| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1162851 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2016 | 8 Pages |
•Electrophoretic mobility control was used to alleviate ion suppression due to ion pairing agent.•An integrated electrophoretic mobility control device with a split design was fabricated.•The proposed device could be applied to LC-ESI-MS using a conventional HPLC column.•The device was applied to the analysis of aminoglycosides using the ion pairing agent, HFBA.
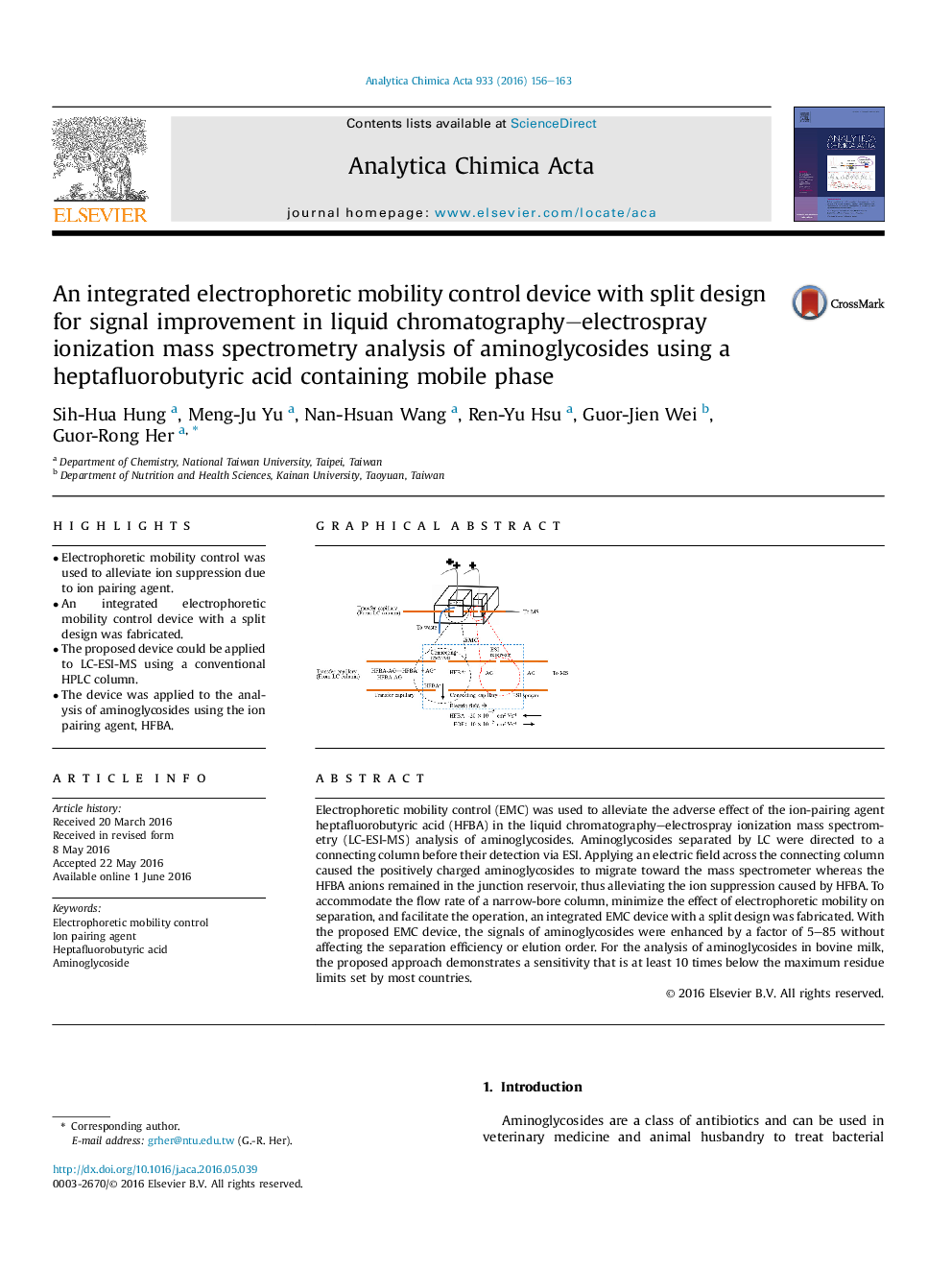
Electrophoretic mobility control (EMC) was used to alleviate the adverse effect of the ion-pairing agent heptafluorobutyric acid (HFBA) in the liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS) analysis of aminoglycosides. Aminoglycosides separated by LC were directed to a connecting column before their detection via ESI. Applying an electric field across the connecting column caused the positively charged aminoglycosides to migrate toward the mass spectrometer whereas the HFBA anions remained in the junction reservoir, thus alleviating the ion suppression caused by HFBA. To accommodate the flow rate of a narrow-bore column, minimize the effect of electrophoretic mobility on separation, and facilitate the operation, an integrated EMC device with a split design was fabricated. With the proposed EMC device, the signals of aminoglycosides were enhanced by a factor of 5–85 without affecting the separation efficiency or elution order. For the analysis of aminoglycosides in bovine milk, the proposed approach demonstrates a sensitivity that is at least 10 times below the maximum residue limits set by most countries.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide