| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 679160 | Bioresource Technology | 2016 | 9 Pages |
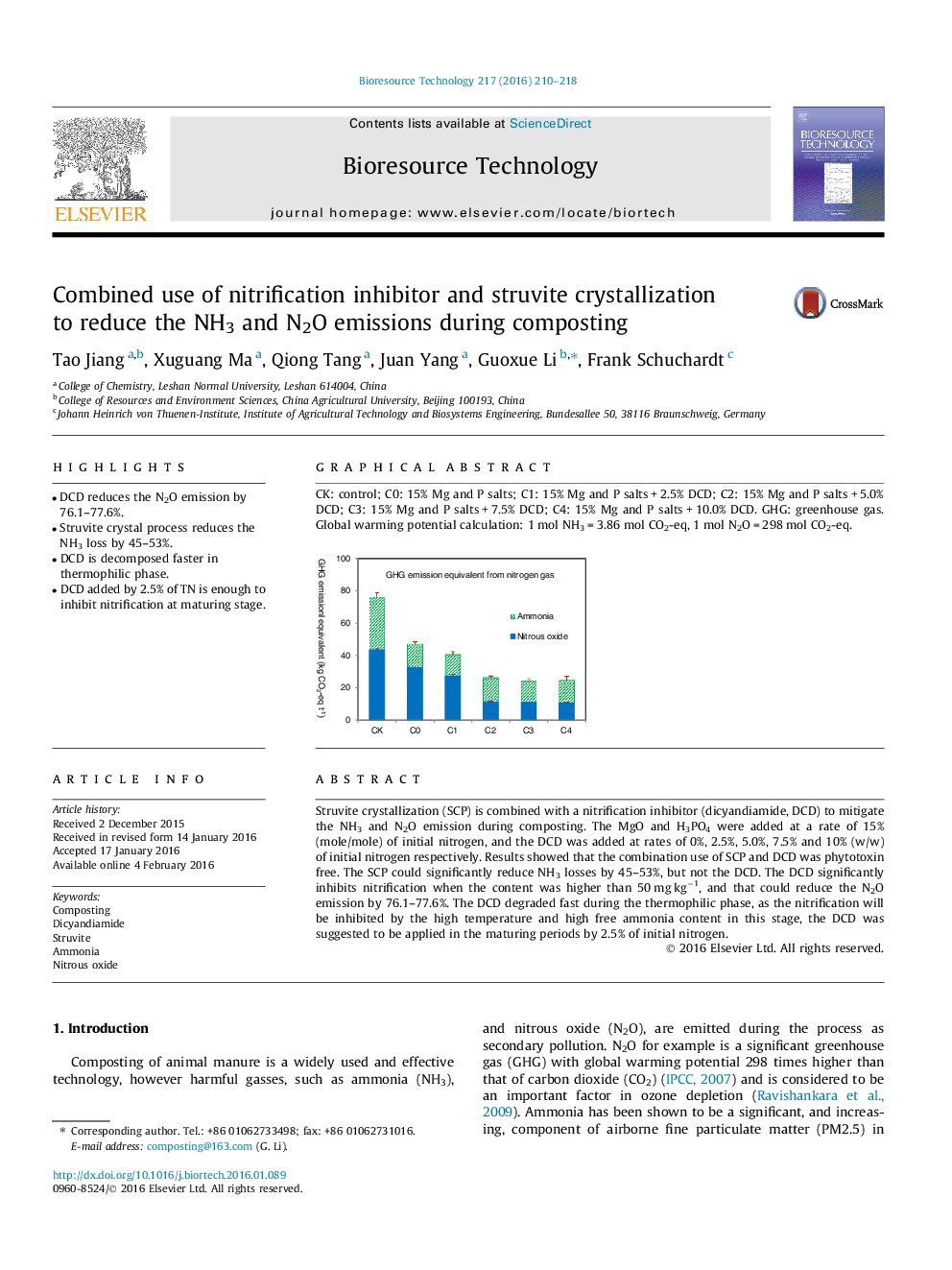
•DCD reduces the N2O emission by 76.1–77.6%.•Struvite crystal process reduces the NH3 loss by 45–53%.•DCD is decomposed faster in thermophilic phase.•DCD added by 2.5% of TN is enough to inhibit nitrification at maturing stage.
Struvite crystallization (SCP) is combined with a nitrification inhibitor (dicyandiamide, DCD) to mitigate the NH3 and N2O emission during composting. The MgO and H3PO4 were added at a rate of 15% (mole/mole) of initial nitrogen, and the DCD was added at rates of 0%, 2.5%, 5.0%, 7.5% and 10% (w/w) of initial nitrogen respectively. Results showed that the combination use of SCP and DCD was phytotoxin free. The SCP could significantly reduce NH3 losses by 45–53%, but not the DCD. The DCD significantly inhibits nitrification when the content was higher than 50 mg kg−1, and that could reduce the N2O emission by 76.1–77.6%. The DCD degraded fast during the thermophilic phase, as the nitrification will be inhibited by the high temperature and high free ammonia content in this stage, the DCD was suggested to be applied in the maturing periods by 2.5% of initial nitrogen.
Graphical abstractCK: control; C0: 15% Mg and P salts; C1: 15% Mg and P salts + 2.5% DCD; C2: 15% Mg and P salts + 5.0% DCD; C3: 15% Mg and P salts + 7.5% DCD; C4: 15% Mg and P salts + 10.0% DCD. GHG: greenhouse gas. Global warming potential calculation: 1 mol NH3 = 3.86 mol CO2-eq, 1 mol N2O = 298 mol CO2-eq.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide