| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6291346 | Experimental Parasitology | 2013 | 8 Pages |
â¢It was shown that IL-22 brought about Th1 cytokine responses.â¢IFN-γ level in the LACK + IL-22 group was significantly higher than LACK group.â¢IL-4 level in the LACK + IL-22 group was significantly lower than LACK group.â¢Results show effectiveness of IL-22 in survival rate.
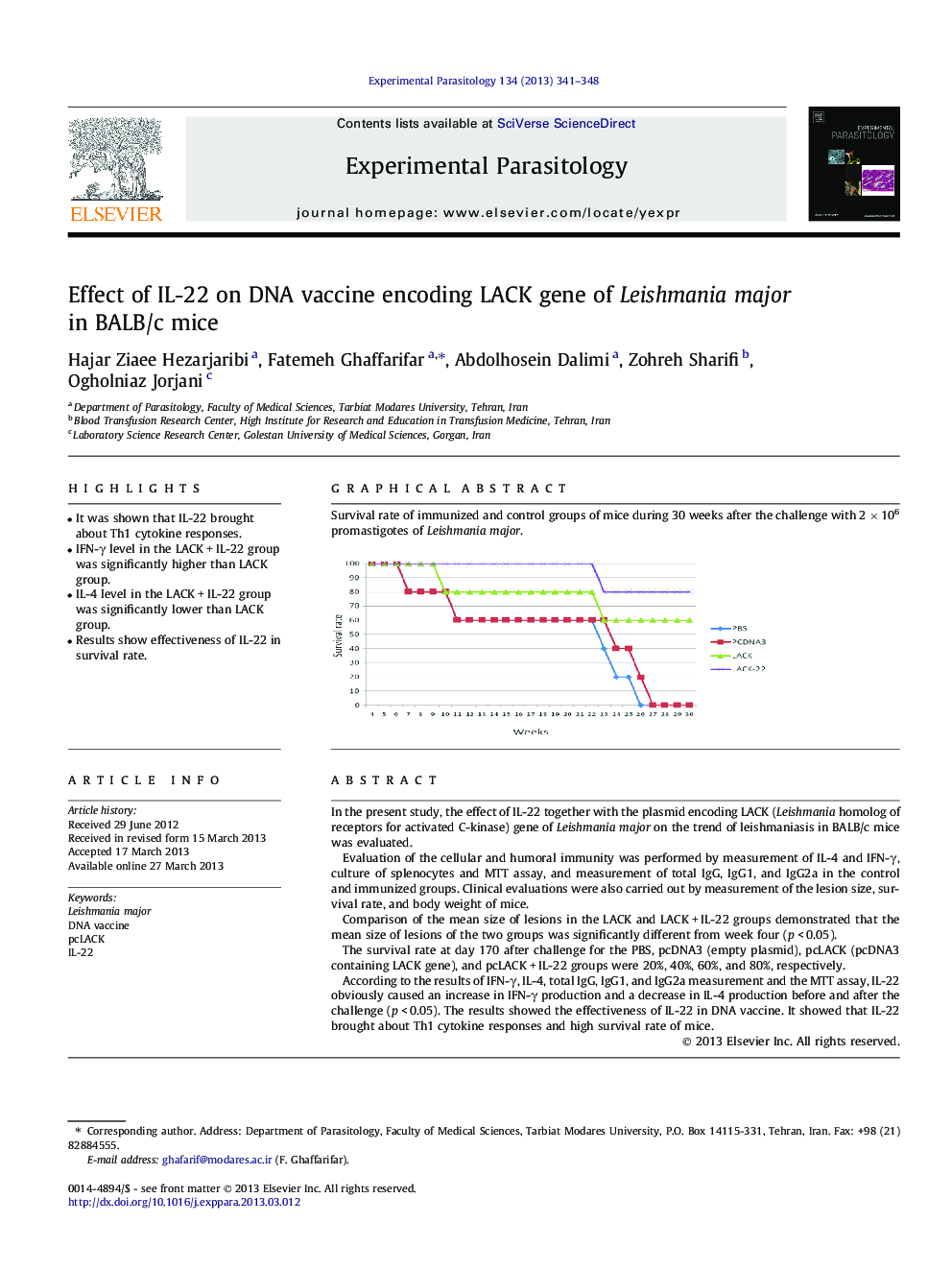
In the present study, the effect of IL-22 together with the plasmid encoding LACK (Leishmania homolog of receptors for activated C-kinase) gene of Leishmania major on the trend of leishmaniasis in BALB/c mice was evaluated.Evaluation of the cellular and humoral immunity was performed by measurement of IL-4 and IFN-γ, culture of splenocytes and MTT assay, and measurement of total IgG, IgG1, and IgG2a in the control and immunized groups. Clinical evaluations were also carried out by measurement of the lesion size, survival rate, and body weight of mice.Comparison of the mean size of lesions in the LACK and LACK + IL-22 groups demonstrated that the mean size of lesions of the two groups was significantly different from week four (p < 0.05).The survival rate at day 170 after challenge for the PBS, pcDNA3 (empty plasmid), pcLACK (pcDNA3 containing LACK gene), and pcLACK + IL-22 groups were 20%, 40%, 60%, and 80%, respectively.According to the results of IFN-γ, IL-4, total IgG, IgG1, and IgG2a measurement and the MTT assay, IL-22 obviously caused an increase in IFN-γ production and a decrease in IL-4 production before and after the challenge (p < 0.05). The results showed the effectiveness of IL-22 in DNA vaccine. It showed that IL-22 brought about Th1 cytokine responses and high survival rate of mice.
Graphical abstractSurvival rate of immunized and control groups of mice during 30 weeks after the challenge with 2Â ÃÂ 106 promastigotes of Leishmania major.Download full-size image