| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 680922 | Bioresource Technology | 2014 | 7 Pages |
•Microbial fuel cells fed with different cheese wastes/wastewaters are examined.•MFCs effectively reduce organics and suspended solids with electricity production.•Low-strength wastewater is a suitable substrate for MFCs.•Energy consumption should be reduced by optimizing the operating conditions.•MFCs should be properly linked to other treatment methods.
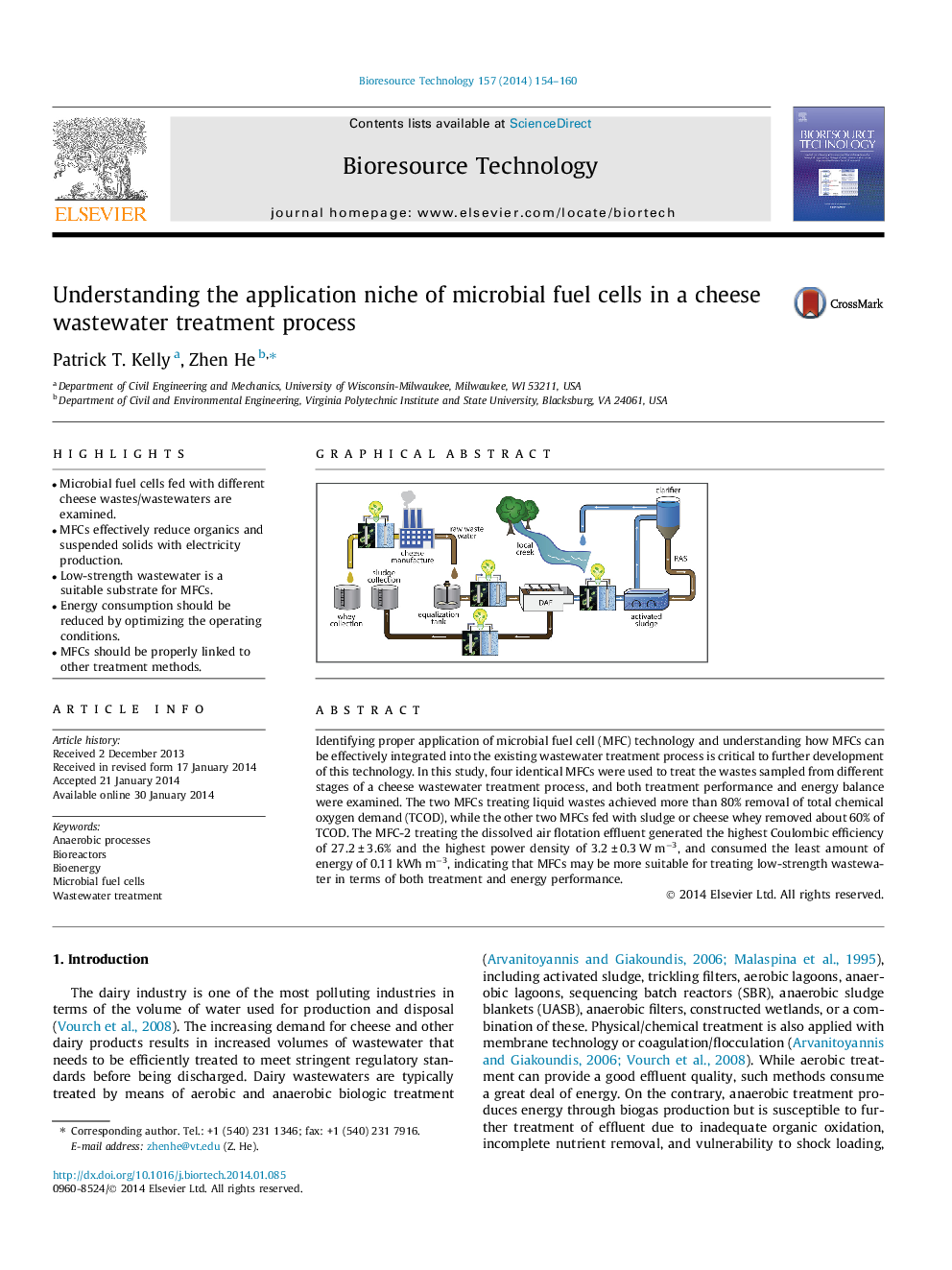
Identifying proper application of microbial fuel cell (MFC) technology and understanding how MFCs can be effectively integrated into the existing wastewater treatment process is critical to further development of this technology. In this study, four identical MFCs were used to treat the wastes sampled from different stages of a cheese wastewater treatment process, and both treatment performance and energy balance were examined. The two MFCs treating liquid wastes achieved more than 80% removal of total chemical oxygen demand (TCOD), while the other two MFCs fed with sludge or cheese whey removed about 60% of TCOD. The MFC-2 treating the dissolved air flotation effluent generated the highest Coulombic efficiency of 27.2 ± 3.6% and the highest power density of 3.2 ± 0.3 W m−3, and consumed the least amount of energy of 0.11 kWh m−3, indicating that MFCs may be more suitable for treating low-strength wastewater in terms of both treatment and energy performance.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide