| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6480744 | Construction and Building Materials | 2017 | 9 Pages |
â¢A novel method to study the absolute volume change of cement pastes is proposed.â¢Helium pycnometry is proved to be superior than traditional chemical shrinkage test.â¢Helium pycnometry is found suitable on studying the hydration process of cement.â¢Data of helium pycnometry is accurate, continuous and automatically obtained.
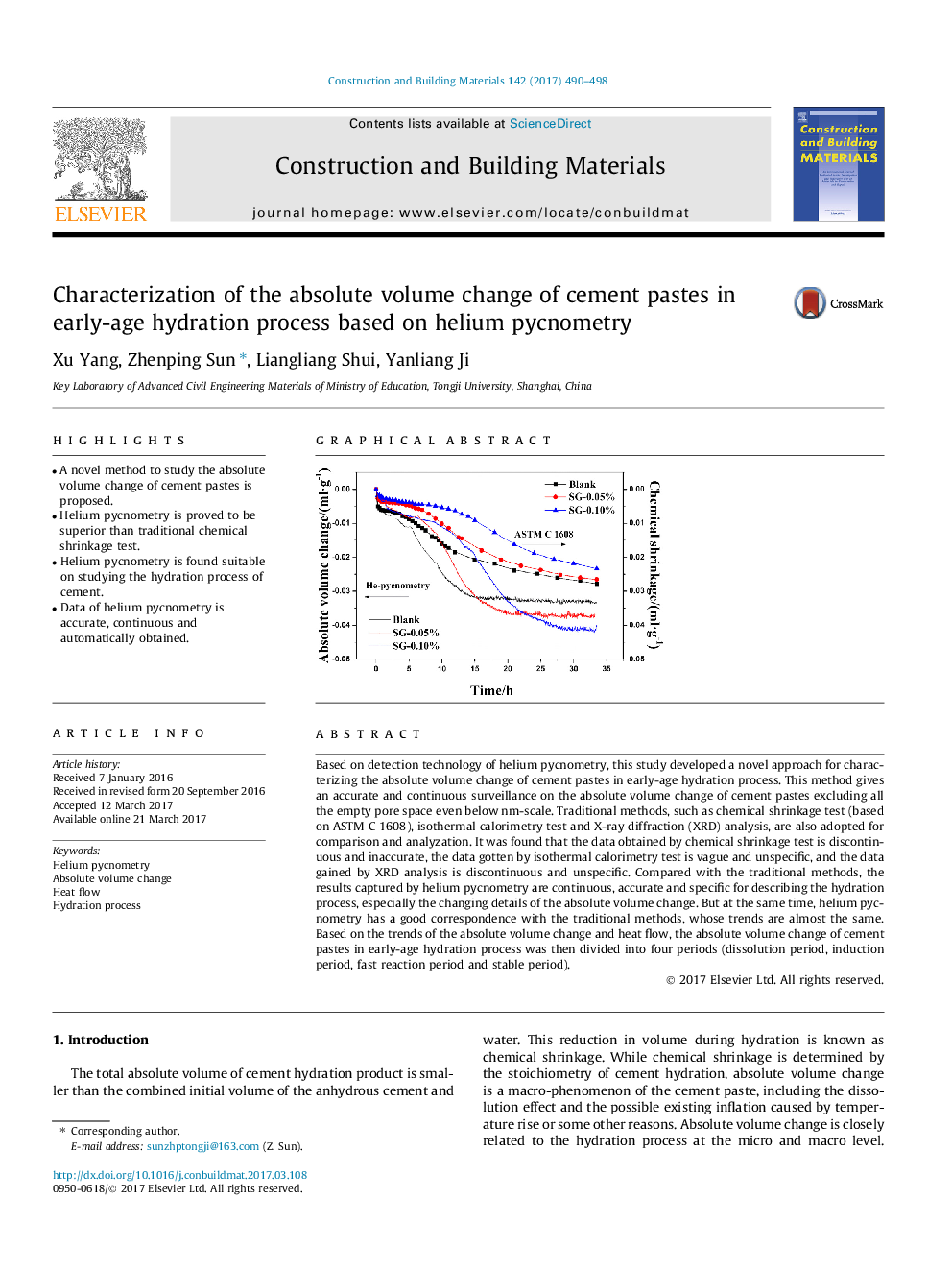
Based on detection technology of helium pycnometry, this study developed a novel approach for characterizing the absolute volume change of cement pastes in early-age hydration process. This method gives an accurate and continuous surveillance on the absolute volume change of cement pastes excluding all the empty pore space even below nm-scale. Traditional methods, such as chemical shrinkage test (based on ASTM C 1608), isothermal calorimetry test and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, are also adopted for comparison and analyzation. It was found that the data obtained by chemical shrinkage test is discontinuous and inaccurate, the data gotten by isothermal calorimetry test is vague and unspecific, and the data gained by XRD analysis is discontinuous and unspecific. Compared with the traditional methods, the results captured by helium pycnometry are continuous, accurate and specific for describing the hydration process, especially the changing details of the absolute volume change. But at the same time, helium pycnometry has a good correspondence with the traditional methods, whose trends are almost the same. Based on the trends of the absolute volume change and heat flow, the absolute volume change of cement pastes in early-age hydration process was then divided into four periods (dissolution period, induction period, fast reaction period and stable period).
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (148KB)Download full-size image