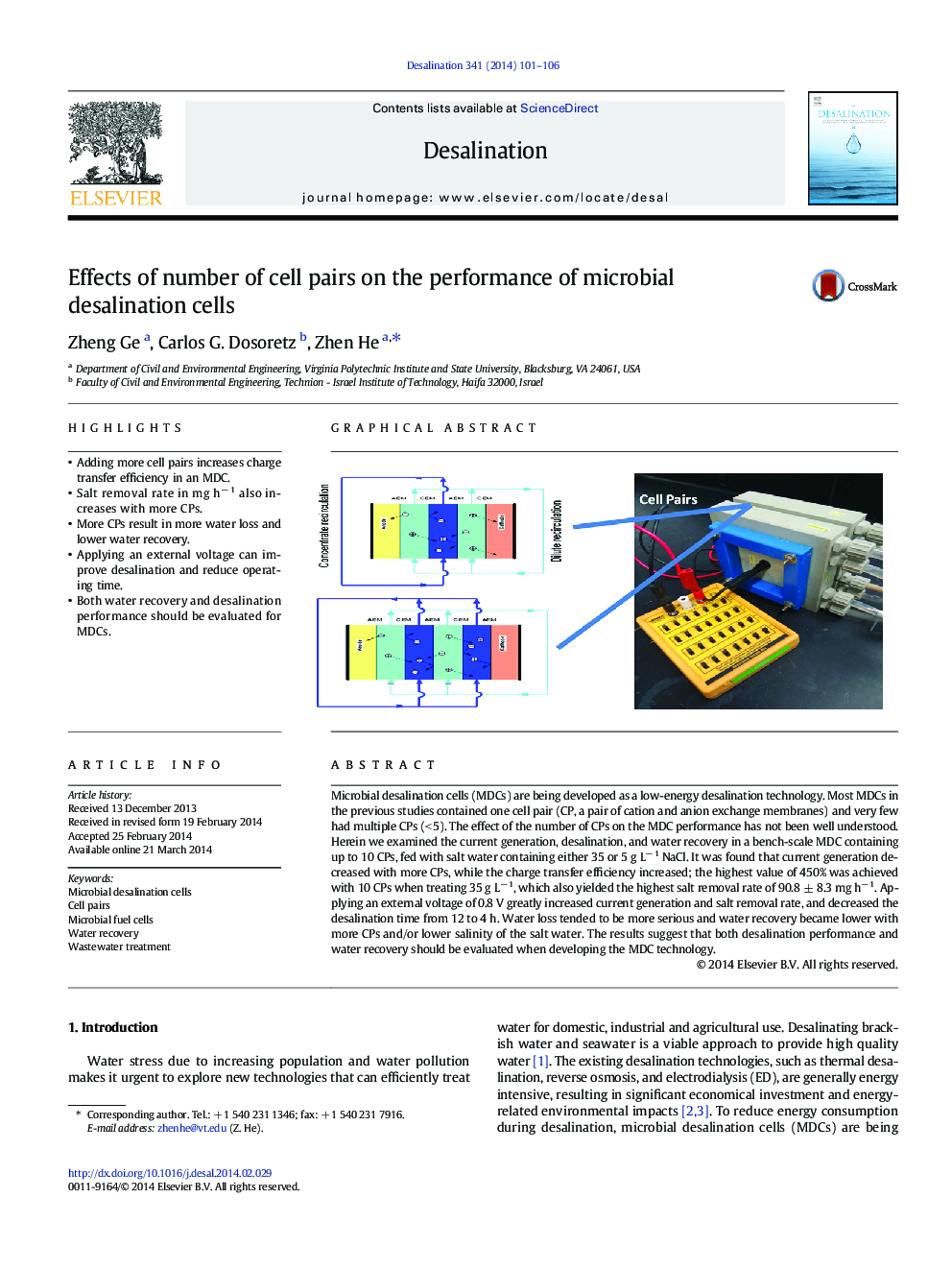
•Adding more cell pairs increases charge transfer efficiency in an MDC.•Salt removal rate in mg h− 1 also increases with more CPs.•More CPs result in more water loss and lower water recovery.•Applying an external voltage can improve desalination and reduce operating time.•Both water recovery and desalination performance should be evaluated for MDCs.
Microbial desalination cells (MDCs) are being developed as a low-energy desalination technology. Most MDCs in the previous studies contained one cell pair (CP, a pair of cation and anion exchange membranes) and very few had multiple CPs (< 5). The effect of the number of CPs on the MDC performance has not been well understood. Herein we examined the current generation, desalination, and water recovery in a bench-scale MDC containing up to 10 CPs, fed with salt water containing either 35 or 5 g L− 1 NaCl. It was found that current generation decreased with more CPs, while the charge transfer efficiency increased; the highest value of 450% was achieved with 10 CPs when treating 35 g L− 1, which also yielded the highest salt removal rate of 90.8 ± 8.3 mg h− 1. Applying an external voltage of 0.8 V greatly increased current generation and salt removal rate, and decreased the desalination time from 12 to 4 h. Water loss tended to be more serious and water recovery became lower with more CPs and/or lower salinity of the salt water. The results suggest that both desalination performance and water recovery should be evaluated when developing the MDC technology.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide