| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1163430 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2015 | 8 Pages |
•A versatile glass spray mass spectrometry (GS-MS) platform for direct cell-based drug assay was developed in this paper.•It has characteristics of the atmospheric pressure ionization method.•It is multifunctional for cell co-culture, bioassays, qualitative and quantitative intracellular drug absorption measurement.•GS-MS has the potential to increase the use of mass spectrometry in biological analysis.
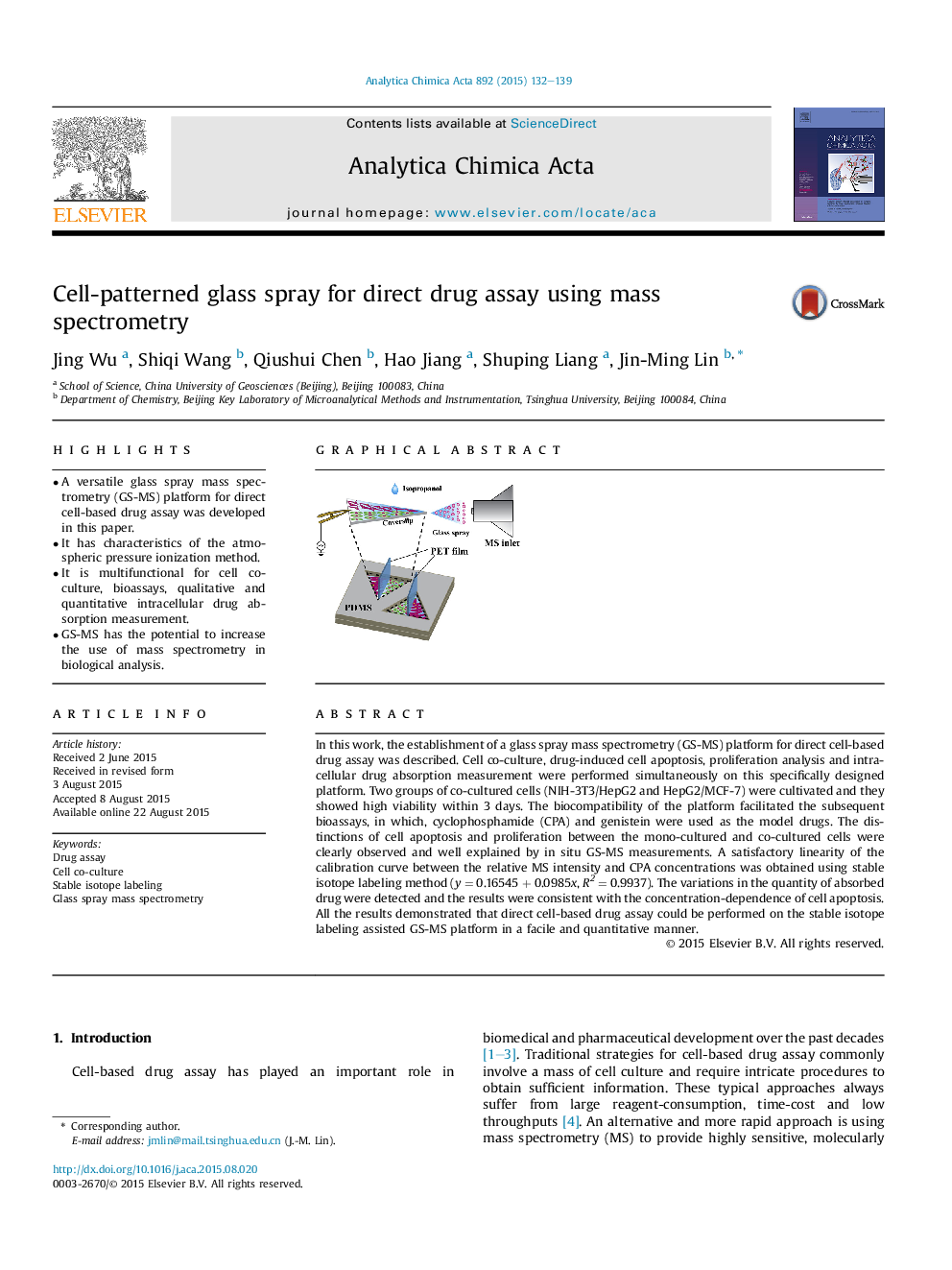
In this work, the establishment of a glass spray mass spectrometry (GS-MS) platform for direct cell-based drug assay was described. Cell co-culture, drug-induced cell apoptosis, proliferation analysis and intracellular drug absorption measurement were performed simultaneously on this specifically designed platform. Two groups of co-cultured cells (NIH-3T3/HepG2 and HepG2/MCF-7) were cultivated and they showed high viability within 3 days. The biocompatibility of the platform facilitated the subsequent bioassays, in which, cyclophosphamide (CPA) and genistein were used as the model drugs. The distinctions of cell apoptosis and proliferation between the mono-cultured and co-cultured cells were clearly observed and well explained by in situ GS-MS measurements. A satisfactory linearity of the calibration curve between the relative MS intensity and CPA concentrations was obtained using stable isotope labeling method (y = 0.16545 + 0.0985x, R2 = 0.9937). The variations in the quantity of absorbed drug were detected and the results were consistent with the concentration-dependence of cell apoptosis. All the results demonstrated that direct cell-based drug assay could be performed on the stable isotope labeling assisted GS-MS platform in a facile and quantitative manner.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide