| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1163653 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2015 | 13 Pages |
•Fatty acid profiles of the olive oil samples were used for determining their geographical origin.•A likelihood ratio approach served as a method for evidential value assessment.•Various likelihood ratio models were proposed for solving the classification problem.•Models based on kernel density estimation are based on a new approach to the choice of the amount of smoothing.•Empirical cross entropy was employed to measure the performance of the LR methods.
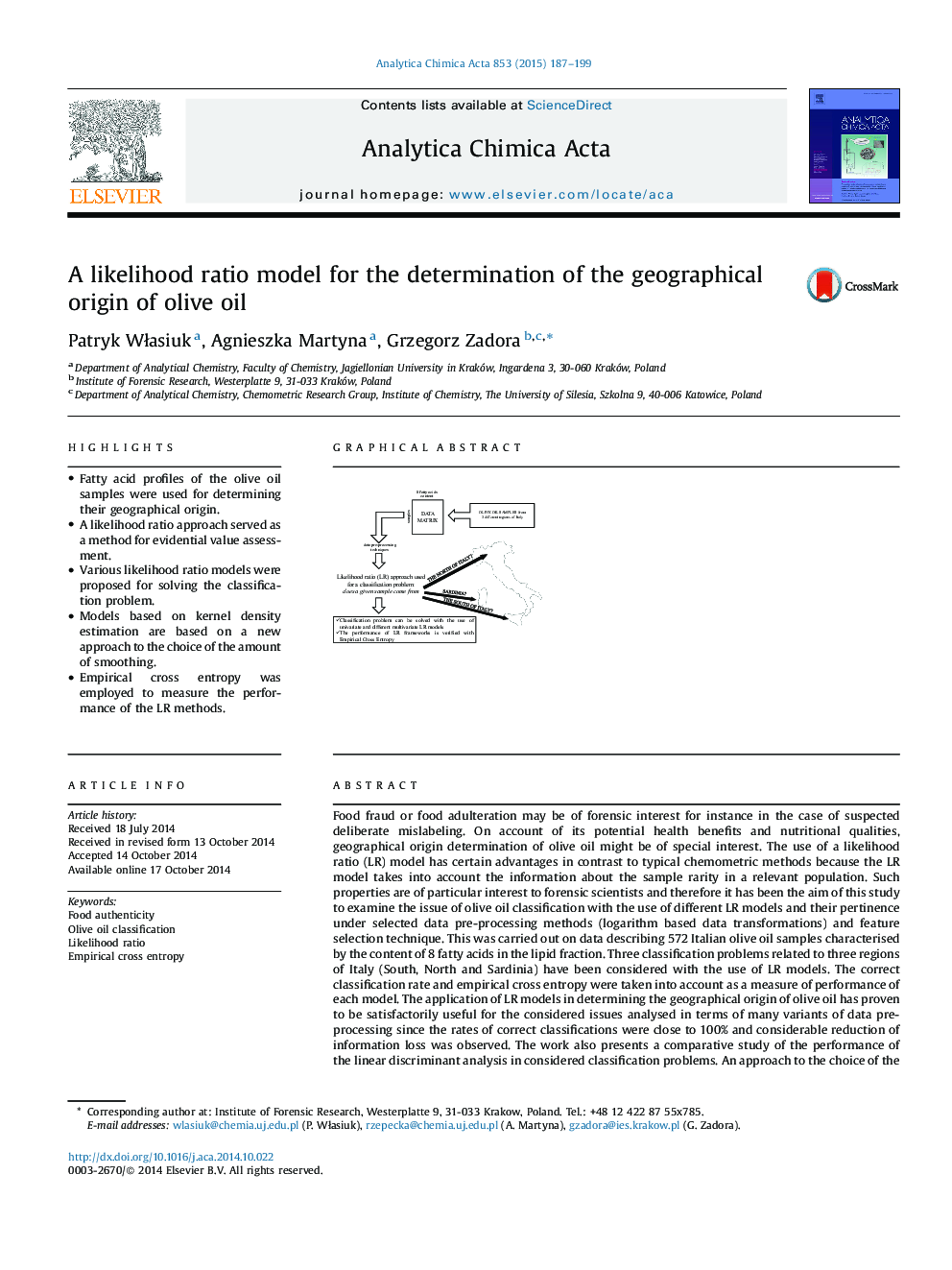
Food fraud or food adulteration may be of forensic interest for instance in the case of suspected deliberate mislabeling. On account of its potential health benefits and nutritional qualities, geographical origin determination of olive oil might be of special interest. The use of a likelihood ratio (LR) model has certain advantages in contrast to typical chemometric methods because the LR model takes into account the information about the sample rarity in a relevant population. Such properties are of particular interest to forensic scientists and therefore it has been the aim of this study to examine the issue of olive oil classification with the use of different LR models and their pertinence under selected data pre-processing methods (logarithm based data transformations) and feature selection technique. This was carried out on data describing 572 Italian olive oil samples characterised by the content of 8 fatty acids in the lipid fraction. Three classification problems related to three regions of Italy (South, North and Sardinia) have been considered with the use of LR models. The correct classification rate and empirical cross entropy were taken into account as a measure of performance of each model. The application of LR models in determining the geographical origin of olive oil has proven to be satisfactorily useful for the considered issues analysed in terms of many variants of data pre-processing since the rates of correct classifications were close to 100% and considerable reduction of information loss was observed. The work also presents a comparative study of the performance of the linear discriminant analysis in considered classification problems. An approach to the choice of the value of the smoothing parameter is highlighted for the kernel density estimation based LR models as well.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide