| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 680501 | Bioresource Technology | 2014 | 6 Pages |
•Innovative application of microaeration directly in UASB reactor.•Reliable and stable H2S removal efficiency in long-term operation.•Sulfur and COD balance in microaerated UASB reactor.•Evaluation of the effects of microaeration on the activity of granular sludge.
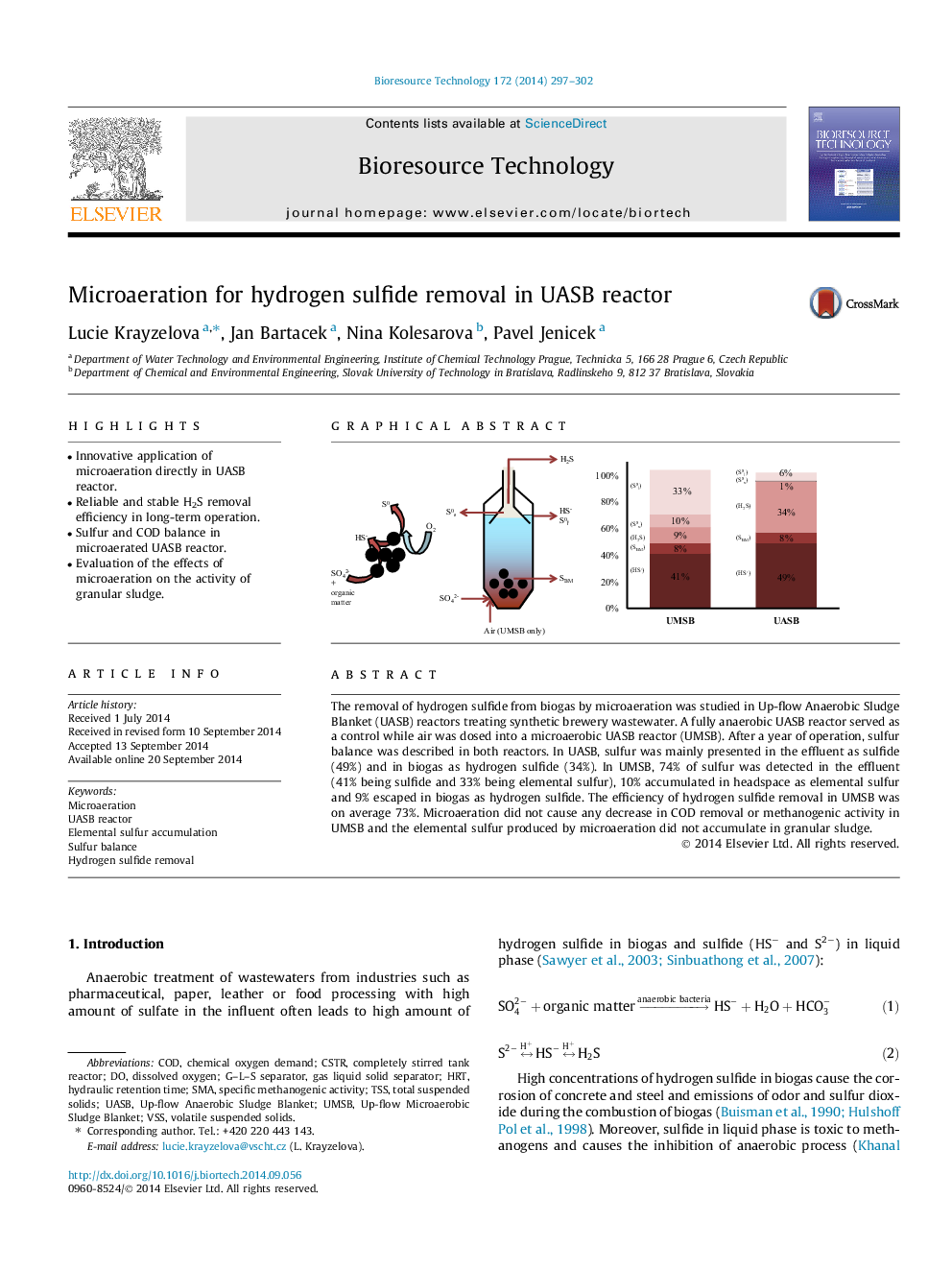
The removal of hydrogen sulfide from biogas by microaeration was studied in Up-flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) reactors treating synthetic brewery wastewater. A fully anaerobic UASB reactor served as a control while air was dosed into a microaerobic UASB reactor (UMSB). After a year of operation, sulfur balance was described in both reactors. In UASB, sulfur was mainly presented in the effluent as sulfide (49%) and in biogas as hydrogen sulfide (34%). In UMSB, 74% of sulfur was detected in the effluent (41% being sulfide and 33% being elemental sulfur), 10% accumulated in headspace as elemental sulfur and 9% escaped in biogas as hydrogen sulfide. The efficiency of hydrogen sulfide removal in UMSB was on average 73%. Microaeration did not cause any decrease in COD removal or methanogenic activity in UMSB and the elemental sulfur produced by microaeration did not accumulate in granular sludge.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide