| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6454283 | Applied Catalysis B: Environmental | 2017 | 13 Pages |
â¢A heterojunction MIL-125/Ag/C3N4 nanocomposite was implemented as an efficient visible-light response photocatalysts.â¢Ag nanoparticles (NPs) were photodeposited on the surface of g-C3N4 and MIL-125 to increase visible-light absorption and reducing the recombination of electron-holes.â¢MIL-125/Ag/C3N4 nanocomposite is efficient visible-light response photocatalysts for the photoreduction of nitrocompounds in the green catalytic routes.â¢MIL-125/Ag/C3N4 nanocomposite is efficient visible-light response photocatalysts for the photoxidation of alcohols in the O2 atmosphere and ambient temperature.
Photocatalytic synthesis using visible light is a desirable chemical process because of its potential to utilize sunlight. A heterostructured MIL-125/Ag/g-C3N4 nanocomposite was implemented as an efficient bifunctional visible-light response catalyst for the photoreduction of nitrocompounds and the oxidation of alcohols. The photocatalyst was prepared via an accessible method and characterized by XRD, SEM, TEM, XPS, FT-IR, N2 adsorption-desorption isotherm, UV-vis DRS, PL and EIS. The reactive efficiency of the photocatalyst depends on two primary factors, one is the light adsorption of catalysts, Ag nanoparticles (NPs) were photodeposited on the surface of g-C3N4 and MIL-125 to increase visible-light absorption via the surface plasmon resonance. And the other is the separation efficiency of the photogenerated charge carrier. As an electron-conduction bridge in the interface between MIL-125 and g-C3N4, Ag NPs could facilitate the direct migration of photoinduced electrons from g-C3N4 to MIL-125 and retard the recombination of electron-holes. Therefore, the MIL-125/Ag/g-C3N4 sample shows highest photocatalytic activity compared with MIL-125, g-C3N4, MIL-125/Ag and MIL-125/g-C3N4. A corresponding photocatalytic mechanism of these reactions was discussed in detail. Moreover, the photoreduction of nitrocompounds and oxidation of the alcohols with superior conversions and selectivities were obtained, and the catalyst can be recycled four times. It is concluded that MIL-125/Ag/g-C3N4 would be a promising visible light photocatalyst in the field of selective organic transformations.
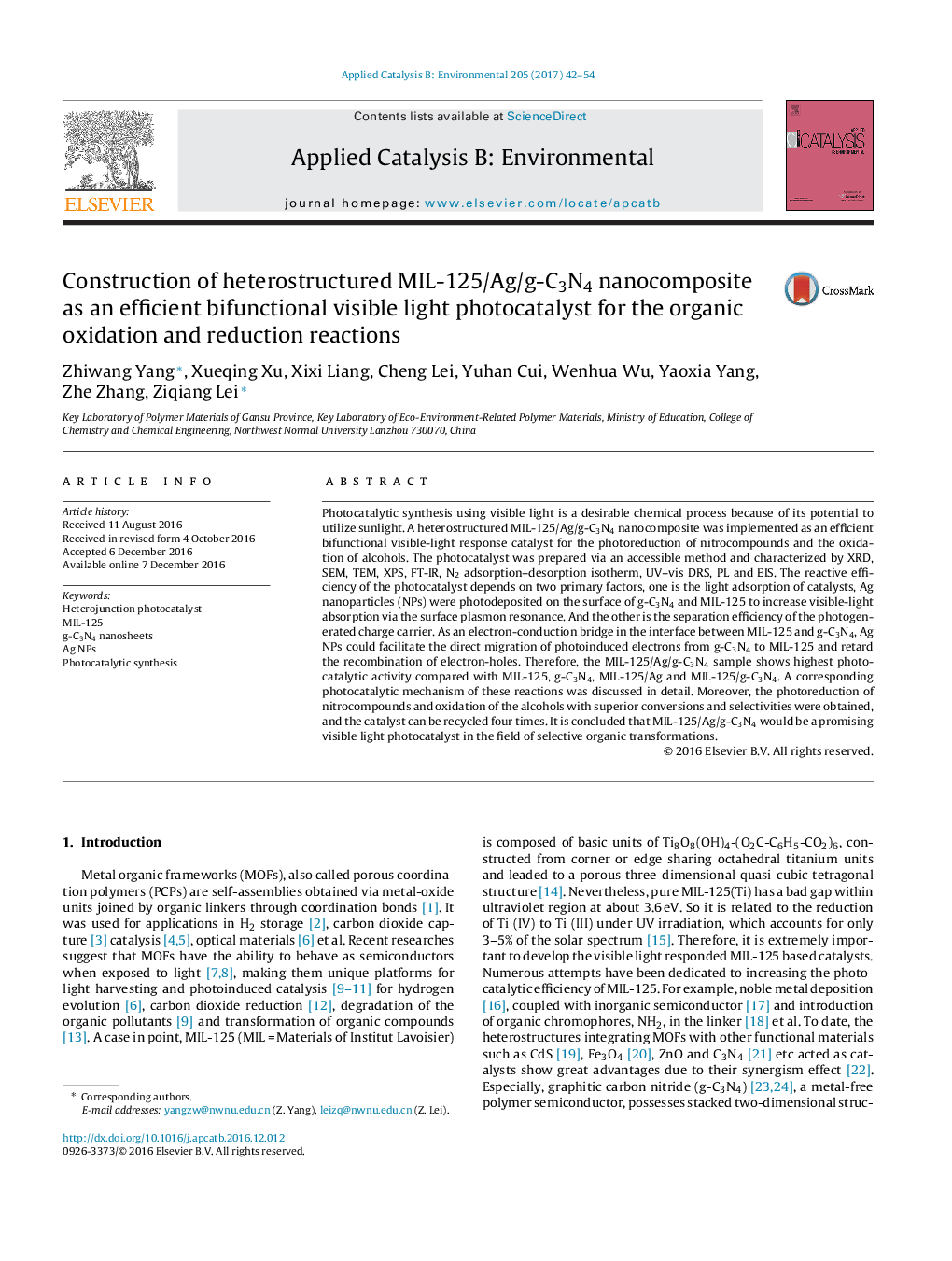
Graphical abstractA heterojunction MIL-125/Ag/g-C3N4 nanocomposite was implemented as an efficient visible-light response photocatalysts for the photoreduction of nitrocompounds and oxidation of the alcohols with superior conversions and selectivities. Ag nanoparticles (NPs) were photodeposited on the surface of g-C3N4 and MIL-125 to increase visible-light absorption via the surface plasmon resonance. Moreover, as an electron-conduction bridge, in the interface between MIL-125 and g-C3N4, it is facilitate the direct migration of photoinduced electrons from g-C3N4 to MIL-125, which is conductive to retarding the recombination of electron-holes. Therefore, the MIL-125/Ag/g-C3N4 sample shows highest photocatalytic compared with the MIL-125, g-C3N4, The MIL-125/Ag and MIL-125/g-C3N4. Moreover, catalyst can be recycled four times for the photoreduction of nitrocompounds and oxidation of the alcohols. It is concluded that MIL-125/Ag/g-C3N4 would be an promising visible light photocatalyst in the field of selective organic transformations.Download high-res image (156KB)Download full-size image