| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1163363 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2015 | 6 Pages |
•Novel approach for electrochemical detection of non-electroactive OPs was proposed.•PAM was used as electroactive probe for the first time.•The detection system displayed high sensitivity and promptness.•The developed sensor was used in real samples with satisfactory results.
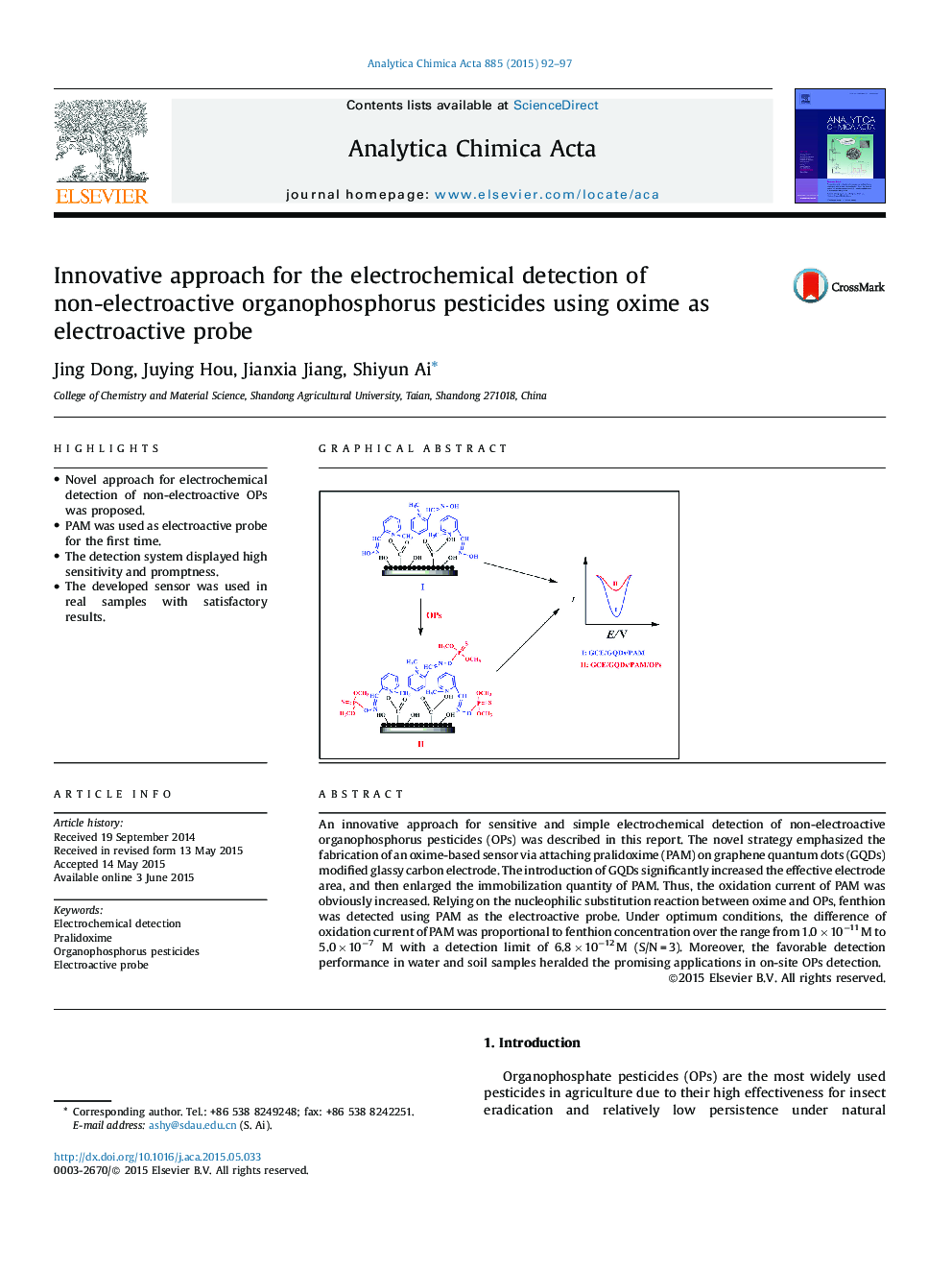
An innovative approach for sensitive and simple electrochemical detection of non-electroactive organophosphorus pesticides (OPs) was described in this report. The novel strategy emphasized the fabrication of an oxime-based sensor via attaching pralidoxime (PAM) on graphene quantum dots (GQDs) modified glassy carbon electrode. The introduction of GQDs significantly increased the effective electrode area, and then enlarged the immobilization quantity of PAM. Thus, the oxidation current of PAM was obviously increased. Relying on the nucleophilic substitution reaction between oxime and OPs, fenthion was detected using PAM as the electroactive probe. Under optimum conditions, the difference of oxidation current of PAM was proportional to fenthion concentration over the range from 1.0 × 10−11 M to 5.0 × 10−7 M with a detection limit of 6.8 × 10−12 M (S/N = 3). Moreover, the favorable detection performance in water and soil samples heralded the promising applications in on-site OPs detection.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide