| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6467792 | Chemical Engineering Science | 2016 | 12 Pages |
â¢Sparging pure nitrogen has negative effect on the production of methane in AD.â¢Recirculation of biogas in anaerobic digestion can enhance production of CH4.â¢The methane production rate increases with pure CO2 in microbubble sparging.
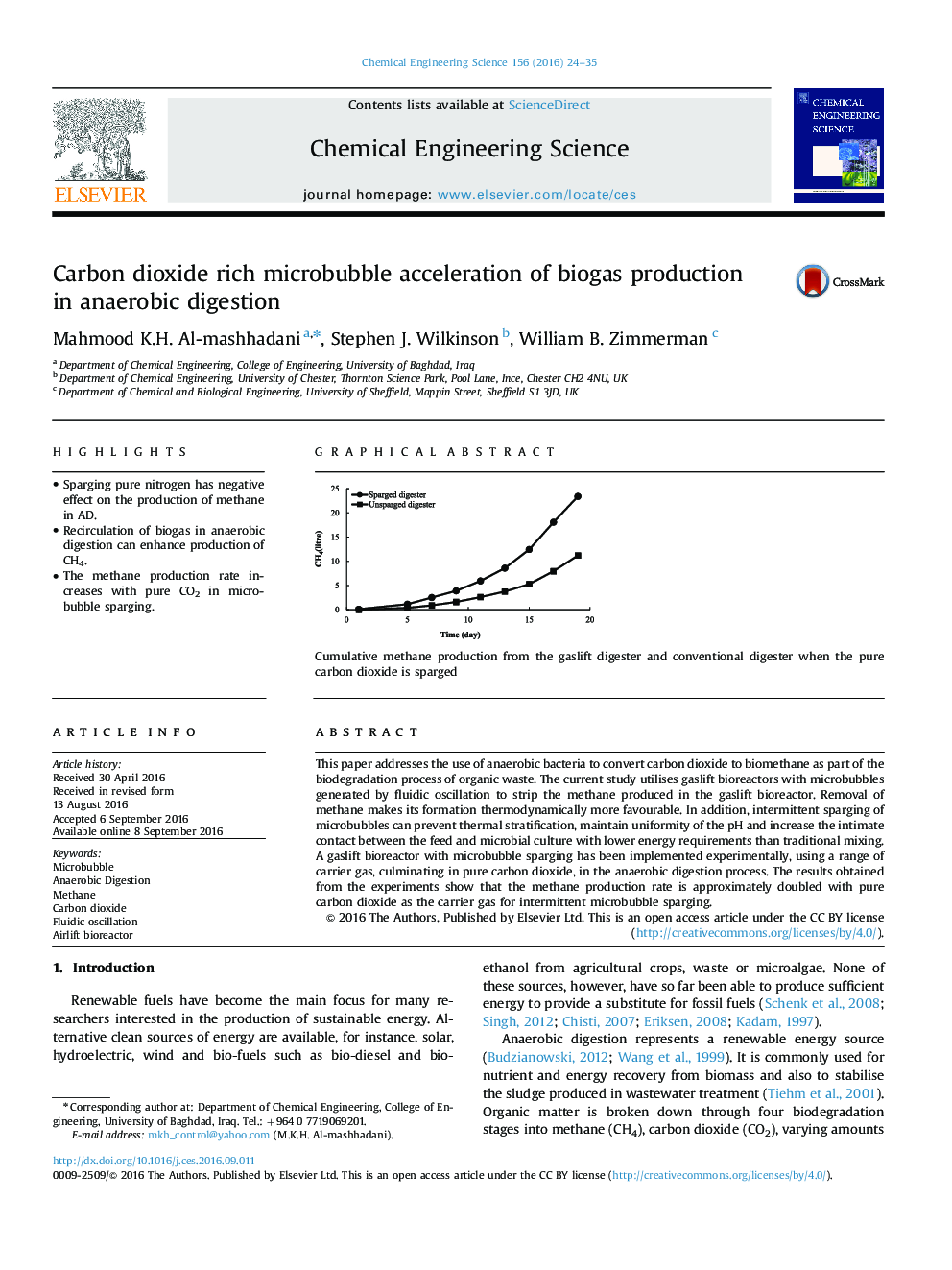
This paper addresses the use of anaerobic bacteria to convert carbon dioxide to biomethane as part of the biodegradation process of organic waste. The current study utilises gaslift bioreactors with microbubbles generated by fluidic oscillation to strip the methane produced in the gaslift bioreactor. Removal of methane makes its formation thermodynamically more favourable. In addition, intermittent sparging of microbubbles can prevent thermal stratification, maintain uniformity of the pH and increase the intimate contact between the feed and microbial culture with lower energy requirements than traditional mixing. A gaslift bioreactor with microbubble sparging has been implemented experimentally, using a range of carrier gas, culminating in pure carbon dioxide, in the anaerobic digestion process. The results obtained from the experiments show that the methane production rate is approximately doubled with pure carbon dioxide as the carrier gas for intermittent microbubble sparging.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (99KB)Download full-size imageCumulative methane production from the gaslift digester and conventional digester when the pure carbon dioxide is sparged