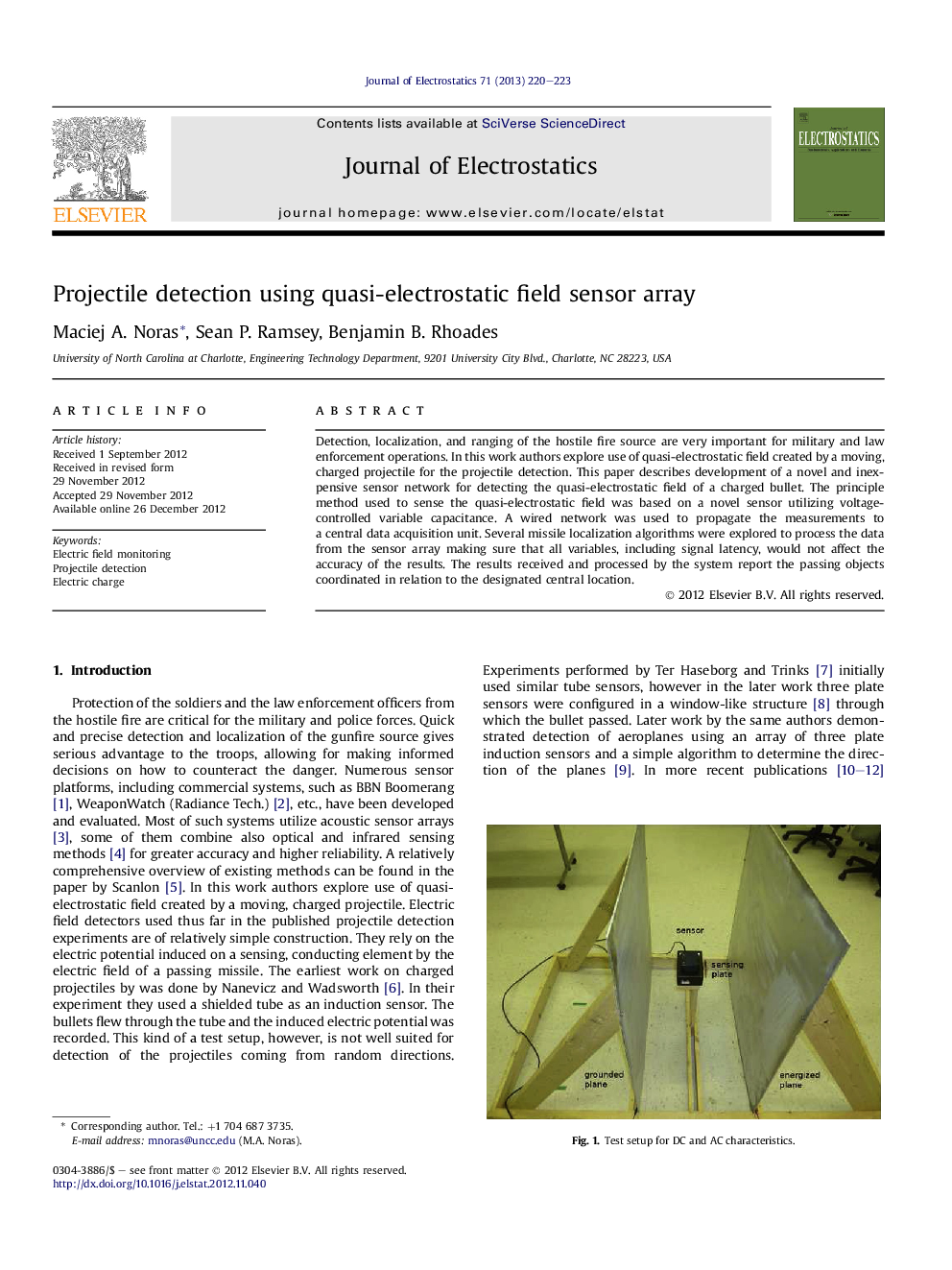
| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 726735 | Journal of Electrostatics | 2013 | 4 Pages |
Detection, localization, and ranging of the hostile fire source are very important for military and law enforcement operations. In this work authors explore use of quasi-electrostatic field created by a moving, charged projectile for the projectile detection. This paper describes development of a novel and inexpensive sensor network for detecting the quasi-electrostatic field of a charged bullet. The principle method used to sense the quasi-electrostatic field was based on a novel sensor utilizing voltage-controlled variable capacitance. A wired network was used to propagate the measurements to a central data acquisition unit. Several missile localization algorithms were explored to process the data from the sensor array making sure that all variables, including signal latency, would not affect the accuracy of the results. The results received and processed by the system report the passing objects coordinated in relation to the designated central location.