| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 623687 | Desalination | 2014 | 8 Pages |
•Changing the separation performance of the membranes by adding a multi-functional group salt•Alteration in the surface properties and surface pore sizes of the membranes•Increasing the color separation capability from 45 to near 80%•Improving the antifouling properties of the modified membranes
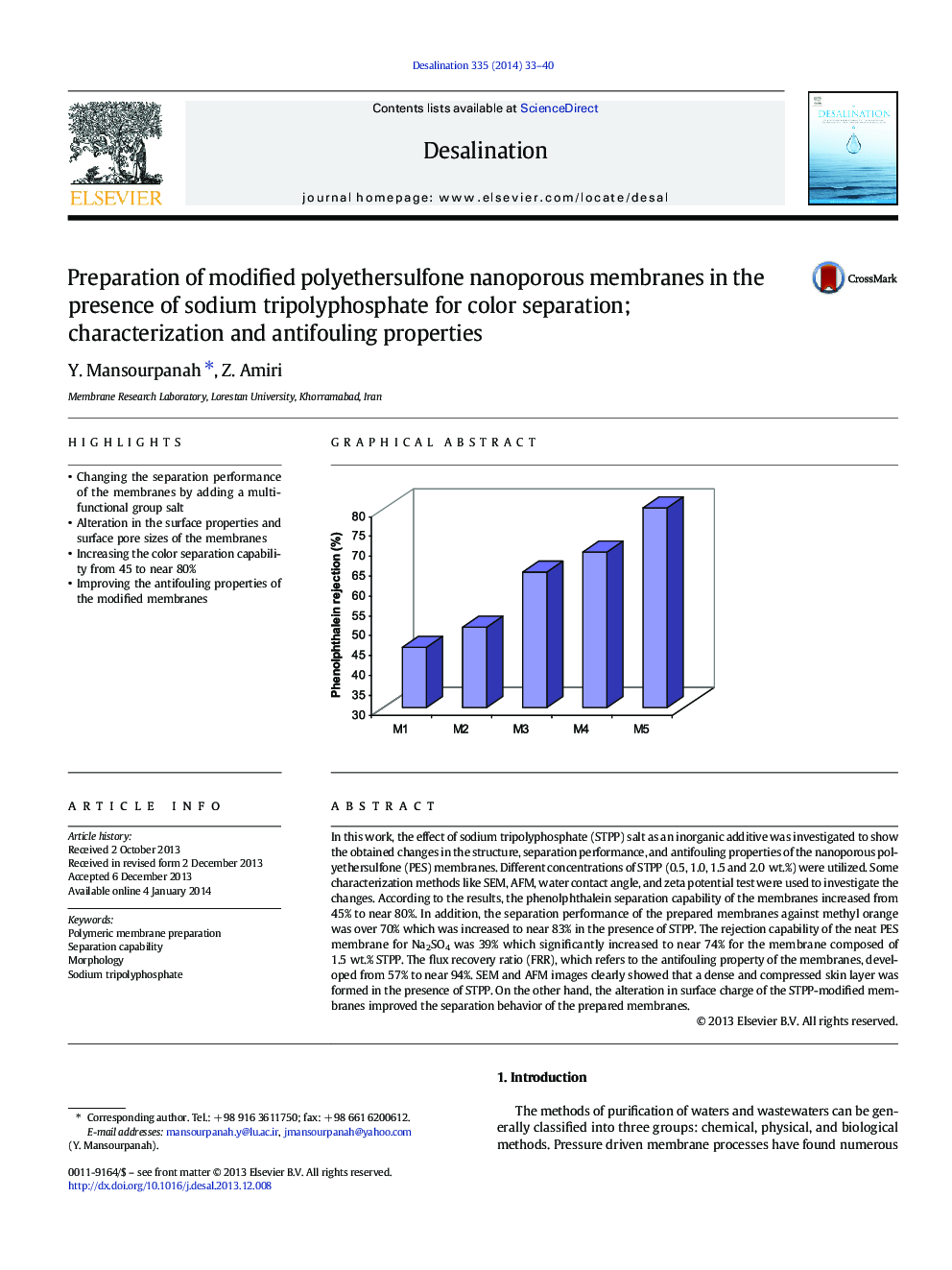
In this work, the effect of sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP) salt as an inorganic additive was investigated to show the obtained changes in the structure, separation performance, and antifouling properties of the nanoporous polyethersulfone (PES) membranes. Different concentrations of STPP (0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 wt.%) were utilized. Some characterization methods like SEM, AFM, water contact angle, and zeta potential test were used to investigate the changes. According to the results, the phenolphthalein separation capability of the membranes increased from 45% to near 80%. In addition, the separation performance of the prepared membranes against methyl orange was over 70% which was increased to near 83% in the presence of STPP. The rejection capability of the neat PES membrane for Na2SO4 was 39% which significantly increased to near 74% for the membrane composed of 1.5 wt.% STPP. The flux recovery ratio (FRR), which refers to the antifouling property of the membranes, developed from 57% to near 94%. SEM and AFM images clearly showed that a dense and compressed skin layer was formed in the presence of STPP. On the other hand, the alteration in surface charge of the STPP-modified membranes improved the separation behavior of the prepared membranes.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide