| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 679499 | Bioresource Technology | 2015 | 8 Pages |
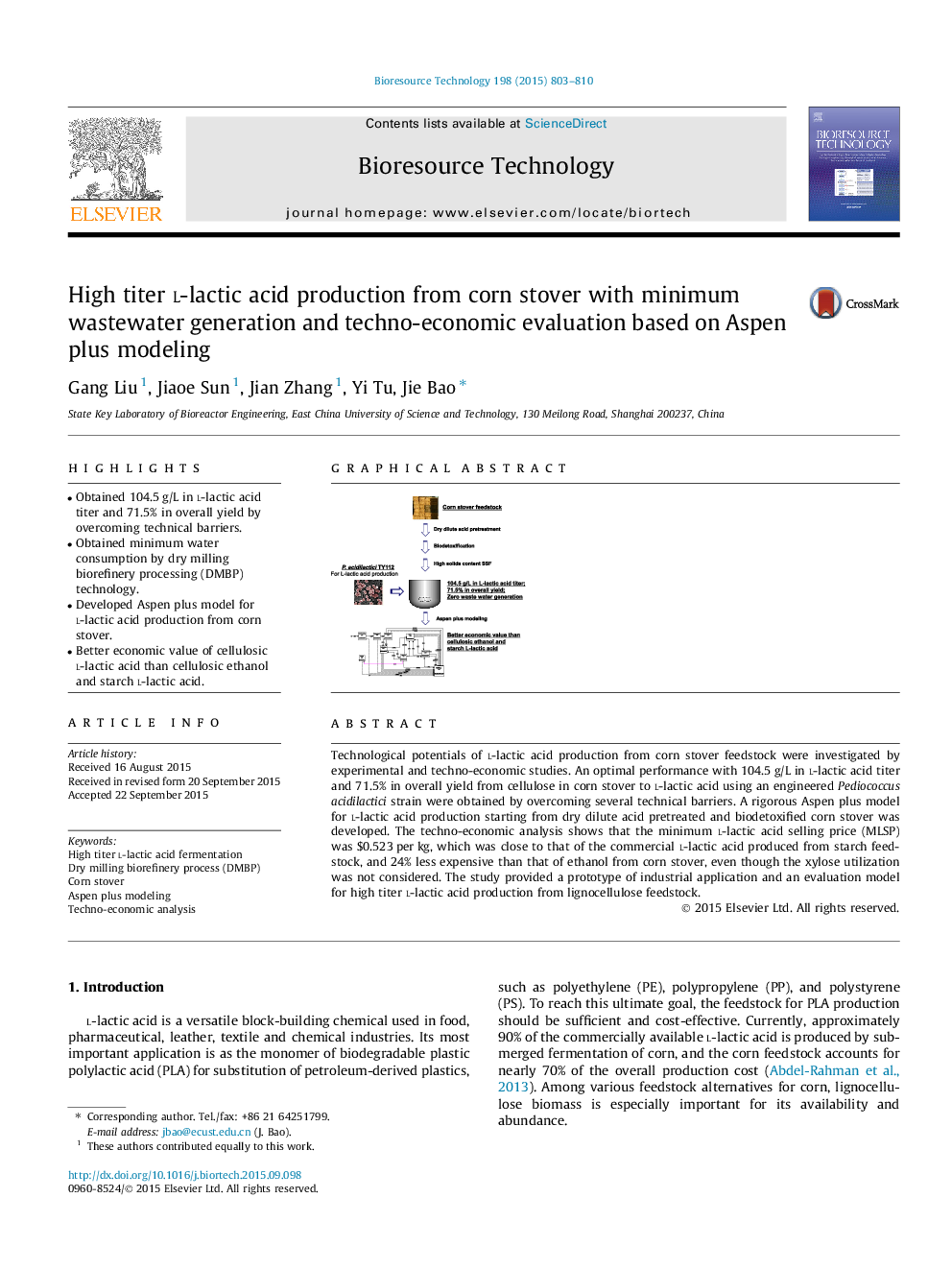
•Obtained 104.5 g/L in l-lactic acid titer and 71.5% in overall yield by overcoming technical barriers.•Obtained minimum water consumption by dry milling biorefinery processing (DMBP) technology.•Developed Aspen plus model for l-lactic acid production from corn stover.•Better economic value of cellulosic l-lactic acid than cellulosic ethanol and starch l-lactic acid.
Technological potentials of l-lactic acid production from corn stover feedstock were investigated by experimental and techno-economic studies. An optimal performance with 104.5 g/L in l-lactic acid titer and 71.5% in overall yield from cellulose in corn stover to l-lactic acid using an engineered Pediococcus acidilactici strain were obtained by overcoming several technical barriers. A rigorous Aspen plus model for l-lactic acid production starting from dry dilute acid pretreated and biodetoxified corn stover was developed. The techno-economic analysis shows that the minimum l-lactic acid selling price (MLSP) was $0.523 per kg, which was close to that of the commercial l-lactic acid produced from starch feedstock, and 24% less expensive than that of ethanol from corn stover, even though the xylose utilization was not considered. The study provided a prototype of industrial application and an evaluation model for high titer l-lactic acid production from lignocellulose feedstock.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide