| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 680293 | Bioresource Technology | 2015 | 8 Pages |
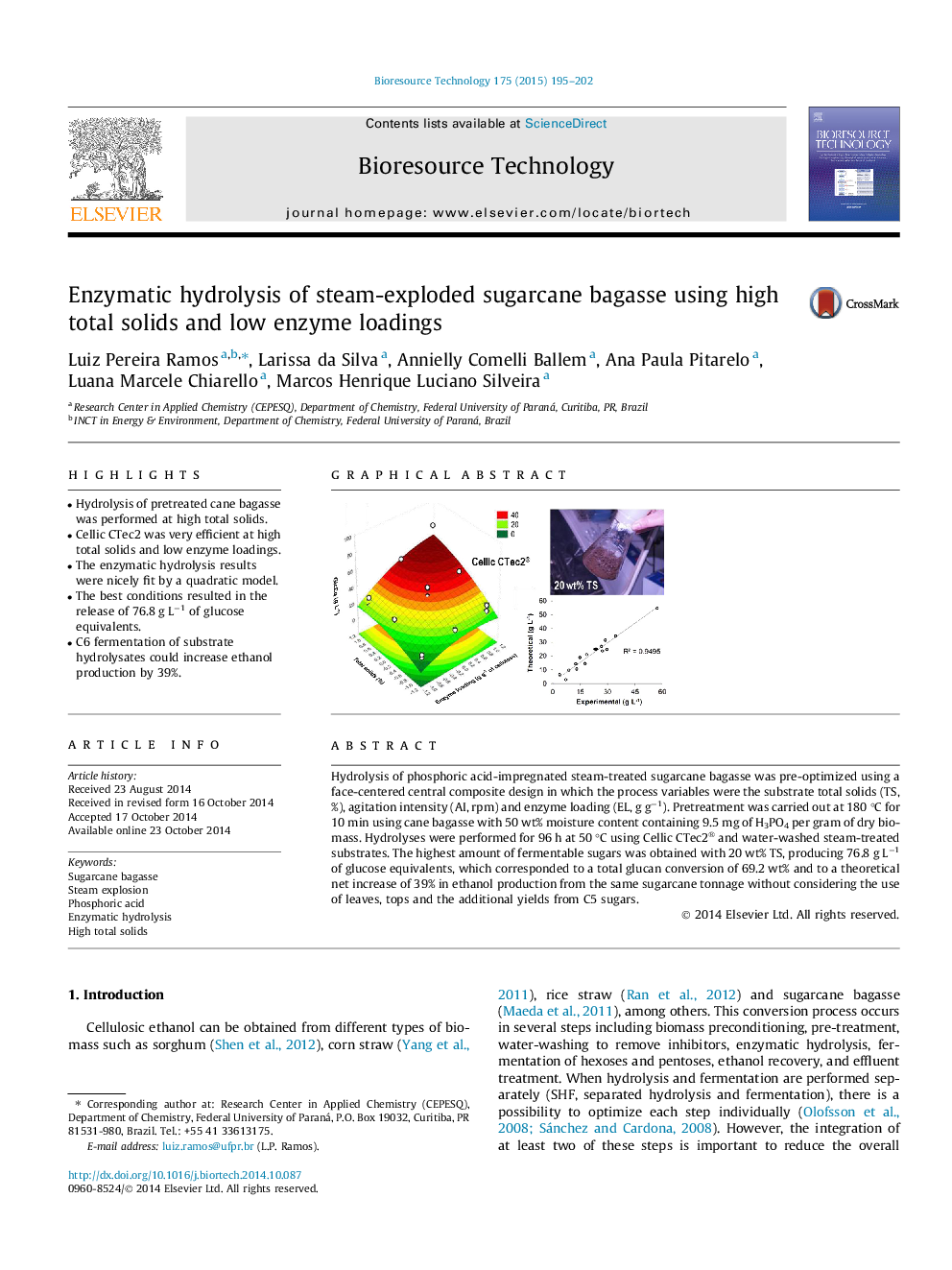
•Hydrolysis of pretreated cane bagasse was performed at high total solids.•Cellic CTec2 was very efficient at high total solids and low enzyme loadings.•The enzymatic hydrolysis results were nicely fit by a quadratic model.•The best conditions resulted in the release of 76.8 g L−1 of glucose equivalents.•C6 fermentation of substrate hydrolysates could increase ethanol production by 39%.
Hydrolysis of phosphoric acid-impregnated steam-treated sugarcane bagasse was pre-optimized using a face-centered central composite design in which the process variables were the substrate total solids (TS, %), agitation intensity (AI, rpm) and enzyme loading (EL, g g−1). Pretreatment was carried out at 180 °C for 10 min using cane bagasse with 50 wt% moisture content containing 9.5 mg of H3PO4 per gram of dry biomass. Hydrolyses were performed for 96 h at 50 °C using Cellic CTec2® and water-washed steam-treated substrates. The highest amount of fermentable sugars was obtained with 20 wt% TS, producing 76.8 g L−1 of glucose equivalents, which corresponded to a total glucan conversion of 69.2 wt% and to a theoretical net increase of 39% in ethanol production from the same sugarcane tonnage without considering the use of leaves, tops and the additional yields from C5 sugars.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide