| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1163042 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2016 | 10 Pages |
•A novel magnetic effervescent tablet was prepared for the detection of fungicides.•Extractions were screened by PB design and optimized through CCD design.•Analytes could be rapidly and efficiently extracted upon field inspection.•The extractant could be separated without centrifugation.
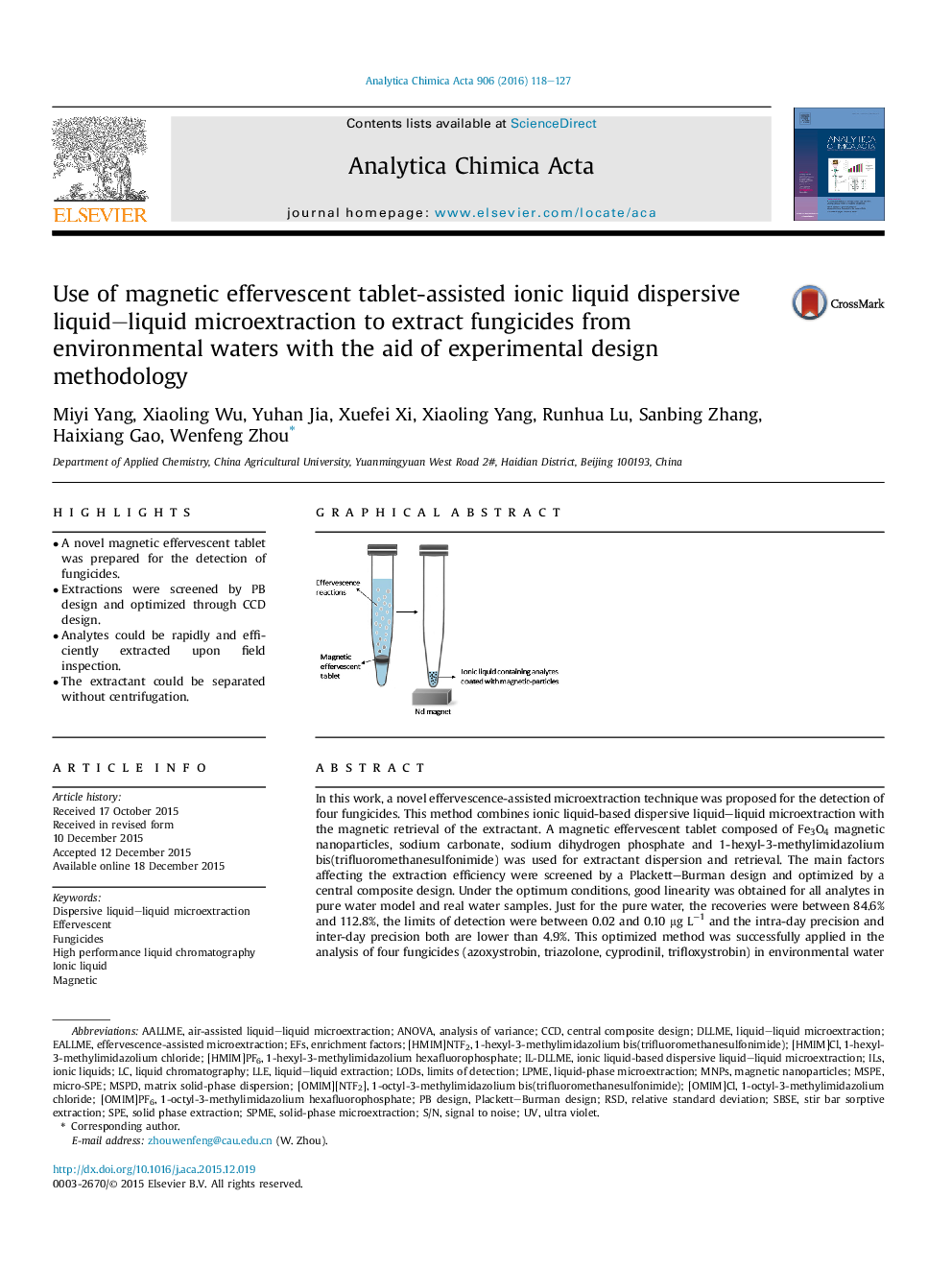
In this work, a novel effervescence-assisted microextraction technique was proposed for the detection of four fungicides. This method combines ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction with the magnetic retrieval of the extractant. A magnetic effervescent tablet composed of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles, sodium carbonate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate and 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonimide) was used for extractant dispersion and retrieval. The main factors affecting the extraction efficiency were screened by a Plackett–Burman design and optimized by a central composite design. Under the optimum conditions, good linearity was obtained for all analytes in pure water model and real water samples. Just for the pure water, the recoveries were between 84.6% and 112.8%, the limits of detection were between 0.02 and 0.10 μg L−1 and the intra-day precision and inter-day precision both are lower than 4.9%. This optimized method was successfully applied in the analysis of four fungicides (azoxystrobin, triazolone, cyprodinil, trifloxystrobin) in environmental water samples and the recoveries ranged between 70.7% and 105%. The procedure promising to be a time-saving, environmentally friendly, and efficient field sampling technique.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide