| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 679033 | Bioresource Technology | 2016 | 10 Pages |
•Citrus peel and fruit juices waste streams are rich in limonene molecule.•Limonene can be used in the nutritional, pharmaceutical and cosmetic fields.•Traditional techniques to recover limonene involve the use of polluting solvents.•Cost-benefit analysis is required to estimate the most viable extracting technique.•Anaerobic digestion and fermentation are suitable post-limonene extraction processes.
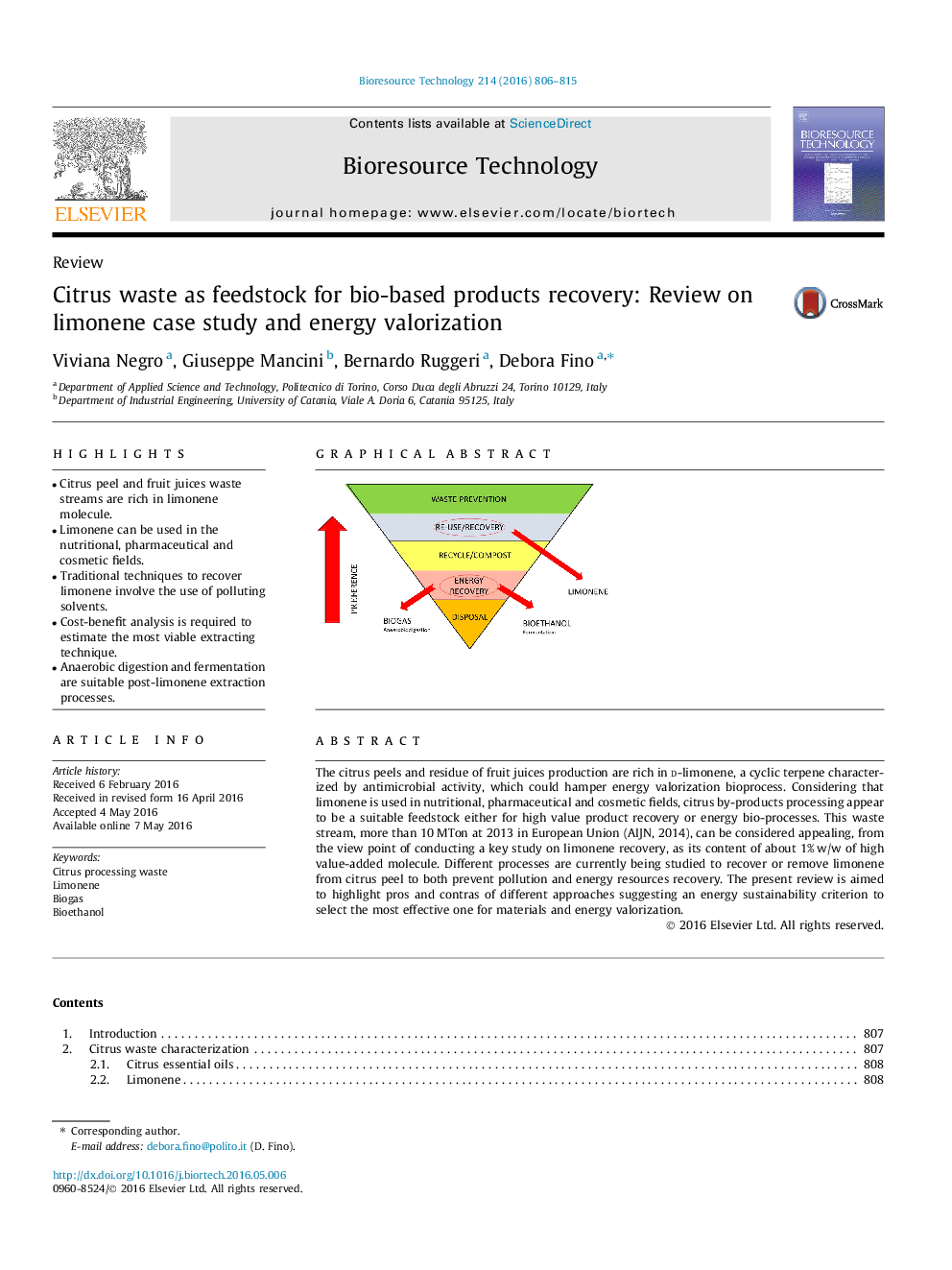
The citrus peels and residue of fruit juices production are rich in d-limonene, a cyclic terpene characterized by antimicrobial activity, which could hamper energy valorization bioprocess. Considering that limonene is used in nutritional, pharmaceutical and cosmetic fields, citrus by-products processing appear to be a suitable feedstock either for high value product recovery or energy bio-processes. This waste stream, more than 10 MTon at 2013 in European Union (AIJN, 2014), can be considered appealing, from the view point of conducting a key study on limonene recovery, as its content of about 1% w/w of high value-added molecule. Different processes are currently being studied to recover or remove limonene from citrus peel to both prevent pollution and energy resources recovery. The present review is aimed to highlight pros and contras of different approaches suggesting an energy sustainability criterion to select the most effective one for materials and energy valorization.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide