| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6467499 | Chemical Engineering Science | 2017 | 8 Pages |
â¢Cellobiose is a zero-calorie sweetener and dietary fiber.â¢Value-added cellobiose was synthesized from sucrose by an enzyme cocktail.â¢A kinetic model was developed for data accommodation and process optimization.â¢Use of thermophilic enzymes at elevated temperatures increases reaction rate.
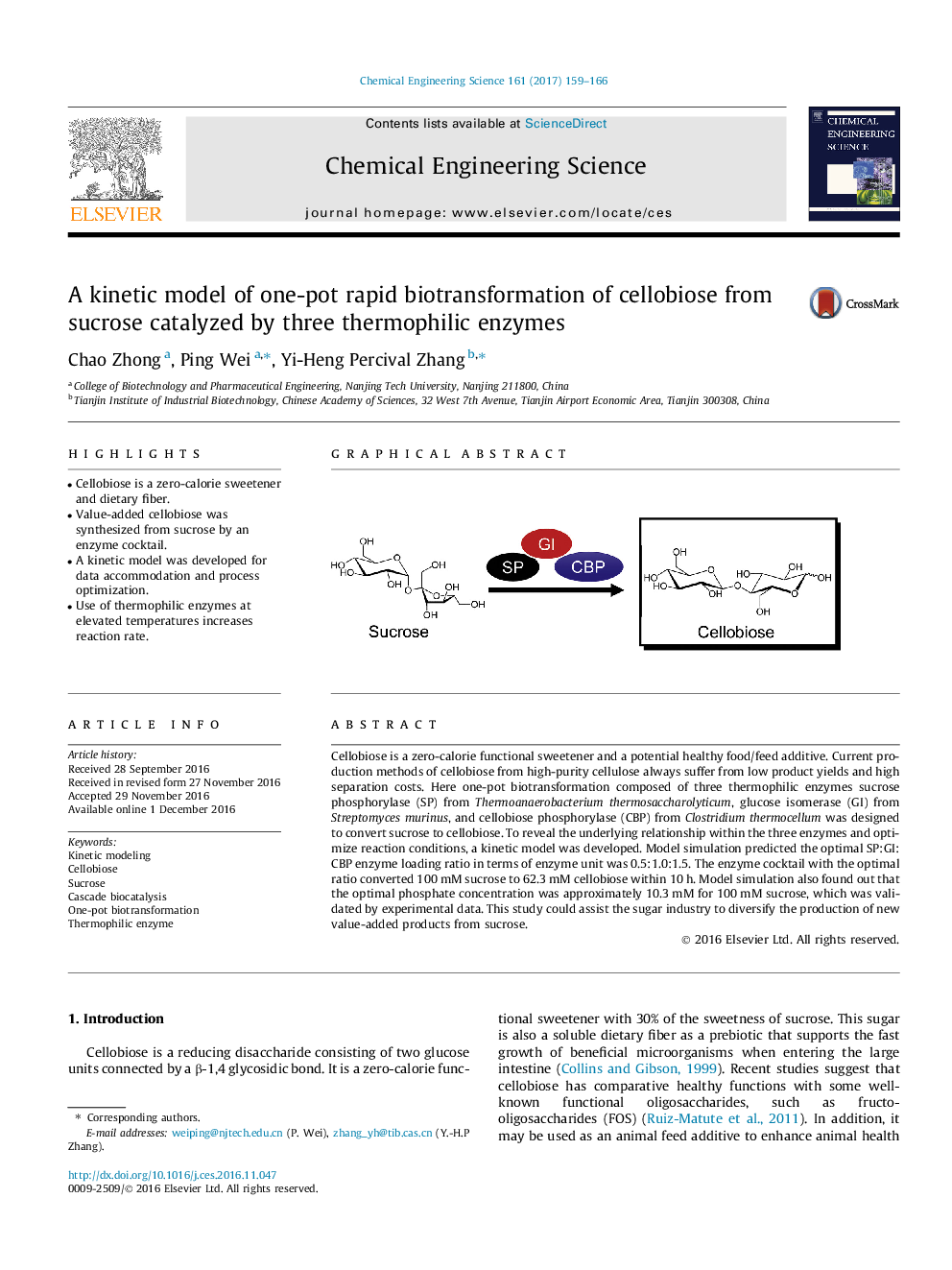
Cellobiose is a zero-calorie functional sweetener and a potential healthy food/feed additive. Current production methods of cellobiose from high-purity cellulose always suffer from low product yields and high separation costs. Here one-pot biotransformation composed of three thermophilic enzymes sucrose phosphorylase (SP) from Thermoanaerobacterium thermosaccharolyticum, glucose isomerase (GI) from Streptomyces murinus, and cellobiose phosphorylase (CBP) from Clostridium thermocellum was designed to convert sucrose to cellobiose. To reveal the underlying relationship within the three enzymes and optimize reaction conditions, a kinetic model was developed. Model simulation predicted the optimal SP:GI:CBP enzyme loading ratio in terms of enzyme unit was 0.5:1.0:1.5. The enzyme cocktail with the optimal ratio converted 100Â mM sucrose to 62.3Â mM cellobiose within 10Â h. Model simulation also found out that the optimal phosphate concentration was approximately 10.3Â mM for 100Â mM sucrose, which was validated by experimental data. This study could assist the sugar industry to diversify the production of new value-added products from sucrose.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (103KB)Download full-size image