| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6329020 | Science of The Total Environment | 2014 | 9 Pages |
â¢A method to quantify the predictive uncertainty of machine learning was developed.â¢Two machine learning techniques were integrated to improve their predictions.â¢The sources of uncertainty in model prediction were identified.â¢A possible way for reducing prediction uncertainty was suggested.â¢A better technique to evaluate the performance of models is found and recommended.
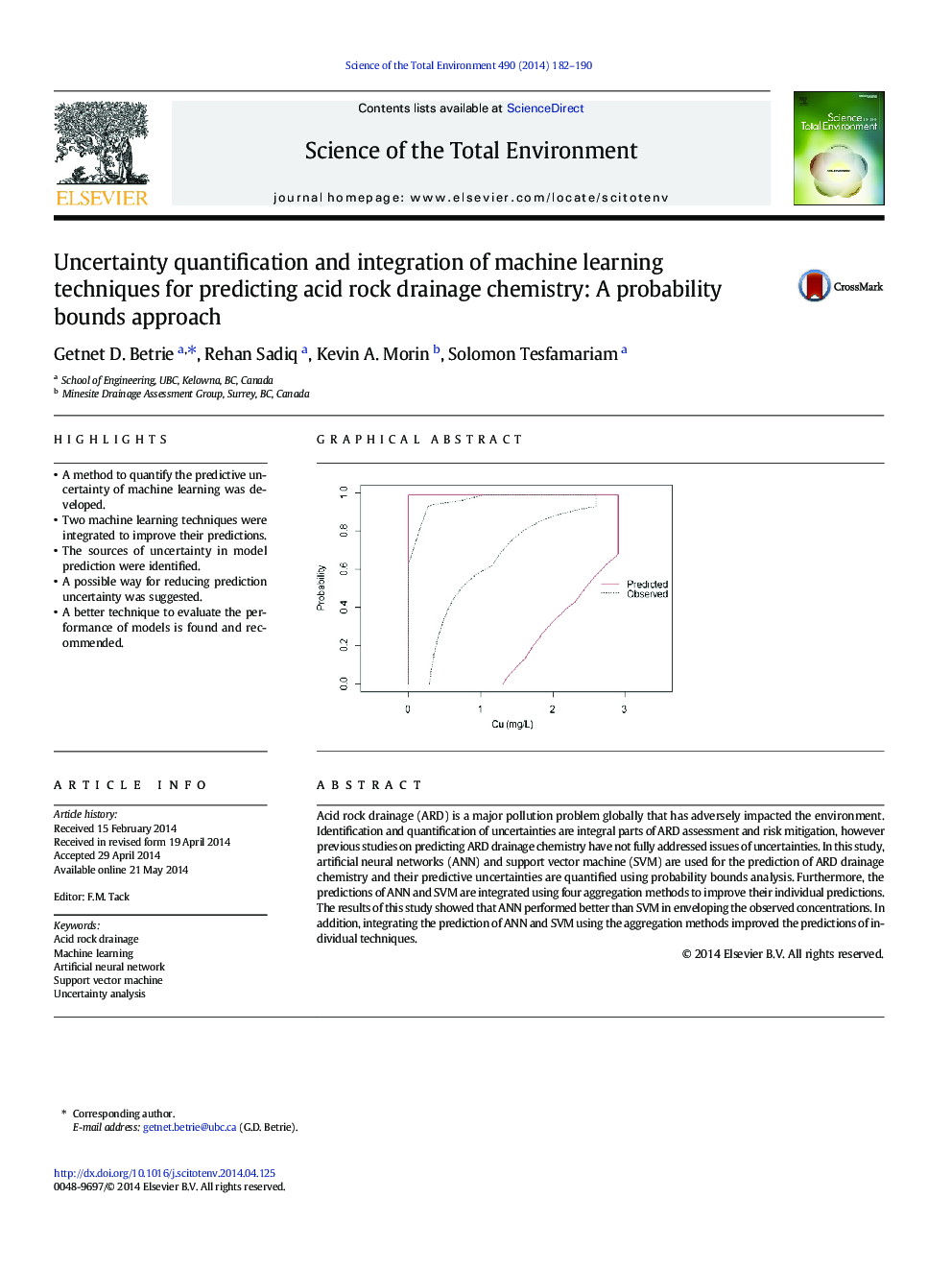
Acid rock drainage (ARD) is a major pollution problem globally that has adversely impacted the environment. Identification and quantification of uncertainties are integral parts of ARD assessment and risk mitigation, however previous studies on predicting ARD drainage chemistry have not fully addressed issues of uncertainties. In this study, artificial neural networks (ANN) and support vector machine (SVM) are used for the prediction of ARD drainage chemistry and their predictive uncertainties are quantified using probability bounds analysis. Furthermore, the predictions of ANN and SVM are integrated using four aggregation methods to improve their individual predictions. The results of this study showed that ANN performed better than SVM in enveloping the observed concentrations. In addition, integrating the prediction of ANN and SVM using the aggregation methods improved the predictions of individual techniques.
Graphical abstractDownload full-size image