| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6474097 | Fuel | 2017 | 15 Pages |
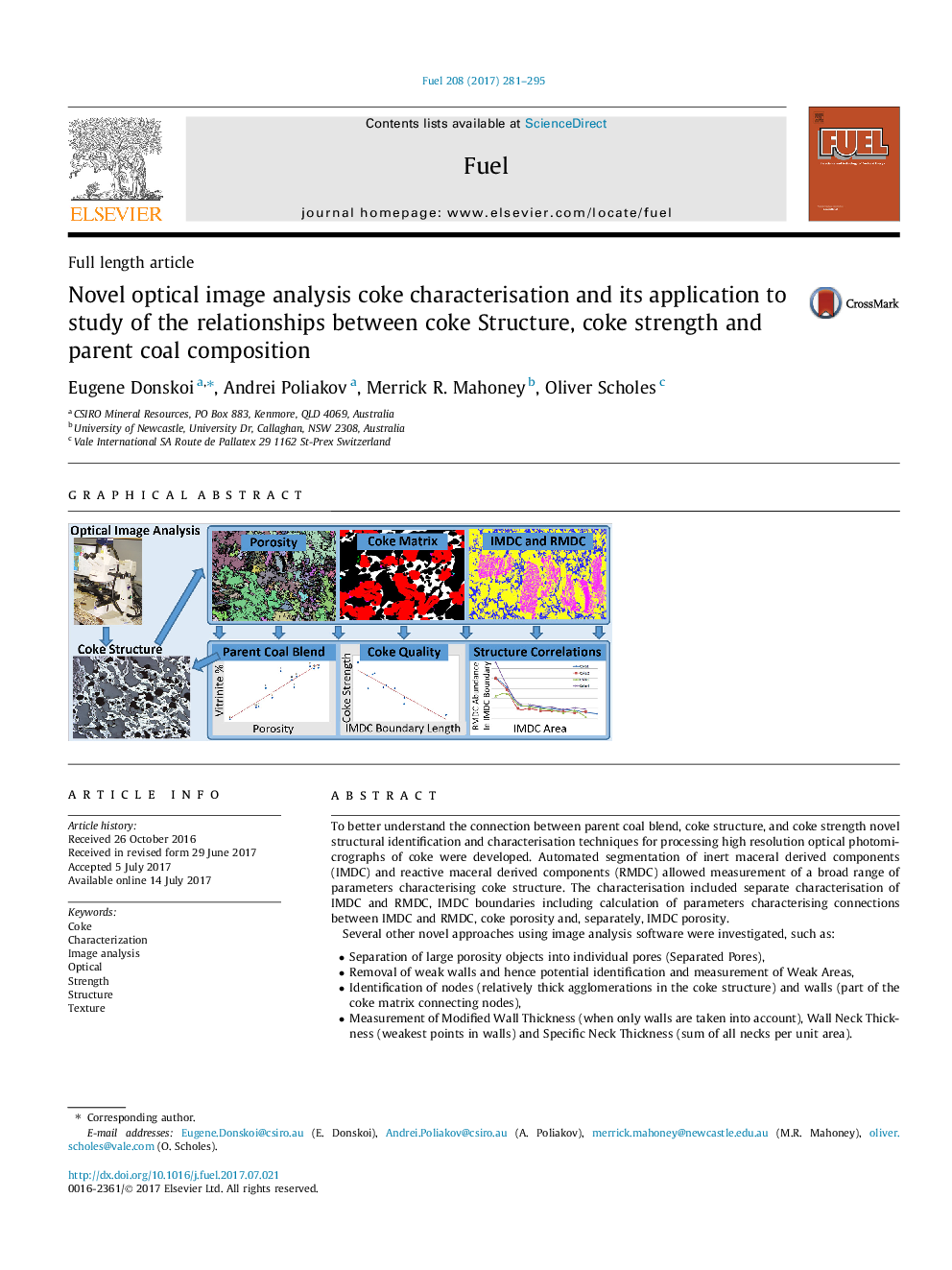
To better understand the connection between parent coal blend, coke structure, and coke strength novel structural identification and characterisation techniques for processing high resolution optical photomicrographs of coke were developed. Automated segmentation of inert maceral derived components (IMDC) and reactive maceral derived components (RMDC) allowed measurement of a broad range of parameters characterising coke structure. The characterisation included separate characterisation of IMDC and RMDC, IMDC boundaries including calculation of parameters characterising connections between IMDC and RMDC, coke porosity and, separately, IMDC porosity.Several other novel approaches using image analysis software were investigated, such as:â¢Separation of large porosity objects into individual pores (Separated Pores),â¢Removal of weak walls and hence potential identification and measurement of Weak Areas,â¢Identification of nodes (relatively thick agglomerations in the coke structure) and walls (part of the coke matrix connecting nodes),â¢Measurement of Modified Wall Thickness (when only walls are taken into account), Wall Neck Thickness (weakest points in walls) and Specific Neck Thickness (sum of all necks per unit area).Application of these novel characterisation techniques to a set of coke samples produced a substantial amount of data, which revealed many strong correlations between novel parameters characterising coke structure, and also between these parameters, coke strength indices and parent coal composition. This demonstrated the usefulness of the newly developed characterisation methodologies and gave a significantly improved understanding of coke structure and its connection with coke strength and parent coal blend. It should also be noted that these novel approaches to structural/textural characterisation can be applied to carbonaceous materials other than coke or other structural materials such as sinter, ore, and ceramics.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (426KB)Download full-size image