| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8022341 | Materials Letters | 2013 | 4 Pages |
Abstract
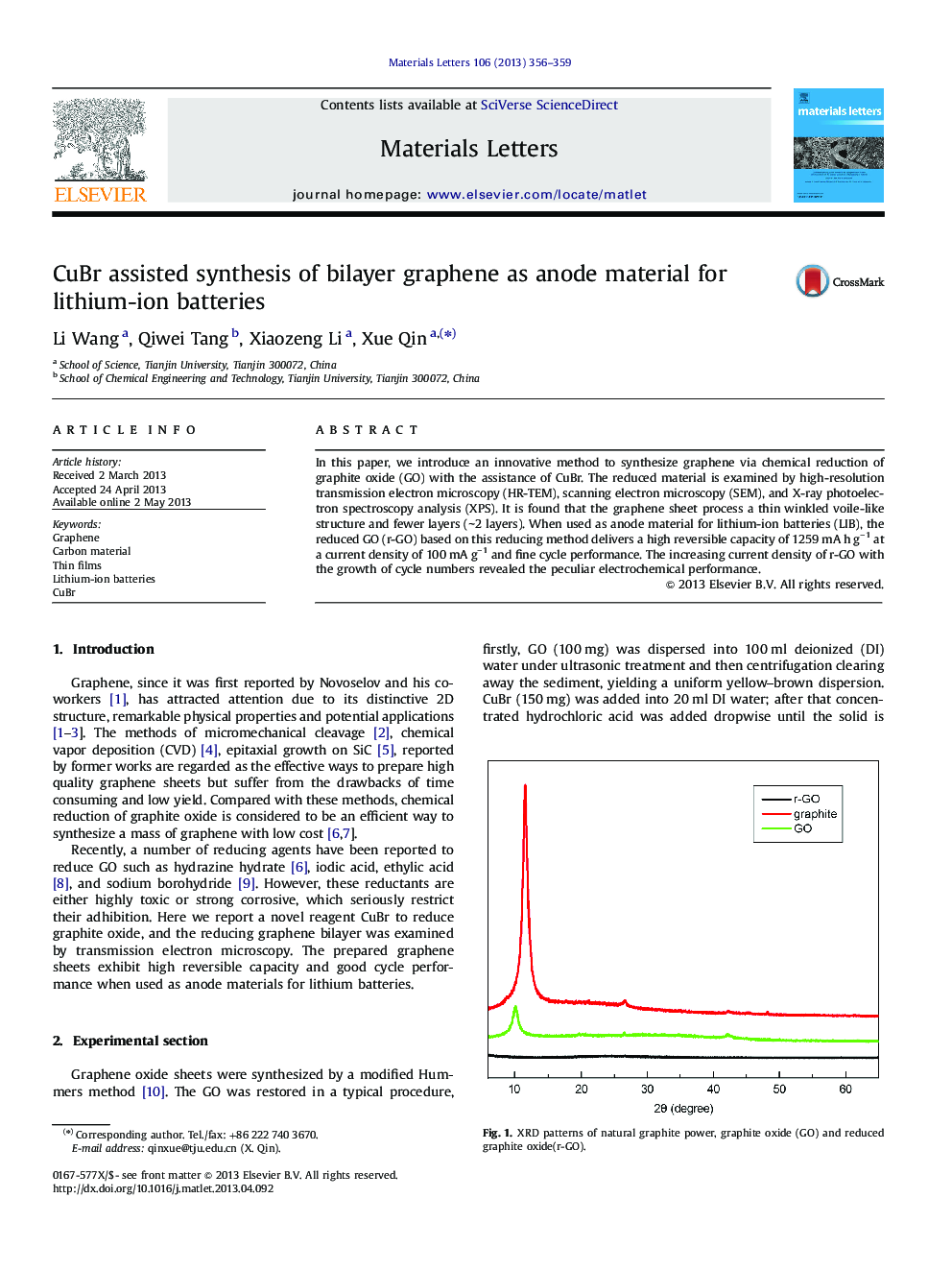
In this paper, we introduce an innovative method to synthesize graphene via chemical reduction of graphite oxide (GO) with the assistance of CuBr. The reduced material is examined by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis (XPS). It is found that the graphene sheet process a thin winkled voile-like structure and fewer layers (â¼2 layers). When used as anode material for lithium-ion batteries (LIB), the reduced GO (r-GO) based on this reducing method delivers a high reversible capacity of 1259 mA h gâ1 at a current density of 100 mA gâ1 and fine cycle performance. The increasing current density of r-GO with the growth of cycle numbers revealed the peculiar electrochemical performance.
Related Topics
Physical Sciences and Engineering
Materials Science
Nanotechnology
Authors
Li Wang, Qiwei Tang, Xiaozeng Li, Xue Qin,