| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1163290 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2015 | 10 Pages |
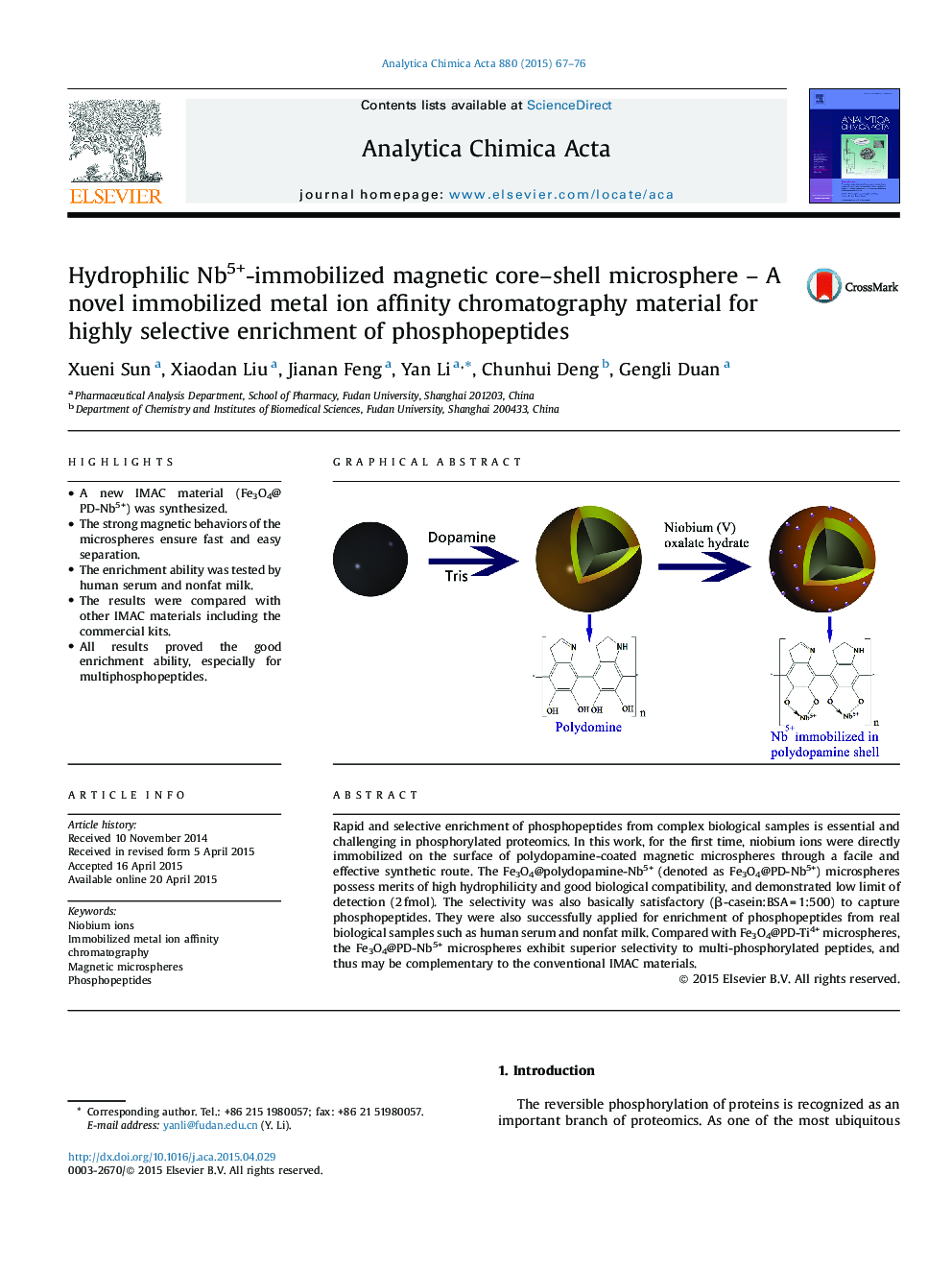
•A new IMAC material (Fe3O4@PD-Nb5+) was synthesized.•The strong magnetic behaviors of the microspheres ensure fast and easy separation.•The enrichment ability was tested by human serum and nonfat milk.•The results were compared with other IMAC materials including the commercial kits.•All results proved the good enrichment ability, especially for multiphosphopeptides.
Rapid and selective enrichment of phosphopeptides from complex biological samples is essential and challenging in phosphorylated proteomics. In this work, for the first time, niobium ions were directly immobilized on the surface of polydopamine-coated magnetic microspheres through a facile and effective synthetic route. The Fe3O4@polydopamine-Nb5+ (denoted as Fe3O4@PD-Nb5+) microspheres possess merits of high hydrophilicity and good biological compatibility, and demonstrated low limit of detection (2 fmol). The selectivity was also basically satisfactory (β-casein:BSA = 1:500) to capture phosphopeptides. They were also successfully applied for enrichment of phosphopeptides from real biological samples such as human serum and nonfat milk. Compared with Fe3O4@PD-Ti4+ microspheres, the Fe3O4@PD-Nb5+ microspheres exhibit superior selectivity to multi-phosphorylated peptides, and thus may be complementary to the conventional IMAC materials.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide