| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6474717 | Fuel | 2017 | 10 Pages |
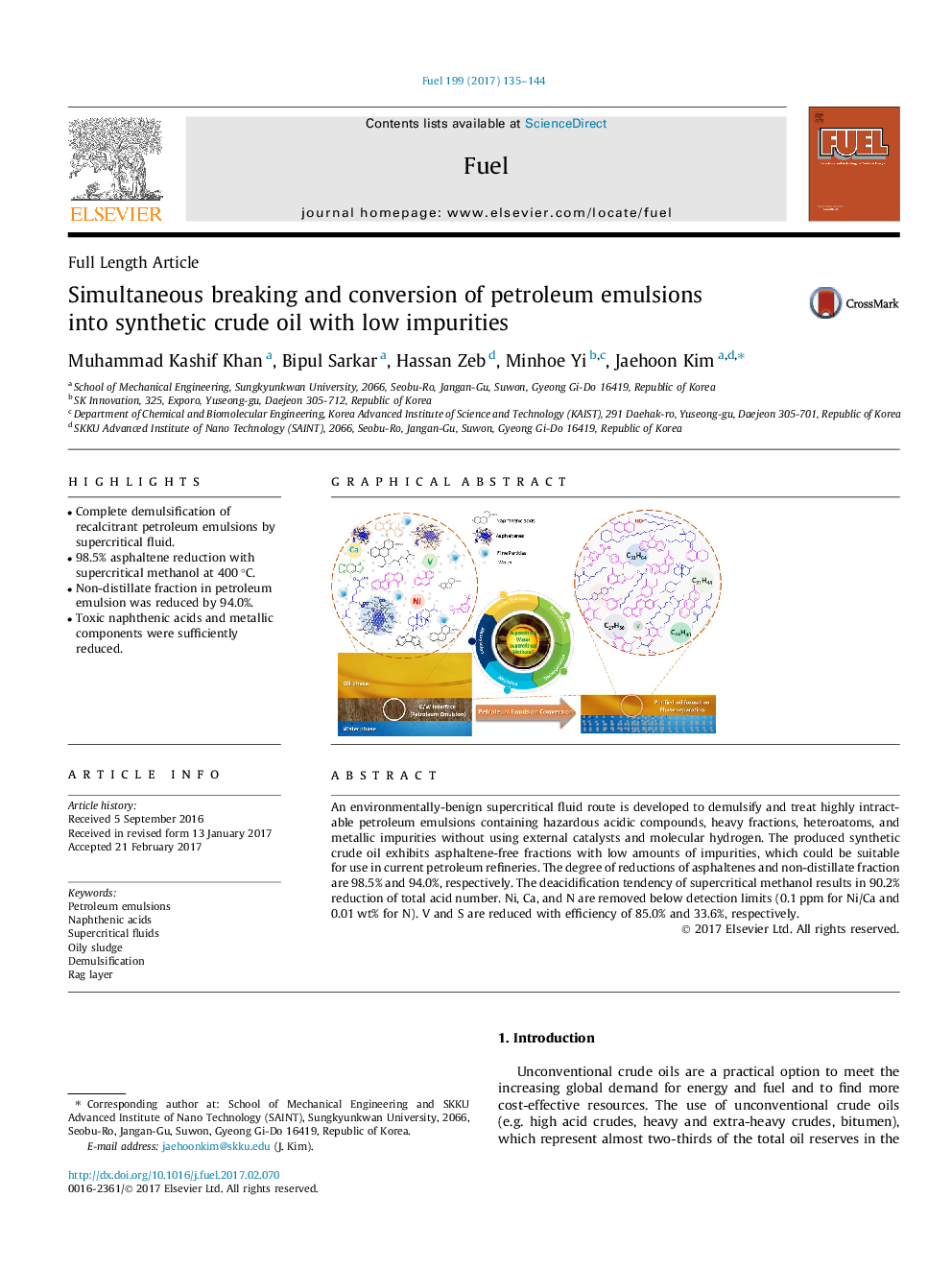
â¢Complete demulsification of recalcitrant petroleum emulsions by supercritical fluid.â¢98.5% asphaltene reduction with supercritical methanol at 400 °C.â¢Non-distillate fraction in petroleum emulsion was reduced by 94.0%.â¢Toxic naphthenic acids and metallic components were sufficiently reduced.
An environmentally-benign supercritical fluid route is developed to demulsify and treat highly intractable petroleum emulsions containing hazardous acidic compounds, heavy fractions, heteroatoms, and metallic impurities without using external catalysts and molecular hydrogen. The produced synthetic crude oil exhibits asphaltene-free fractions with low amounts of impurities, which could be suitable for use in current petroleum refineries. The degree of reductions of asphaltenes and non-distillate fraction are 98.5% and 94.0%, respectively. The deacidification tendency of supercritical methanol results in 90.2% reduction of total acid number. Ni, Ca, and N are removed below detection limits (0.1Â ppm for Ni/Ca and 0.01Â wt% for N). V and S are reduced with efficiency of 85.0% and 33.6%, respectively.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (136KB)Download full-size image