| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 679468 | Bioresource Technology | 2015 | 8 Pages |
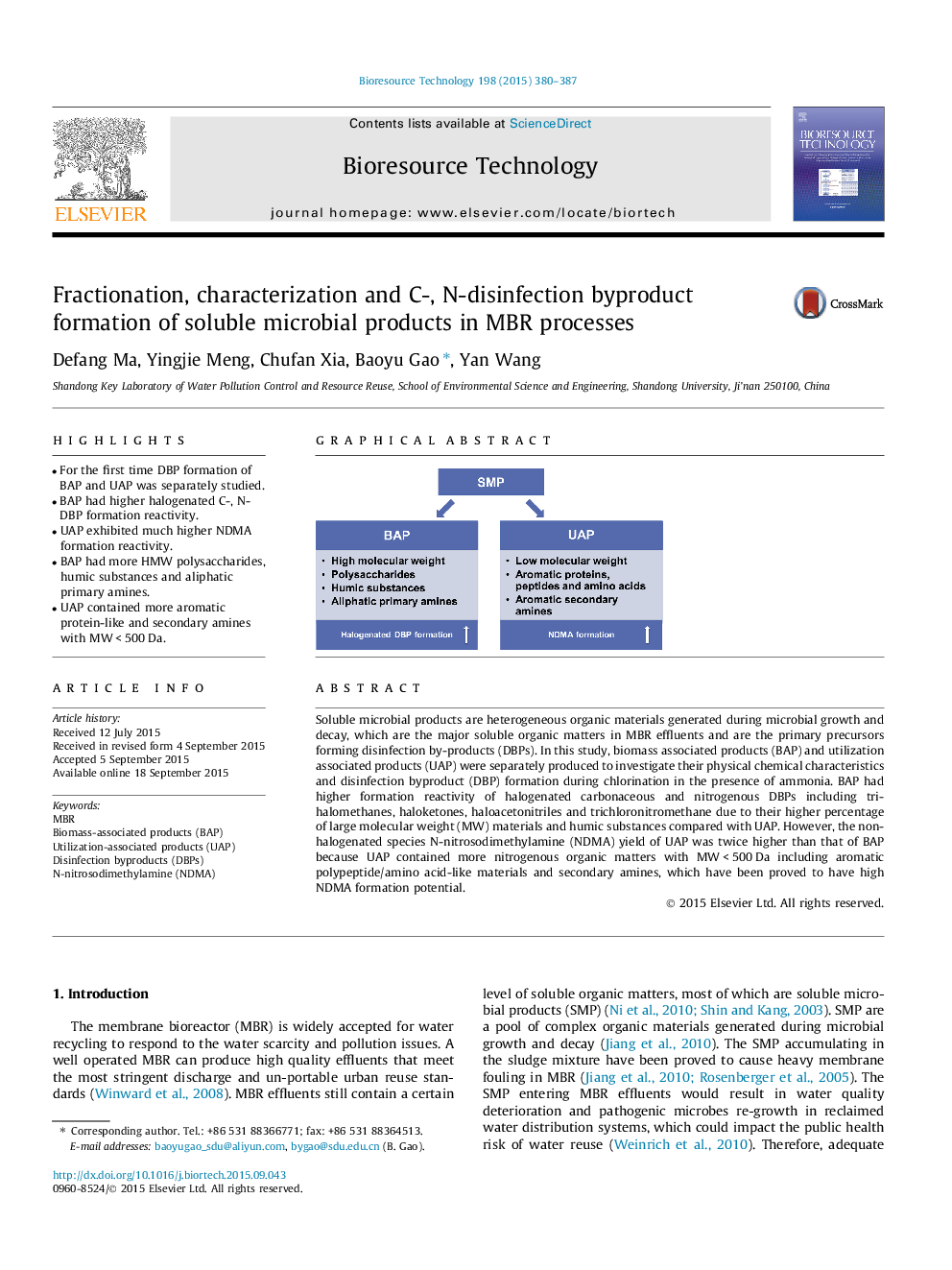
•For the first time DBP formation of BAP and UAP was separately studied.•BAP had higher halogenated C-, N-DBP formation reactivity.•UAP exhibited much higher NDMA formation reactivity.•BAP had more HMW polysaccharides, humic substances and aliphatic primary amines.•UAP contained more aromatic protein-like and secondary amines with MW < 500 Da.
Soluble microbial products are heterogeneous organic materials generated during microbial growth and decay, which are the major soluble organic matters in MBR effluents and are the primary precursors forming disinfection by-products (DBPs). In this study, biomass associated products (BAP) and utilization associated products (UAP) were separately produced to investigate their physical chemical characteristics and disinfection byproduct (DBP) formation during chlorination in the presence of ammonia. BAP had higher formation reactivity of halogenated carbonaceous and nitrogenous DBPs including trihalomethanes, haloketones, haloacetonitriles and trichloronitromethane due to their higher percentage of large molecular weight (MW) materials and humic substances compared with UAP. However, the nonhalogenated species N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) yield of UAP was twice higher than that of BAP because UAP contained more nitrogenous organic matters with MW < 500 Da including aromatic polypeptide/amino acid-like materials and secondary amines, which have been proved to have high NDMA formation potential.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide