| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 713238 | IFAC-PapersOnLine | 2015 | 6 Pages |
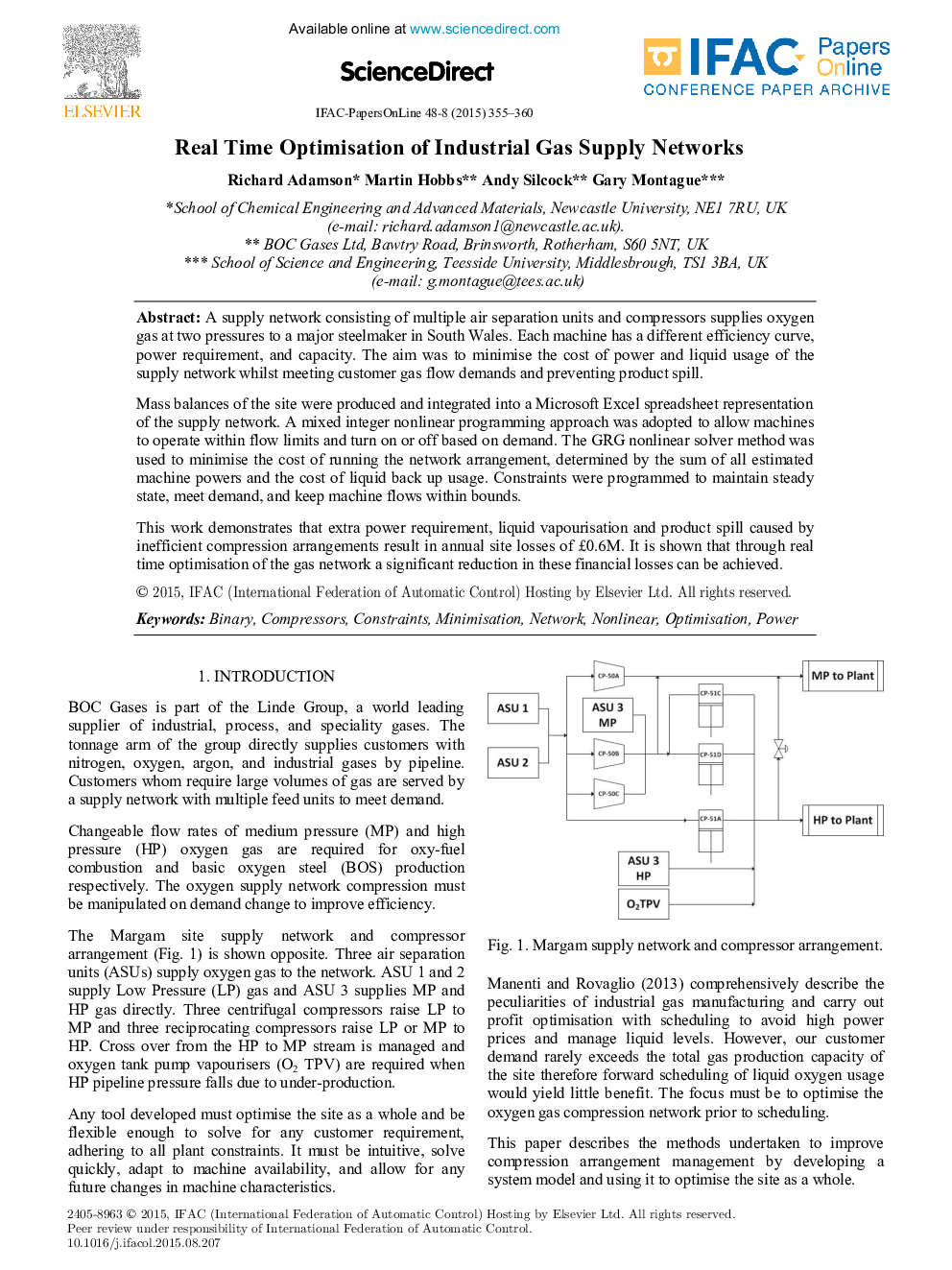
A supply network consisting of multiple air separation units and compressors supplies oxygen gas at two pressures to a major steelmaker in South Wales. Each machine has a different efficiency curve, power requirement, and capacity. The aim was to minimise the cost of power and liquid usage of the supply network whilst meeting customer gas flow demands and preventing product spill.Mass balances of the site were produced and integrated into a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet representation of the supply network. A mixed integer nonlinear programming approach was adopted to allow machines to operate within flow limits and turn on or off based on demand. The GRG nonlinear solver method was used to minimise the cost of running the network arrangement, determined by the sum of all estimated machine powers and the cost of liquid back up usage. Constraints were programmed to maintain steady state, meet demand, and keep machine flows within bounds.This work demonstrates that extra power requirement, liquid vapourisation and product spill caused by inefficient compression arrangements result in annual site losses of £0.6M. It is shown that through real time optimisation of the gas network a significant reduction in these financial losses can be achieved.