| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9089461 | Anaesthesia & Intensive Care Medicine | 2005 | 4 Pages |
Abstract
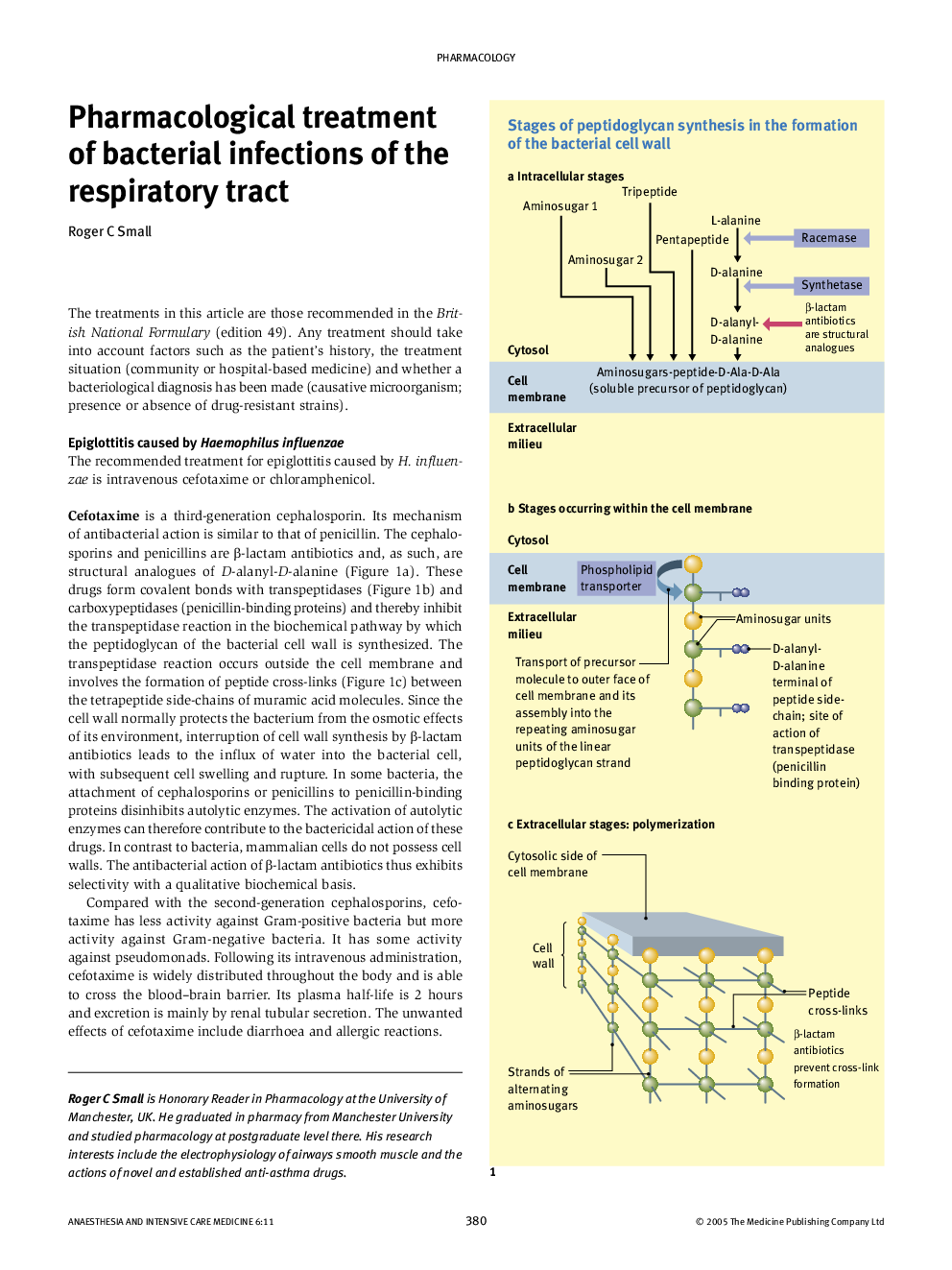
Treatment of bacterial infections of the respiratory tract should allow for factors such as the patient's history, the treatment situation and the result of any bacteriological diagnosis. Epiglottitis attributable to Haemophilus influenzae is treated with cefotaxime (a cephalosporin inhibitor of bacterial cell wall synthesis) or with chloramphenicol (an inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis). Exacerbations of chronic bronchitis are treated with broad spectrum penicillins (inhibitors of bacterial cell wall synthesis), tetracyclines or macrolides (both inhibitors of bacterial protein synthesis). Community acquired pneumonias are treated with penicillins or a macrolide such as erythromycin. If community acquired pneumonia is severe, a combination of a macrolide and a cephalosporin is indicated. When Staphylococcus aureus is the suspected cause of severe community acquired pneumonia, flucloxacillin (a penicillin that is resistant to β-lactamase) should be added to the treatment regimen. Suspected atypical pneumonia is treated with a macrolide or an antibiotic from the tetracycline group (inhibitors of bacterial protein synthesis). If Legionella pneumophila is the suspected causative organism in severe community acquired pneumonia, rifampicin (an inhibitor of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase) should be used in combination with a macrolide. Hospital acquired pneumonia is treated with broad-spectrum cephalosporins or anti-pseudomonal penicillins, such as ticarcillin or piperacillin. In severe cases, an aminoglycoside inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis (e.g. gentamicin) may be used. The treatment of tuberculosis requires specialized knowledge and involves the use of combinations of rifampicin with inhibitors of tubercular mycolic acid synthesis (e.g. isoniazid or pyrazinamide) or with an inhibitor of tubercular arabinosyl transferase (e.g. ethambutol).
Keywords
Related Topics
Health Sciences
Medicine and Dentistry
Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine
Authors
Roger C Small,