| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 713513 | IFAC Proceedings Volumes | 2013 | 5 Pages |
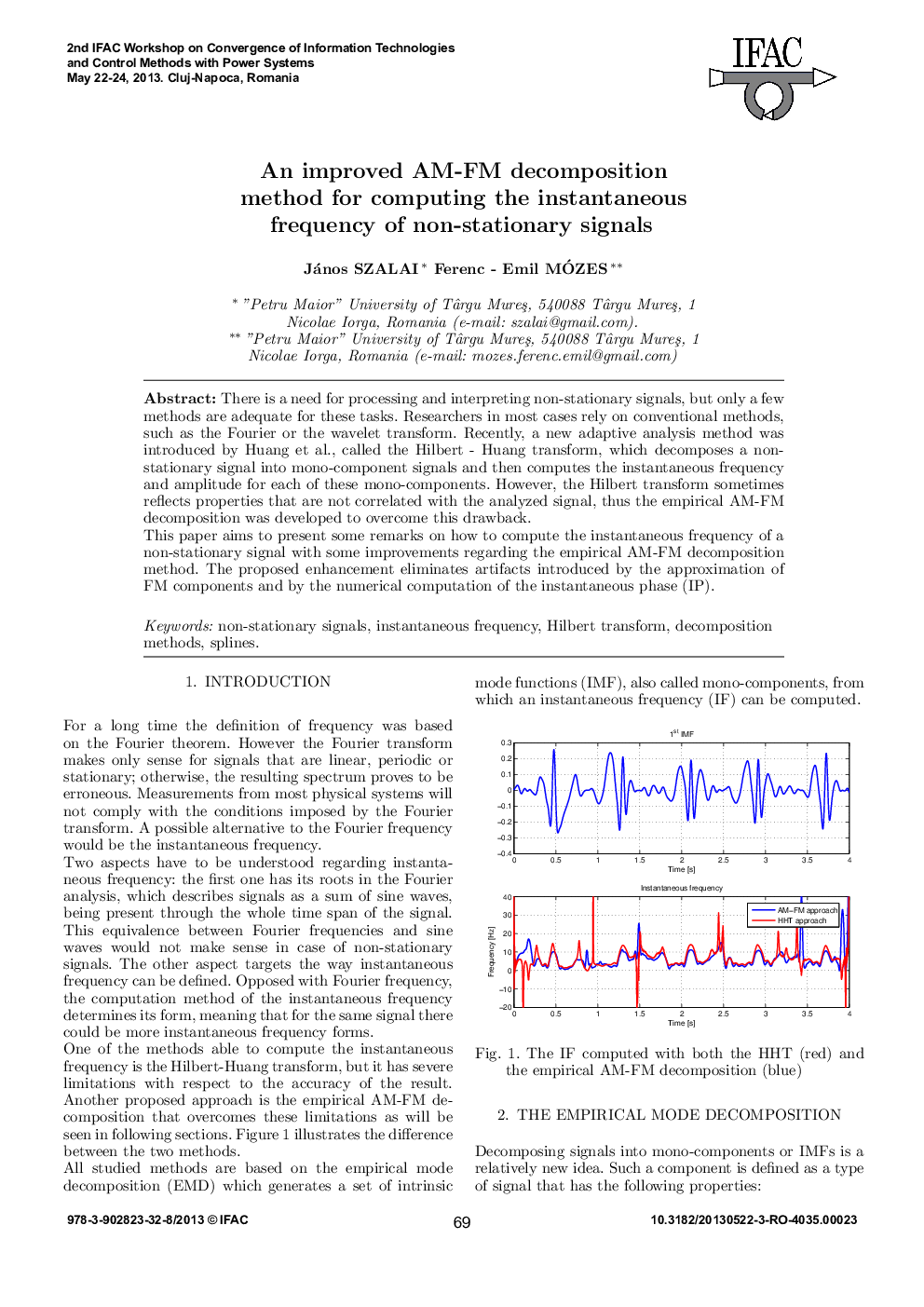
There is a need for processing and interpreting non-stationary signals, but only a few methods are adequate for these tasks. Researchers in most cases rely on conventional methods, such as the Fourier or the wavelet transform. Recently, a new adaptive analysis method was introduced by Huang et al., called the Hilbert – Huang transform, which decomposes a non-stationary signal into mono-component signals and then computes the instantaneous frequency and amplitude for each of these mono-components. However, the Hilbert transform sometimes reflects properties that are not correlated with the analyzed signal, thus the empirical AM-FM decomposition was developed to overcome this drawback.This paper aims to present some remarks on how to compute the instantaneous frequency of a non-stationary signal with some improvements regarding the empirical AM-FM decomposition method. The proposed enhancement eliminates artifacts introduced by the approximation of FM components and by the numerical computation of the instantaneous phase (IP).