| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7004801 | Wear | 2013 | 5 Pages |
Abstract
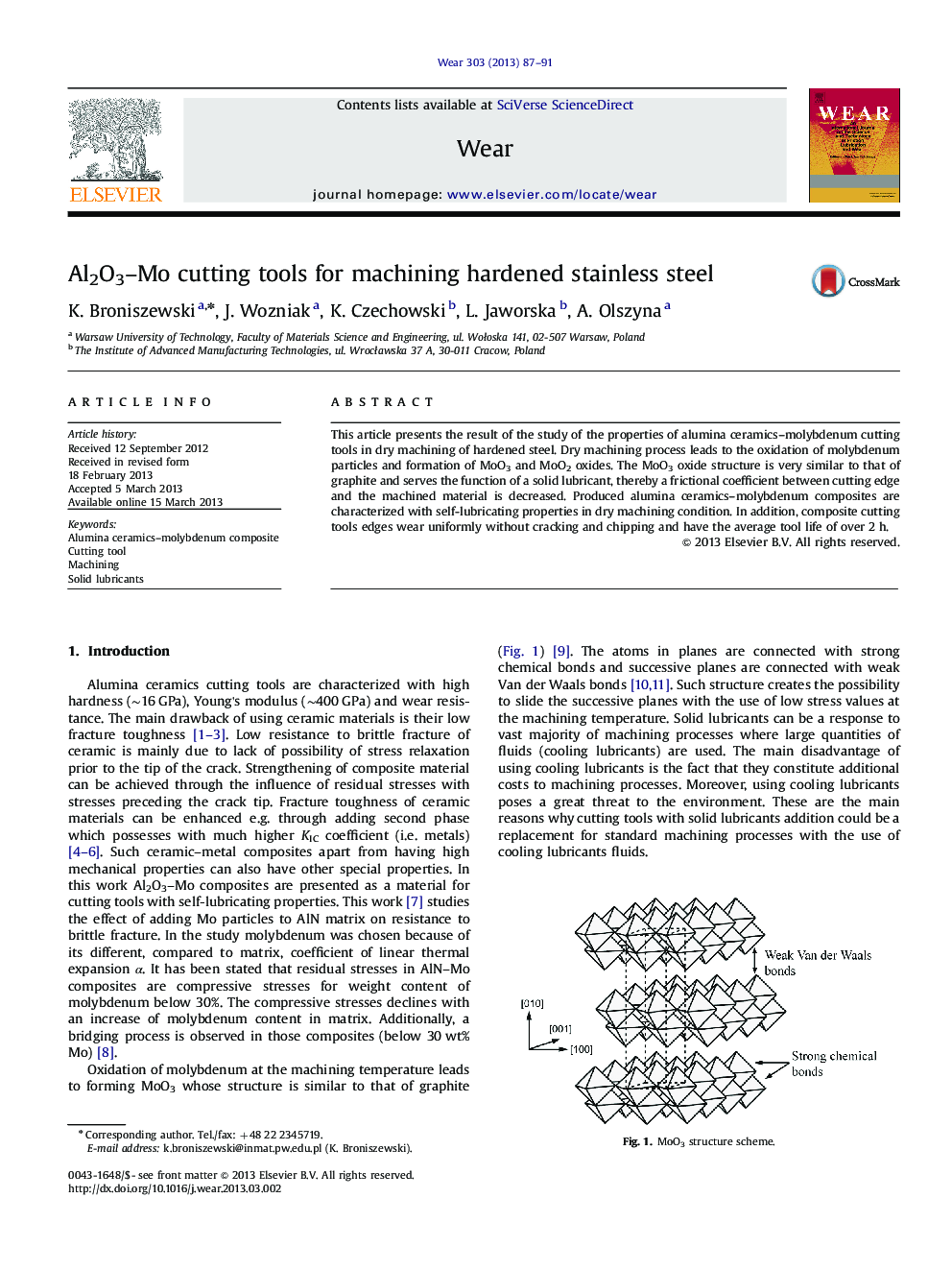
This article presents the result of the study of the properties of alumina ceramics-molybdenum cutting tools in dry machining of hardened steel. Dry machining process leads to the oxidation of molybdenum particles and formation of MoO3 and MoO2 oxides. The MoO3 oxide structure is very similar to that of graphite and serves the function of a solid lubricant, thereby a frictional coefficient between cutting edge and the machined material is decreased. Produced alumina ceramics-molybdenum composites are characterized with self-lubricating properties in dry machining condition. In addition, composite cutting tools edges wear uniformly without cracking and chipping and have the average tool life of over 2Â h.
Related Topics
Physical Sciences and Engineering
Chemical Engineering
Colloid and Surface Chemistry
Authors
K. Broniszewski, J. Wozniak, K. Czechowski, L. Jaworska, A. Olszyna,