| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1163311 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2015 | 6 Pages |
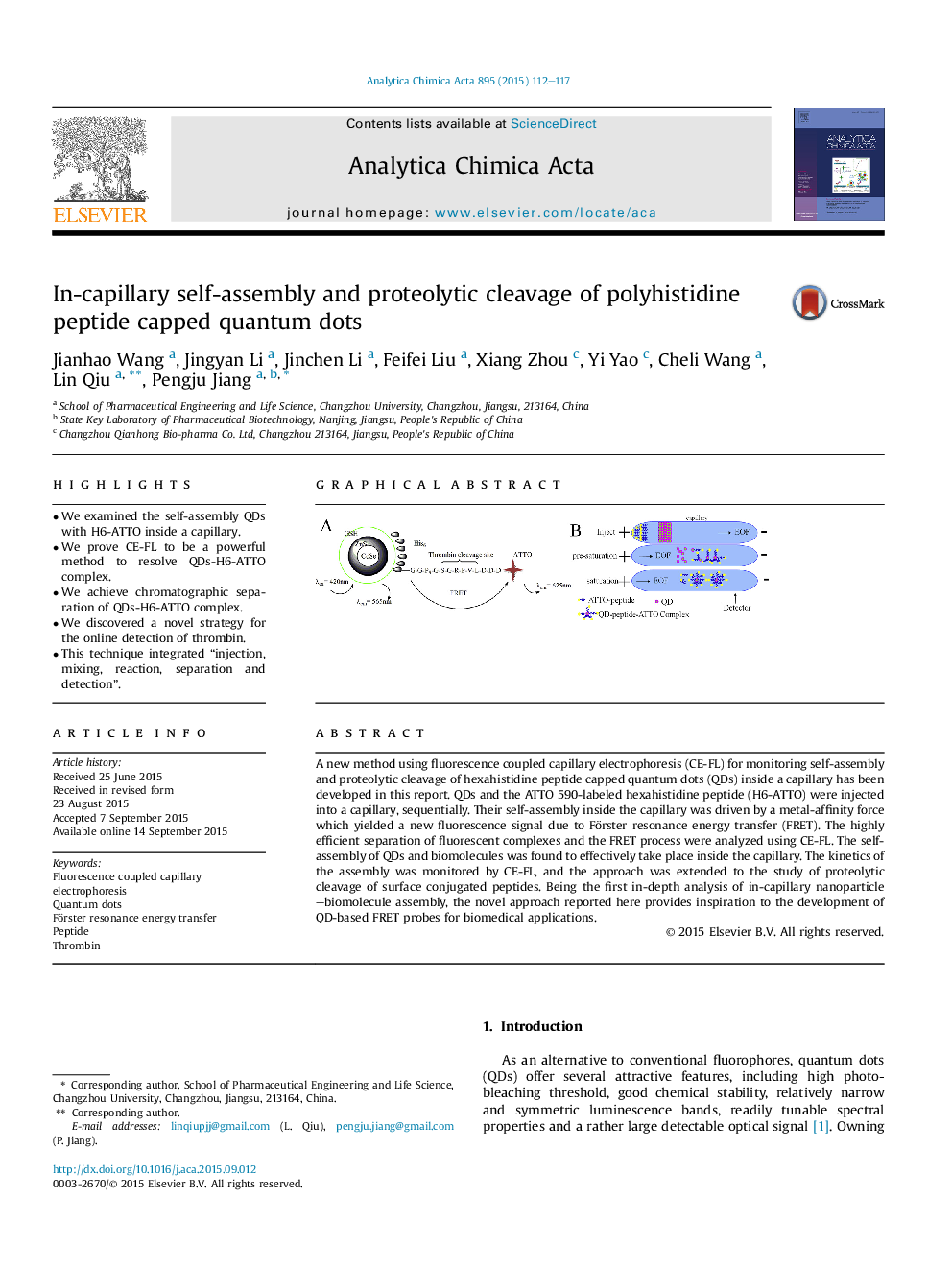
•We examined the self-assembly QDs with H6-ATTO inside a capillary.•We prove CE-FL to be a powerful method to resolve QDs-H6-ATTO complex.•We achieve chromatographic separation of QDs-H6-ATTO complex.•We discovered a novel strategy for the online detection of thrombin.•This technique integrated “injection, mixing, reaction, separation and detection”.
A new method using fluorescence coupled capillary electrophoresis (CE-FL) for monitoring self-assembly and proteolytic cleavage of hexahistidine peptide capped quantum dots (QDs) inside a capillary has been developed in this report. QDs and the ATTO 590-labeled hexahistidine peptide (H6-ATTO) were injected into a capillary, sequentially. Their self-assembly inside the capillary was driven by a metal-affinity force which yielded a new fluorescence signal due to Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET). The highly efficient separation of fluorescent complexes and the FRET process were analyzed using CE-FL. The self-assembly of QDs and biomolecules was found to effectively take place inside the capillary. The kinetics of the assembly was monitored by CE-FL, and the approach was extended to the study of proteolytic cleavage of surface conjugated peptides. Being the first in-depth analysis of in-capillary nanoparticle–biomolecule assembly, the novel approach reported here provides inspiration to the development of QD-based FRET probes for biomedical applications.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide