| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1162867 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2016 | 9 Pages |
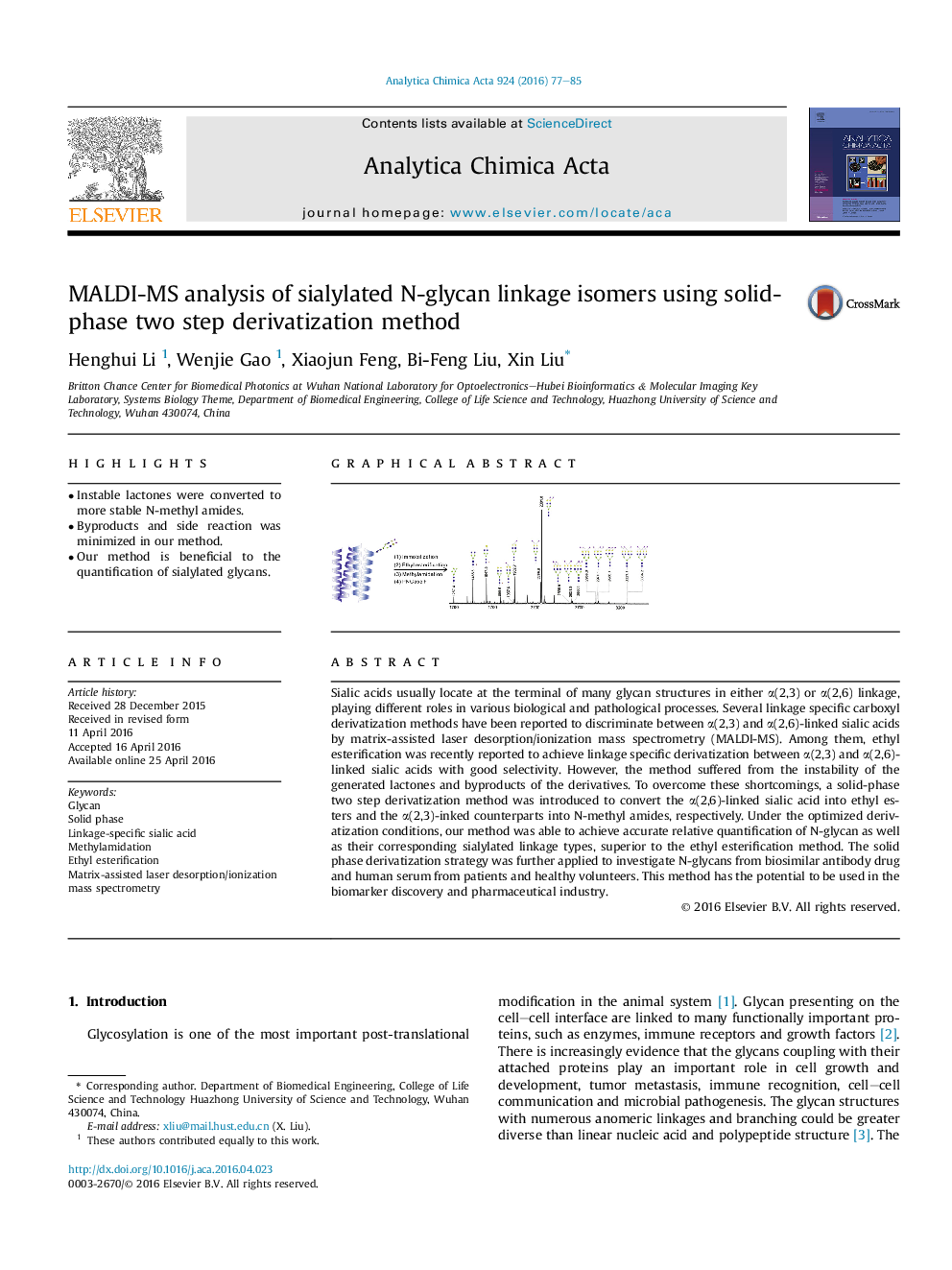
•Instable lactones were converted to more stable N-methyl amides.•Byproducts and side reaction was minimized in our method.•Our method is beneficial to the quantification of sialylated glycans.
Sialic acids usually locate at the terminal of many glycan structures in either α(2,3) or α(2,6) linkage, playing different roles in various biological and pathological processes. Several linkage specific carboxyl derivatization methods have been reported to discriminate between α(2,3) and α(2,6)-linked sialic acids by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS). Among them, ethyl esterification was recently reported to achieve linkage specific derivatization between α(2,3) and α(2,6)-linked sialic acids with good selectivity. However, the method suffered from the instability of the generated lactones and byproducts of the derivatives. To overcome these shortcomings, a solid-phase two step derivatization method was introduced to convert the α(2,6)-linked sialic acid into ethyl esters and the α(2,3)-inked counterparts into N-methyl amides, respectively. Under the optimized derivatization conditions, our method was able to achieve accurate relative quantification of N-glycan as well as their corresponding sialylated linkage types, superior to the ethyl esterification method. The solid phase derivatization strategy was further applied to investigate N-glycans from biosimilar antibody drug and human serum from patients and healthy volunteers. This method has the potential to be used in the biomarker discovery and pharmaceutical industry.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide