| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6467498 | Chemical Engineering Science | 2017 | 9 Pages |
â¢RLs isolated from cholinium IL-pretreated straw had different structural features.â¢Gly-RL had the highest carboxylic acid and the lowest phenolic hydroxyl contents.â¢Gly-RL displayed the weakest non-productive enzyme adsorption.â¢Negative effect of RLs stemmed from their inhibition to cellulase-mediated reactions.
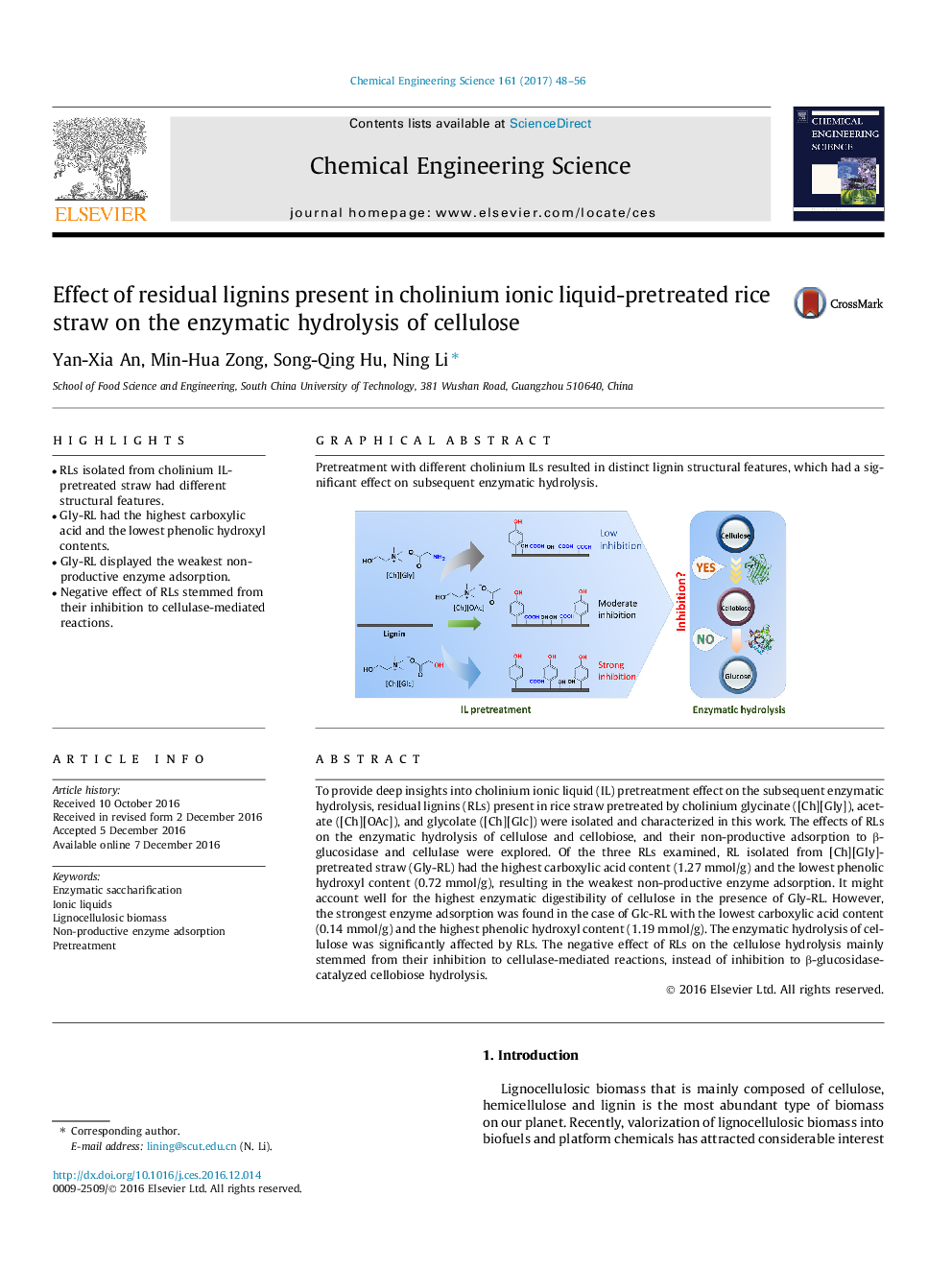
To provide deep insights into cholinium ionic liquid (IL) pretreatment effect on the subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis, residual lignins (RLs) present in rice straw pretreated by cholinium glycinate ([Ch][Gly]), acetate ([Ch][OAc]), and glycolate ([Ch][Glc]) were isolated and characterized in this work. The effects of RLs on the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose and cellobiose, and their non-productive adsorption to β-glucosidase and cellulase were explored. Of the three RLs examined, RL isolated from [Ch][Gly]-pretreated straw (Gly-RL) had the highest carboxylic acid content (1.27 mmol/g) and the lowest phenolic hydroxyl content (0.72 mmol/g), resulting in the weakest non-productive enzyme adsorption. It might account well for the highest enzymatic digestibility of cellulose in the presence of Gly-RL. However, the strongest enzyme adsorption was found in the case of Glc-RL with the lowest carboxylic acid content (0.14 mmol/g) and the highest phenolic hydroxyl content (1.19 mmol/g). The enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose was significantly affected by RLs. The negative effect of RLs on the cellulose hydrolysis mainly stemmed from their inhibition to cellulase-mediated reactions, instead of inhibition to β-glucosidase-catalyzed cellobiose hydrolysis.
Graphical abstractPretreatment with different cholinium ILs resulted in distinct lignin structural features, which had a significant effect on subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis.Download high-res image (175KB)Download full-size image