| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6475416 | Fuel | 2017 | 9 Pages |
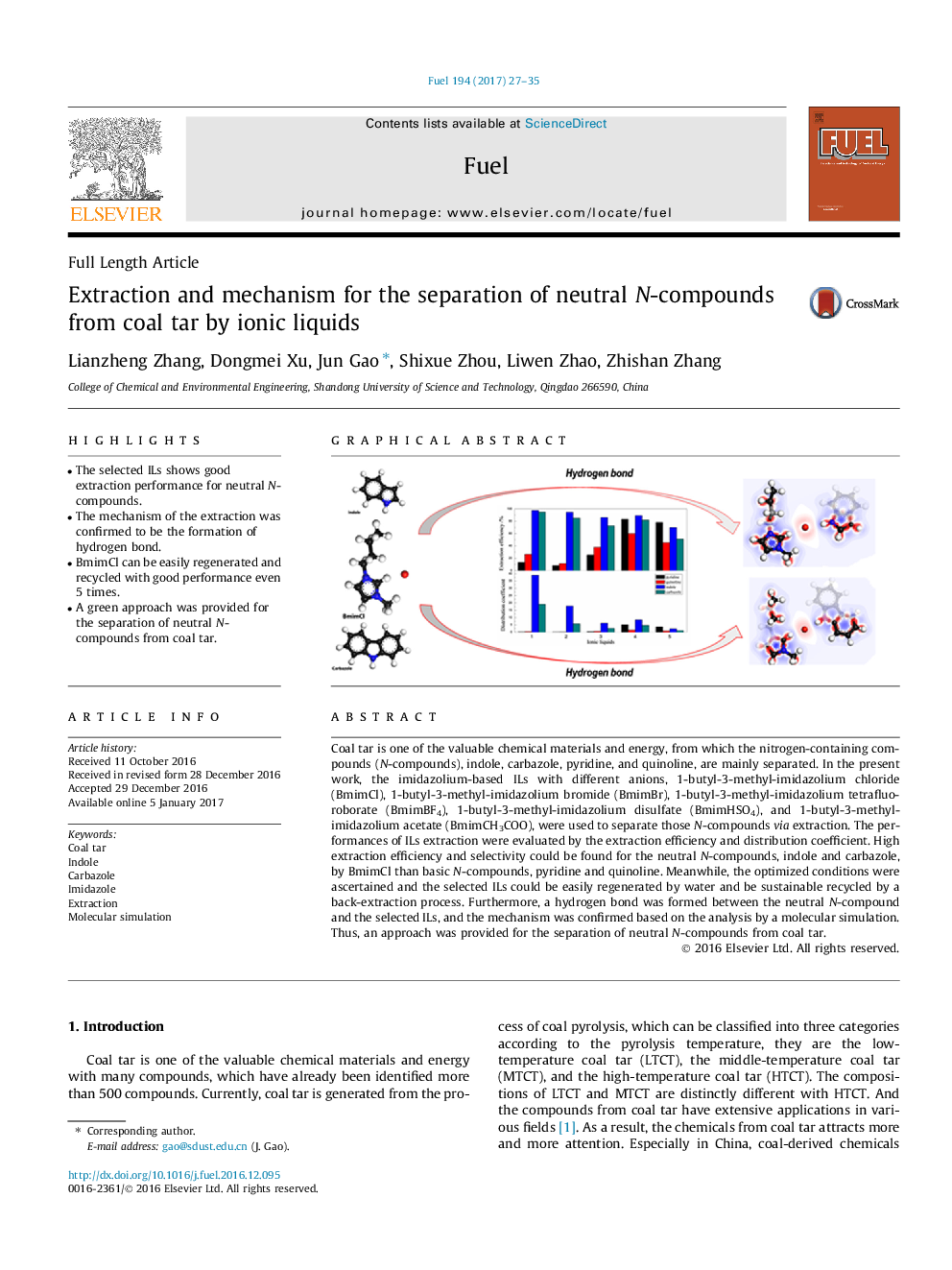
â¢The selected ILs shows good extraction performance for neutral N-compounds.â¢The mechanism of the extraction was confirmed to be the formation of hydrogen bond.â¢BmimCl can be easily regenerated and recycled with good performance even 5 times.â¢A green approach was provided for the separation of neutral N-compounds from coal tar.
Coal tar is one of the valuable chemical materials and energy, from which the nitrogen-containing compounds (N-compounds), indole, carbazole, pyridine, and quinoline, are mainly separated. In the present work, the imidazolium-based ILs with different anions, 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium chloride (BmimCl), 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium bromide (BmimBr), 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium tetrafluoroborate (BmimBF4), 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium disulfate (BmimHSO4), and 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium acetate (BmimCH3COO), were used to separate those N-compounds via extraction. The performances of ILs extraction were evaluated by the extraction efficiency and distribution coefficient. High extraction efficiency and selectivity could be found for the neutral N-compounds, indole and carbazole, by BmimCl than basic N-compounds, pyridine and quinoline. Meanwhile, the optimized conditions were ascertained and the selected ILs could be easily regenerated by water and be sustainable recycled by a back-extraction process. Furthermore, a hydrogen bond was formed between the neutral N-compound and the selected ILs, and the mechanism was confirmed based on the analysis by a molecular simulation. Thus, an approach was provided for the separation of neutral N-compounds from coal tar.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (86KB)Download full-size image