| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 680704 | Bioresource Technology | 2014 | 5 Pages |
•Successful iron incorporation onto the porous carbon surface was achieved.•The significance of impregnation is revealed from the enhanced potential of FeAC.•Above 95% methylene blue removal was observed by using FeAC.•MB uptake was more feasible at ambient temperature.
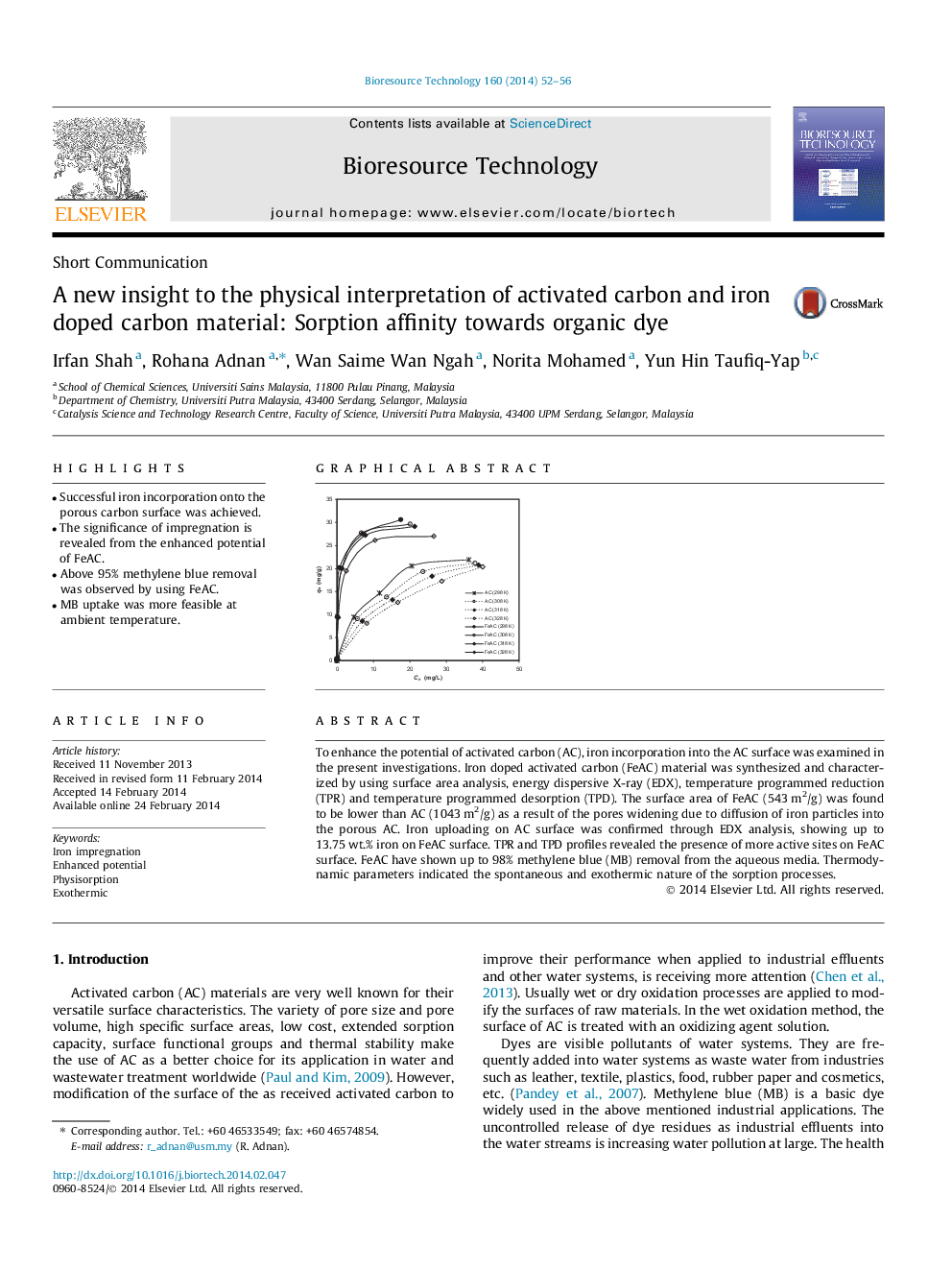
To enhance the potential of activated carbon (AC), iron incorporation into the AC surface was examined in the present investigations. Iron doped activated carbon (FeAC) material was synthesized and characterized by using surface area analysis, energy dispersive X-ray (EDX), temperature programmed reduction (TPR) and temperature programmed desorption (TPD). The surface area of FeAC (543 m2/g) was found to be lower than AC (1043 m2/g) as a result of the pores widening due to diffusion of iron particles into the porous AC. Iron uploading on AC surface was confirmed through EDX analysis, showing up to 13.75 wt.% iron on FeAC surface. TPR and TPD profiles revealed the presence of more active sites on FeAC surface. FeAC have shown up to 98% methylene blue (MB) removal from the aqueous media. Thermodynamic parameters indicated the spontaneous and exothermic nature of the sorption processes.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide