| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1163516 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2015 | 9 Pages |
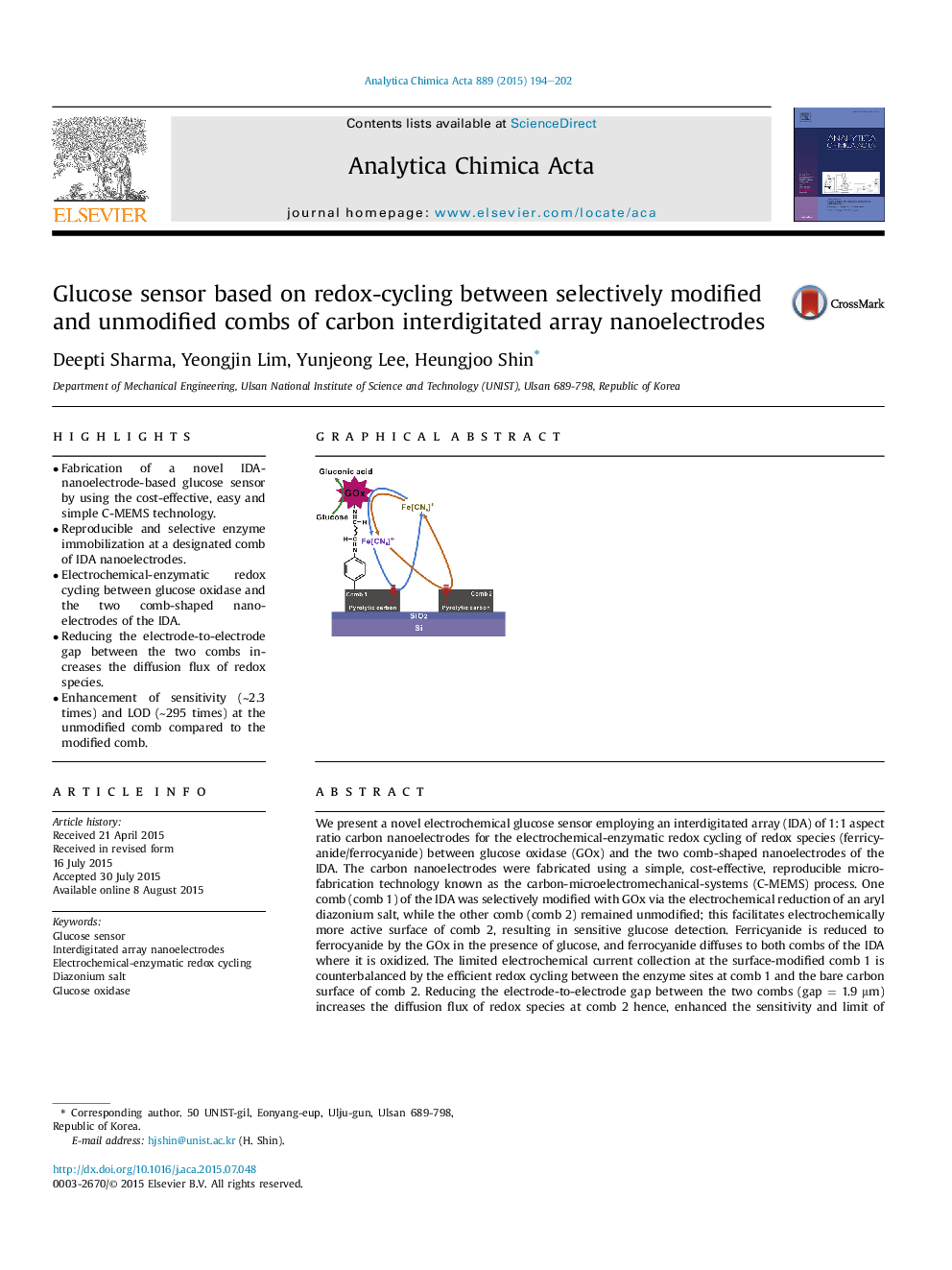
•Fabrication of a novel IDA-nanoelectrode-based glucose sensor by using the cost-effective, easy and simple C-MEMS technology.•Reproducible and selective enzyme immobilization at a designated comb of IDA nanoelectrodes.•Electrochemical-enzymatic redox cycling between glucose oxidase and the two comb-shaped nanoelectrodes of the IDA.•Reducing the electrode-to-electrode gap between the two combs increases the diffusion flux of redox species.•Enhancement of sensitivity (∼2.3 times) and LOD (∼295 times) at the unmodified comb compared to the modified comb.
We present a novel electrochemical glucose sensor employing an interdigitated array (IDA) of 1:1 aspect ratio carbon nanoelectrodes for the electrochemical-enzymatic redox cycling of redox species (ferricyanide/ferrocyanide) between glucose oxidase (GOx) and the two comb-shaped nanoelectrodes of the IDA. The carbon nanoelectrodes were fabricated using a simple, cost-effective, reproducible microfabrication technology known as the carbon-microelectromechanical-systems (C-MEMS) process. One comb (comb 1) of the IDA was selectively modified with GOx via the electrochemical reduction of an aryl diazonium salt, while the other comb (comb 2) remained unmodified; this facilitates electrochemically more active surface of comb 2, resulting in sensitive glucose detection. Ferricyanide is reduced to ferrocyanide by the GOx in the presence of glucose, and ferrocyanide diffuses to both combs of the IDA where it is oxidized. The limited electrochemical current collection at the surface-modified comb 1 is counterbalanced by the efficient redox cycling between the enzyme sites at comb 1 and the bare carbon surface of comb 2. Reducing the electrode-to-electrode gap between the two combs (gap = 1.9 μm) increases the diffusion flux of redox species at comb 2 hence, enhanced the sensitivity and limit of detection of the glucose sensor by ∼2.3 and ∼295 times, respectively at comb 2 compared to comb 1. The developed IDA-based glucose sensor demonstrated good amperometric response to glucose, affording two linear ranges from 0.001 to 1 mM and from 1 to 10 mM, with limits of detection of 0.4 and 61 μM and sensitivities of 823.2 and 70.0 μA mM−1 cm−2, respectively.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide