| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1163077 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2016 | 7 Pages |
•A catalytic DNA circuit for enzyme-free and colorimetric detection of nucleic acids.•The circuit can detect 4 pM of the target DNA after a 2-h incubation.•The circuit can truly discriminate a spurious target with one nucleotide mismatch.
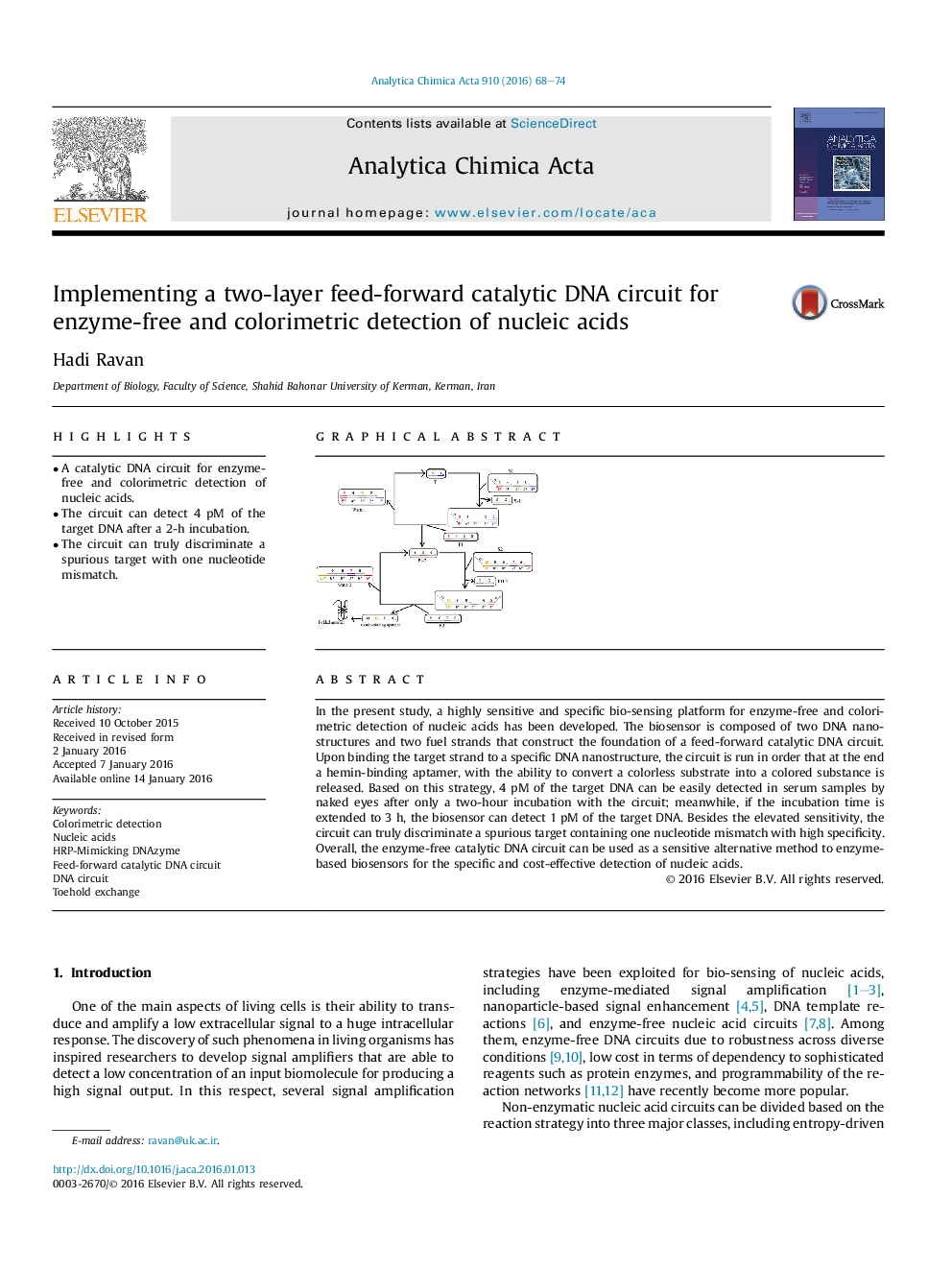
In the present study, a highly sensitive and specific bio-sensing platform for enzyme-free and colorimetric detection of nucleic acids has been developed. The biosensor is composed of two DNA nanostructures and two fuel strands that construct the foundation of a feed-forward catalytic DNA circuit. Upon binding the target strand to a specific DNA nanostructure, the circuit is run in order that at the end a hemin-binding aptamer, with the ability to convert a colorless substrate into a colored substance is released. Based on this strategy, 4 pM of the target DNA can be easily detected in serum samples by naked eyes after only a two-hour incubation with the circuit; meanwhile, if the incubation time is extended to 3 h, the biosensor can detect 1 pM of the target DNA. Besides the elevated sensitivity, the circuit can truly discriminate a spurious target containing one nucleotide mismatch with high specificity. Overall, the enzyme-free catalytic DNA circuit can be used as a sensitive alternative method to enzyme-based biosensors for the specific and cost-effective detection of nucleic acids.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide